The process of personnel management in business. Summary: Human resource management as a specific area of management
FEATURES HUMAN RESOURCES IN SMALL BUSINESSES
annotationThis article is about small business HR management. The relevance of the chosen topic is determined by the needs of improving the practice of personnel management in small business. Therefore, the search and creation of the required personnel management system is carried out on the basis of a qualitatively new approach to the effective organization of personnel management.
ESPECIALLY PERSONNEL MANAGEMENT IN SMALL BUSINESS
Serochudinov Evgeniy Sergeevich 1, Anikina Polina Borisovna 2
1 Tyumen State Academy of World Economics Management and Law, Associate Professor
2 Tyumen State Academy of World Economics Management and Law, 2nd year student
Abstract
The article is dedicated to staff management in small business. The relevance of chosen theme is defined by interest in improvement of staff management practice in small business. Therefore searching and building of required staff management system are based on a new level of quality approach to effective organization of staff management.
Personnel Management- one of the most important components of management, which uses a set of ideas and techniques for the effective construction and management of organizations and projects.
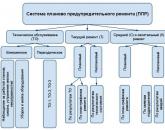
The personnel management process includes the following stages:
1) Personnel selection;
2) Personnel adaptation;
3) Personnel assessment;
4) Training and development of personnel;
5) Corporate culture;
6) Motivation of staff
Recruiting and managing personnel is considered one of the main tasks in running any business. If in big company a specialized department is engaged in the selection of personnel, then in a small business such work is most often forced by the entrepreneur himself.
Distinctive features of small business require professionalism and skill in the field of personnel management from the manager. Features of personnel management of a small enterprise are as follows:
1) flexible organization of work and the complex nature of activities;
2) lack of a multilevel organizational structure;
3) the competence of employees;
4) the minimum level of bureaucracy in work;
5) there is virtually no organizational preparation;
6) a small business makes excessive demands on the employee's own qualities;
7) the principles of personnel selection from time to time are aimed not at direct, but at indirect confirmation of professional suitability;
8) social insecurity of employees;
9) the difference in the initial conditions of enterprises /
Another feature of personnel management is also highlighted - it is a wide choice of employees. The existing unemployment provides managers with the opportunity to hire employees for low wages. At the same time, there is an opportunity to save on social benefits and working conditions.
There are many methods of personnel management (see Fig. 1)

Figure 1 - Methods of personnel management.
Alternative methods are also distinguished, such as:
1) mentoring;
3) job shadowing
4) "Off-duty career"
The main goal of mentoring is personnel development, in which a more experienced employee can share his professional knowledge with another, less experienced employee for a certain period of time. After that, the employee will be able to carry out the assignments entrusted to him with absolute responsibility.
The goal of buddying is considered to be achievement production tasks... This method is based on providing each other with information, objective feedback... Sometimes buddying is called informal mentoring equal to coaching.
Job Shadowing is currently one of the best-known methods of personnel training abroad. Its essence lies in the supervision of the actions of the employee of the enterprise and the study of the characteristics of his activities.
There are a number of non-job career alternatives:
1) special assignment;
2) your project;
3) individualization;
4) status functions;
6) corporate competitions;
7) reserve;
8) role structuring.
The analysis of personnel management was carried out in the staff of the hotel "Yugorskaya".
The personnel management process in a hotel is represented by the following components:
Staff recruitment;
Personnel adaptation;
Staff development;
Motivating staff.
The selection of personnel at the Yugorskaya Hotel comes from various sources. Responsible for personnel selection - HR department. The HR department performs the following tasks:
Search for suitable applicants from among the employees of the organization itself;
The most common method is to promote vacancy data. For the purpose of this management, the management of the hotel notifies absolutely each of the employees about the new position, which gives them the opportunity to submit applications before other applications are discussed. A number of the most suitable candidates are selected from the total number of applicants at the Yugorskaya Hotel.
In addition, the hotel management conducts regular education and training programs for employees, helping them to achieve their full potential. The hotel management allocates funds for training and retraining of employees, however, in an insufficient amount. In addition, the concept of training is not perfect, so the training takes place in the workplace, where the employee can help the newcomer to master the labor operations, and the specialist gives lectures to a group of employees at their workplace.
After considering the process of personnel management at the Yugorskaya hotel, we can conclude that there are problems in this system that need to be addressed - these are:
1) lack of qualified personnel;
2) disregard for employee education and training programs;
3) unsatisfactory staff motivation system.
Rationally, it is necessary to form a personnel management service and hire a highly qualified specialist for the position of the head of the service - for an effective personnel management system. The introduction of the position of the manager of the personnel management service will make it possible to carry out high-quality selection and recruitment of personnel, which will certainly have to improve the quality of services provided by the hotel and receive the expected income.
Table 1 - The costs of organizing the position of the head of the personnel management service.
Thus, in the Yugorskaya hotel, the expected costs of creating a position and its special equipment, according to calculations, will amount to 425,500 rubles.
The economic effect from the introduction of the head of the personnel management service into the position is determined by the formula:
Table 2-Forecast economic indicators hotel "Yugorskaya" taking into account the recommendations
Thus, the expected economic effect from the introduction into the staff of the position of the head of the personnel management service will be:
2,200,000 - 1,500,000 - 230,000 - 425,500 = 44,500 rubles
From the calculations, we see that the measure for the introduction of the position of the head of the personnel management service in the hotel is economically justified and expedient.
At the Yugorskaya hotel, the learning process is proposed to be carried out without interrupting working hours, directly at the Yugorskaya hotel. Further, it is proposed to conclude an agreement on conducting a refresher course with the Surgut Institute of World Economy and Business. The Institute has permission to educational activities, and therefore training costs are charged to the cost of services.
For professional development to be more effective in a hotel, management should support staff retraining directly financially.
It is necessary to apply modern methods of education and training of personnel, such as job shadowing. After the introduction of this method at the Yugorskaya Hotel, the likelihood of hiring unmotivated workers will decrease, the staff's ability to provide information in an accessible form will improve, and the awareness of their own actions at work.
In the course of considering the motivational structure of the hotel "Yugorskaya", the absence of intangible incentives was revealed. To develop an incentive mechanism, a study was conducted among employees, the purpose of which was to identify non-economic expectations from the hotel.
Table 4 - Motivational expectations of the hotel "Yugorskaya"
|
Factors affecting motivation |
Percentage of respondents (%) |
|
The psychological climate in the team |
|
|
Work area and benefits |
|
|
Delegation of authority |
|
|
Communication and communication |
|
|
Encouraging creativity |
|
|
Development and learning |
|
|
Interest in work |
|
|
Hotel policy |
Based on this study, the following motivation methods have been developed:
Timely resolution of conflict situations;
Formation and elaboration of socially significant traditions and rituals;
Organization of delegation of authority;
Implementation of the practice of informal conversations with the manager and communication on personal topics;
Participation of employees in thematic meetings with the participation of partners and competitors in conferences and forums.
Thus, the study showed that the organization of personnel activities becomes effective with systemic management, including the diagnosis of actions, methods and operations of managerial influence, the establishment of a motivational mechanism for building a system of interaction between various groups of employees in order to implement the objectives of the hotel "Yugorskaya".
UDC 159.9.23
SELECTION AND MANAGEMENT OF PERSONNEL IN THE STRUCTURE OF BUSINESS ACTIVITY
N.N. KAZIEVA
(Dagestan State University)
Topical problems of increasing labor efficiency in the field of entrepreneurial activity due to the optimal selection and management of personnel. Revealed effective methods of personnel policy. A psychological model of work with personnel is proposed.
Keywords: entrepreneurial activity, activity, management, self-management, personnel, personnel policy.
Introduction. Currently, the organization's personnel policy is becoming one of the components of the corporate image, on which the success of the organization largely depends. Changes in the labor market entail changes in personnel policy in organizations, which is reflected in the specific destinies and professional paths of specialists. HR processes are combined into an integral system professional way a person with social processes and situations in society and organization.
The main content of personnel policy and personnel management. The goal of personnel policy should be an economically feasible and psychologically sound (taking into account abilities, skills, aspirations and motivation) distribution of personnel between vacant jobs. Personnel planning, which is a complex activity (planning personnel needs, attracting and reducing personnel, training, retention staff and others), becomes an integrating component of entrepreneurial planning. Kinds workforce planning are determined by both external (changes in the conjuncture and market structure, competitive relations, economic policy, etc.) and internal factors (planned sales volume, equipment, technology, organization of production and labor, staff turnover, etc.).
It is very difficult to make the expectations of a person and the expectations of an organization correspond to each other, since they are made up of many separate expectations, for the coordination of which it is necessary to create a complex and flexible system of linking the interests of a person, groups, divisions and the organization as a whole in the organization. For each person, the combination of expectations about different aspects of work that forms his generalized expectation in relation to the organization is different. Moreover, both the structure of expectations as a whole and the relative degree of significance of individual expectations for an individual depend on many factors (personal characteristics, goals and the specific situation in which he is, characteristics of the organization, etc.).
In turn, the organization expects from a person that he will prove himself as a specialist in a particular field, sharing the values of the organization and contributing to its successful functioning and development; as a team member capable of maintaining good relationships with colleagues, etc. HR management is one of the most important aspects of HR policy in any organization. Since the optimization of personnel processes is associated, first of all, with the impact on people, its effectiveness cannot be achieved without the use of specific tools and technologies that are based on psychology data.
An analysis of the three management strategies - bureaucratic, humanistic, and organizational and cultural - indicates that the first two do not contribute to the creation of a favorable situation of interaction. A bureaucratic strategy does not take into account the human factor, a humanistic strategy distances the goals and values of top management from the goals and values of personnel. Use-oriented management strategy only organizational culture,
implies that the senior management team seeks to connect employees to their goals and values by activating emotions and feelings that awaken loyalty, loyalty and commitment to the company. Thus, the defining feature that distinguishes the use of culture from other forms of government is that culture is transmitted to its participants through the expression of feelings, beliefs and attitudes.
Organizational culture is assessed and assimilated by members of the organization and influences their organizational behavior. Therefore, organizational culture can be considered as a determinant of the social life of an organization - one of the organizational subsystems that performs such significant functions as the adaptation and integration of its employees. Organizational culture is new and underdeveloped, but tends to emphasize relationships, feedback mechanisms, perceptions of correspondence between different elements of an organization.
In the problem of interaction between a person and an organization, the emphasis is shifted to mutual interest and the unity of value-semantic principles. This is reflected in the organizational and cultural approach to management, in which organizations are viewed as normative value systems. The key role in management is played by values, beliefs, interests of people, on which management actions are focused. The use of an organizational and cultural approach to management involves the involvement of emotional factors.
Elements of the organization underlie the selection of criteria for the selection of personnel in the organization. Traditionally, recruiting criteria have been decisive job responsibilities, professional tasks and working conditions. In modern conditions, the traditional approach is complemented in terms of the correspondence of the qualities of personnel to the characteristics of the organization. Any organization is a flexible dynamic structure, the development of which has a certain cyclical nature. At the stage of intensive growth, personnel management is mainly aimed at forming the personnel structure - attracting and hiring personnel, evaluating candidates, placing and adapting personnel. At the stage of stabilization, the most significant issues of assessment and intensification of labor, certification of personnel, formation personnel reserve, development of a labor incentive system. The recession stage requires work to optimize the personnel program and restructure it.
Personnel management is always the implementation of one form or another of power. There are individual differences in leadership preference different forms authorities. Leaders with increased levels of anxiety tend to use sanctioned and traditional power. Leaders who see their success solely as a result of their own merit, professionalism, and a high level of knowledge prefer reward-based power. Expert and charismatic forms of power are attractive to those who are flexible in communication and easily enter into new social contacts.
The choice of forms of power is also determined by the specifics of the situation. In situations in which management is complicated by the action of objective reasons (lack of information; time limit; high degree of responsibility), the leader prefers to use forms of power based on remuneration, sanctions, and expert power.
The effectiveness of the organization's personnel policy depends on taking into account the characteristics of the behavior regulators inherent in its personnel. These regulators traditionally include the value-sense orientations of the individual and its values. Values are explicit or implicit concepts of the desired that characterize an individual or a group and determine the choice of types, means and goals of behavior.
Organizational values, reflecting the employee's conscious attitude towards various organizational factors, are a significant component of the organization. In an organization as a complex system, there are always actual contradictions at the level of values. Most common
the list of values and value alternatives that workers regularly face include: power, law, work, outcome, age, education, equality of people, attitude to risk, helping others, reward or punishment, pleasure.
HR management in the organization is based on the understanding of labor motivation... The motives associated with a person's labor activity can be divided into three groups: the motives of labor activity, the choice of a profession and the choice of a place of work. A specific activity is determined by all these motives.
Numerous concepts of work motivation are concentrated around two theories: entrepreneurs are characterized by the rejection of incentives and the appeal to motivation, to expanding the motivational zones that can induce staff to work effectively. A motivational factor such as “size wages”Does not stand out as dramatically as one might expect. Some of the leading motivational factors include:
Interest in your business;
The desire to meet the high expectations of the leader of the company;
The need to work in an environment of professionals of their level;
It's a pleasure to work among these people.
A significant problem of motivation management is a high level of work motivation in the firm, on the one hand, and the contract system, on the other. Research shows that many professionals are traumatized by the contract system: they view the firm's right to terminate a contract at the end of its term as an expression of control over performance. Service departments are especially vulnerable in these cases. They account for the largest volume of such work, where success is invisible, but failures, on the contrary, are accompanied by the greatest publicity. Therefore, the service departments of firms are the most conflict-prone.
In this regard, intra-organizational movements of personnel should be carried out within the framework of an individually planned career of a professional. Career creates the prerequisites for the creative growth of a professional, his self-actualization in the organization. In this context, the career of a professional acts both as a result, expression, and as a condition for the continuous professionalization of the subject of activity. A poorly planned career is a brake on the professional development of an individual, and in the context of a person's life path is a source of deep dissatisfaction with life in general.
A fundamental feature in the selection of personnel in structures organized successful entrepreneurs, is the rejection of the functional-hierarchical lattice (it does not matter who you were before - it is important whether you will be able to independently implement the task here and now). When selecting personnel, great attention is paid to communication skills and initiative. When hiring personnel, one should take into account the correspondence of the personal characteristics of employees, first of all, value-semantic aspirations, philosophy and values of the organization. Only in this case the values formulated in the philosophy of organization will be really embodied.
Entrepreneurship requires the kind of stress that engenders a mindset to minimize effort. Therefore, entrepreneurs prefer to work with professionals who are able to quickly make decisions and implement tasks. Entrepreneurs want to communicate with a fairly narrow circle of "understanding" people. In the firm, the leader and the management team work with almost every employee. This reveals a specific characteristic of the management culture: not to use second-hand information, but to control, as far as possible, through a direct executor. Obviously, this creates a problem of overwhelming the entrepreneur.
Researchers note that in Russian business structures, when recruiting personnel, management often declares requirements for candidates based on the principle of
types of entrepreneurial culture, and the real assessment of candidates is made according to the principles operating in the clan structure. Entrepreneurial culture representatives do not take root well in a clan organization that considers the value of the employee in terms of their loyalty, and solves the problem of increasing the employee's dependence.
In connection with the tasks of designing an employee's career, it is necessary, first of all, to diagnose the level of professional development of the subject of activity, his life values, focus and depth of development zones of professionally important qualities and skills, as well as the introduction of procedures for correcting a professional's style in order to increase the efficiency of a professional's functioning in a certain system of requirements.
Career planning for specialists is carried out in the context of development plans for the organization itself, those innovative processes that are a condition for its survival and development. Therefore, an essential point in managing personnel processes is taking into account the innovative potential of personnel and the organization as a whole as a system.
In order for employees to work successfully, achieving high results in their activities, to be satisfied with the profession, place of work, certain conditions should be created:
The work should interest the employee, form in him a positive motivation for responsible activities;
Highly professional training of the employee (selection for each employee of such a work activity that would correspond not only to his interests, but also to his individual characteristics);
Optimal organization for efficient work (convenient workplace, aesthetically designed industrial premises, optimal work and rest mode).
Based on the listed prerequisites, it is possible to formulate the main tasks or areas of work of psychologists in the organization:
Formation of positive motivation for work among employees;
Selection, assessment and placement of personnel;
Improving the process of industrial training, increasing the level of professional competence of employees;
Optimization of working conditions.
Professional adaptation is the gradual entry of a new employee into specific conditions of professional work. Social adaptation is adaptation to a set of new roles and connections with the surrounding social environment, as a result of which a certain correspondence of individual needs to organizational requirements is achieved. To the means and methods information support adaptation control can include periodic conversations with an employee at the workplace, conversations with managers of various levels, comprehensive studies of the degree of job satisfaction, analysis of objective data on the employee's activities, etc.
The information obtained is included in the system of organizational support for the adaptation process in the organization. Such a system can be based, for example, on the standards of the organization, which determine the basic procedures for the impact of different levels of management on the adaptation of the employee. An integrated system of information and organizational support for adaptation control allows not only to manage the specified process, to determine the paths of professional growth, but also to implement effective preventive measures to eliminate the reasons for staff turnover in the organization.
The logic of the development of management concepts is a transition from a mechanistic understanding of this phenomenon (early management theories) to a personality-oriented one. Modern researchers and practitioners focus on understanding the significance of the human
factor a. Within the framework of this approach, the priority of the human resource is postulated, due to its uniqueness and limitlessness. The performance of an organization is directly linked to the state of this resource. The key issues of personnel management are the problems of planning and human resource development. At the same time, a resource means not only the professional skills of the organization's employees, but also their individual psychological characteristics, motivation, expectations, value system, etc. ...
Care for the development and training of personnel is of particular importance. By creating conditions for employee mobility and self-regulation, accelerating the process of adaptation to changing production conditions, personnel training includes all efforts to maintain or improve qualification level working through additional training. However, personnel development is not the main task for most entrepreneurs, who do not even have an idea of what types of learning situations are necessary for the development of professional qualities and how their organization could use the creativity of its employees. There is a widespread misconception that the workplace is not a place of learning; educational institutions exist for this purpose.
The model of work with personnel proposed by us as self-management is not yet so actively applied in practice. Traditionally, self-management was considered only as a section related to scientific organization labor leader and only recently began to stand out as an independent area of knowledge. Within the framework of the considered approach, self-management should become effective tool psychological study of employees of the enterprise.
Conclusion. An analysis of the personnel recruitment and management system in the structure of entrepreneurial activity allows us to draw the following conclusions:
The goal of personnel policy is economically feasible and psychologically sound (taking into account abilities, skills, aspirations and motivation) use labor resources, planning of personnel needs, attraction and reduction of personnel, training, retention of personnel, etc .;
The directions of the organization's personnel policy are determined by both external and internal factors;
The effectiveness of the organization's personnel policy depends on taking into account the characteristics of the main regulators of behavior inherent in its personnel, which include, first of all, the value-semantic orientations of the personality and its values;
The problem of understanding the patterns and mechanisms of development, training of personnel and the realization of their creative potential is actualized.
In the field of entrepreneurial activity, there is real opportunity increasing the activity of personnel through the integrated use of modern research and consulting methods, as well as the dependence of an effective personnel policy, taking into account the peculiarities of psychological regulators of behavior inherent in personnel.
Bibliographic list
1. Odegov Yu.G. Personnel management / Yu.G. Odegov, P.V. Zhuravlev. - M., - 1997.
2. Vikhansky O.S. Strategic management/ O.S. Vikhansky. - M., 1998.
3. Vikentieva E.N. Attractiveness of labor in the context of organizational culture // Contemporary problems Psychology of Management: Sat. scientific. tr. / E.N. Vikentieva // RAS. Institute of Psychology, Tver. state un-t; otv. ed. T.P. Emelyanova, A.L. Zhuravlev, G.V. Telyatnikov. - M., 2002. -S. 100-121.
4. Psychology of joint life of small groups and organizations; otv. ed.
A.L. Zhuravlev, E.V. Shorokhov. - M., 2001 .-- 288 p.
5. Chirikova A.E. From incentives to motivation / A.E. Chirikova // ECO: Economics and Organization of Industrial. pr-va. - Novosibirsk, 1997. - No. 9. - S. 142-151.
6. Babaeva L.V. Business - elite of Russia: way of thinking and types of behavior / L.V. Babaeva, A.E. Chirikova // ECO: Economics and Organization of Industrial. pr-va. - Novosibirsk, 1995. - No. 1. - S. 117-145.
7. Mall E.G. Planning your career as a leader / E.G. Mall // Questions of psychology. - 1998. - No. 3. - S. 85-91.
8. Personnel management; ed. Bazarova T.Yu., Eremina B.L. - M .: UNITI, 1998.
9. Raven J. Competence in modern society: identification, development and implementation / J. Raven. - M., 2002 .-- 396 p.
10. Tokarev V. Hypothesis about a new paradigm of management / V. Tokarev // Problems of theory and practice of management. - 2001. - No. 3.
The material was received on 03.10.2011.
1. Odegov Yu.G. Upravlenie personalom / Yu.G. Odegov, P.V. Zhuravlyov. - M., 1997. - In Russian.
2. Vixanskij O.S. Strategicheskoe upravlenie / O.S. Vixanskij. - M., 1998. - In Russian.
3. Vikent "eva E.N. Privlekatel" nost "truda v kontekste organizacionnoj kul" tury "// Sovremenny" e problemy "psixologii upravleniya: sb. Nauch. Tr. / E.N. Vikent" eva // RAN. In-t psixologii, Tver. gos. un-t; otv. red. T.P. Emel "yanova, A. L. Zhuravlyov, G. V. Telyatnikov. - M., 2002. - S. 100-121.
4. Psixologiya sovmestnoj zhiznedeyatel "nosti maly" x grupp i organizacij; otv. red. A.L. Zhuravlyov, E.V. Shoroxova. - M., 2001 .-- 288 s. - In Russian.
5. Chirikova A.E. Ot stimulov - k motivacii / A.E. Chirikova // E "KO: E" konomika i organizaciya prom. pr-va. - Novosibirsk, 1997 .-- # 9. - C.142-151. - In Russian.
6. Babaeva L.V. Biznes - e "lita Rossii: obraz my" shleniya i tipy "povedeniya / LV Babaeva, AE Chirikova // E" KO: E "konomika i organizaciya prom. Pr-va. - Novosibirsk, 1995. - # 1. - S. 117-145.
7. Moll E.G. Planirovanie svoej kar "ery" rukovoditelem / E.G. Moll // Voprosi psixologii. - 1998.
- # 3. - S.85-91. - In Russian.
8. Upravlenie personalom; pod red. Bazarova T. Yu., Eryomina B.L. - M .: YUNITI, 1998. - In
9. Raven Dzh. Kompetentnost "v sovremennom obshhestve: vy" yavlenie, razvitie i realizaciya / Dzh. Raven. - M., 2002 .-- 396 s. - In Russian.
10. Tokarev V. Gipoteza o novoj paradigme upravleniya / V. Tokarev // Problemy "teorii i prak-tiki upravleniya. - 2001. - # 3. - In Russian.
PERSONNEL RECRUITMENT AND MANAGEMENT IN BUSINESS STRUCTURES
(Dagestan State University)
Some current questions of the labor productivity increase in the business area through the optimal personnel recruitment and management are considered. Some effective techniques of the recruitment policy are described. A psychological model of the personnel development is offered.
Keywords: entrepreneurship, activity, management, self-management, personnel, recruitment policy.
Personnel management is one of the most essential components in the work of any large enterprise. Among other things, this is a business process that must be organized in such a way that all employees of the enterprise feel comfortable and can work for the good of the company.
A business process is usually understood as a periodically repeating sequence of certain procedures, interconnected and aimed at creating certain values for consumers. External resources are actively used to organize the business process.
HR business processes
Business processes should be under the control of only one manager - he is responsible for its implementation and the final result. In almost any enterprise, several business processes are usually performed at once, which are classified according to certain criteria.
Business processes in the field of personnel management deserve special attention: they are internal and aimed at consumers who are on the staff of the enterprise. To form a process, it is necessary to know everything about the consumer, since the requirements for the operations performed depend on him.
There are several types of processes aimed at developing an entrepreneurial business. The business process of personnel management is difficult to refer to any familiar classification, since it represents a large number of independent sub-processes: auxiliary, management, etc.
HR process
Modern businessmen strive to stabilize the business in which they are engaged, and make every effort for this. To do this, it is necessary to form high-quality business processes, which represent a clear scheme with the help of which work is easier than usual.
Some entrepreneurs take a long time to come to ordering their own activities. This usually happens after a long period of loss, when the only way out of a difficult situation is to reorganize the company. As an additional measure, businessmen streamline (optimize) the work of absolutely all specialists in their enterprise.
All further work of the enterprise depends on the high-quality selection of employees, which is why selection is the leading activity of the HR department, personnel management. A streamlined recruiting and team building process will allow you to acquire professional staff.
Business processes related to the search and further recruitment of personnel are approved by a number of documents established by the heads of enterprises. In almost every enterprise, such documents are the same, all recruiters operate according to a similar scheme, which, in fact, consists of nine stages.
How do large enterprises choose personnel?
HR processes were created in order to recruit quality workforce for businesses.
Recruiting begins with identifying the needs of the company
It is necessary to understand what kind of specialists are needed to complete the tasks and projects set by the enterprise.
Submission of applications
After the company has decided on the number of required specialists and their qualifications, employees of the HR department are required to apply for the selection of a candidate for local government structures (employment centers, recruitment agencies, etc.). All applications submitted must contain requirements for potential employees (experience, certain skills, knowledge foreign languages), some employers also form requests, indicating the desired age and gender of candidates. The generated application is signed by the head of the enterprise.
Clarification of applications
To ensure a high-quality business process, HR employees have to clarify requests submitted by management. All employees of the enterprise involved in recruiting must understand exactly who should be hired. The specialist is obliged to clarify the following positions:
- name of the available vacancy, its structural unit;
- the reason for the appearance of an open vacancy;
- the place in the organization that the new specialist, his immediate supervisor or the number of subordinates will take;
- duties of a new specialist of the enterprise;
- basic requirements for applicants.
An enterprise intending to find new employees must correctly indicate the requirements for potential candidates:
- the desired age of the employee;
- the level of education;
- work experience necessary to fulfill the internal needs of the enterprise;
- professional skills in a narrow profile (if any).
An HR specialist must have an idea of what professional skills are needed in a particular position, what qualities (personal and business) must have the new employee wanting to get a job. This is necessary to perform a correct analysis of the position for which a new employee is being sought.
Formation of a profile for a vacancy
Only after the management has formulated the requirements for the future employee and the conditions in which he will work within the enterprise have been identified, the HR department specialists should form a general profile of the position with additional information, namely:
- reasonable age restrictions;
- preferences in marital status (not all entrepreneurs are ready to hire an employee with small children);
- requirements for the availability of education;
- health and work experience requirements;
- presence / absence of the necessary skills, abilities and knowledge;
- the presence of certain personal characteristics.
After the profile has been formed, the specialist in charge of this area of work creates a set of measures aimed at finding a new employee. He must endorse this document with the head of the enterprise. After completing this procedure, the profile is sent to the head of the department, who will interview the candidates.
Typically, the list of business process activities for filling a vacancy is as follows:
- designation of the profile of the position that needs to be closed;
- determining the sources with which recruiters will look for a new employee;
- shaping advertisements for further posting on Internet portals, in the media and other multimedia resources;
- creation of a register of questions for a complicated interview (if it is necessary to close a vacancy of a narrow specialization).
Features of the work of HR specialists in the search for employees
After the formation of requirements for an open vacancy, the specialists of the recruiting department within the framework of the business process begin to consider various sources from which potential candidates may come to them:
- the company itself (employees of the personnel reserve);
- specialists who took part in practical exercises within the enterprise;
- search through the media;
- databases of ex-employees of the company (in this case, only those candidates whose professionalism does not raise doubts among the management are considered);
- CV databases created by the HR department;
- search for candidates with the help of employment centers and recruitment agencies;
- search for employees through trade union organizations of universities and secondary vocational schools;
- HR leasing agencies (for temporary work);
- direct search for specialists.
HR business processes are a complex science that requires HR specialists to find an approach to all candidates for positions within the enterprise.
When considering candidates for filling managerial positions, the HR manager should ask them to undergo psychological testing, which helps to identify the presence of the most important personal and professional qualities necessary for working in the company. For such candidates, tests formed by Cattel, Leary, Mehrabian, Eysenck and Keirsey are used.
First candidates for a job
Thanks to the implementation of these measures of the business process, every day the company receives a large number of resumes from candidates for certain vacancies. All requests are processed, and the information appears in special databases. If the candidate suits the HR manager, he contacts him by phone and invites him for an interview.
In some cases, the HR specialist prefers to conduct an initial interview by phone, following the results of which he decides to invite the candidate to the office for a personal interview. There, the applicant is invited to fill out a questionnaire (sometimes there are even several of them), then he must go through an oral interview, following which the manager decides whether the candidate fits the existing requirements or not. If the result of the interview is positive, the applicant is allowed to the next stage of the business process.
 Most of all enterprises in operation today conduct additional psychological tests. Based on the test result, the staff psychologist of the organization is obliged to write a conclusion and reflect in it the psychological characteristics of the applicant, its compatibility with the proposed position, advantages and disadvantages, in some cases even admissible difficulties are indicated when starting a career in a new position.
Most of all enterprises in operation today conduct additional psychological tests. Based on the test result, the staff psychologist of the organization is obliged to write a conclusion and reflect in it the psychological characteristics of the applicant, its compatibility with the proposed position, advantages and disadvantages, in some cases even admissible difficulties are indicated when starting a career in a new position.
Linearity of the business process is the key to success
After the applicant has successfully passed the interview with the HR specialist, he moves on to the next link: now he needs to convince the line manager that he deserves a place in the company. As a rule, business processes, which include a re-interview, are somewhat more complicated than the previous ones, since tricky questions on a narrow topic are heard here, to which the candidate is obliged to give adequate answers.
The HR specialist submits the applicant's resume, his application form and the results of the tests to the manager. In some cases, the interview with the line manager is postponed to another day, but most often it is organized directly on the day on which the meeting with the HR employee is scheduled.
After the interview, the head of the department or his secretary is obliged to notify the candidate about his decision within the next two days. This part of the business process is becoming mandatory in many organizations. When conducting an interview, an employee in a managerial position tries to find out as much as possible about a potential employee, what motivates him, what he wants to achieve within the enterprise.
Enterprise safety comes first
As soon as the manager decides to hire a particular candidate, all the information collected about him goes to the security service of the enterprise for verification. This is an indispensable element of the overwhelming number of business processes, since recently there have been more cases of situations when an employee was admitted to the headquarters, underwent training, and then hard-hitting facts about him were clarified, for example, a criminal record or a huge number of open loans.
Security personnel, having received information about a new employee of the enterprise, are obliged to check all received data in the next three days and submit a corresponding conclusion to the HR department. If a new employee of the company is registered with major violations of the law, the likelihood that he will get this job and start working is close to zero.
Further, the HR specialist who hired the employee is obliged to check all the recommendations from those places of work that the employee indicated in his own questionnaire. Within the framework of this business process, he will have to call all previous jobs and clarify information: position, responsibilities, professionalism, reasons for dismissal, etc.
Hiring an employee
At the final stage of this business process, a decision is made on the hiring of a job seeker. After the candidate passes all the tests on his way, and the employees of the enterprise see no reason to refuse him, a formal decision is made to hire a new employee.
The HR specialist provides his manager with all available information about the new employee. Tom needs to study it and, on this basis, sign the decision on hiring the candidate. In some cases, business leaders conduct their own interviews with potential employees.
As soon as the head of the company has put his official signature on the decision, the HR manager must send the newcomer to the HR department, where he can draw up all the necessary documents. However, this stage is far from the last in the business process of personnel management; there are also several additional parts of it.
 If at one stage or another it turns out that the candidate does not fit the open vacancy, the HR specialist will thank him for his response and refuse. As part of the business process, the candidate's questionnaire is sent to the database, where it will be located either until the expiration of the storage period for documents, or until a potential employee is useful to fill another existing vacancy within the company.
If at one stage or another it turns out that the candidate does not fit the open vacancy, the HR specialist will thank him for his response and refuse. As part of the business process, the candidate's questionnaire is sent to the database, where it will be located either until the expiration of the storage period for documents, or until a potential employee is useful to fill another existing vacancy within the company.
Providing a workplace for an employee
After official notification, the employer is obliged to notify the applicant of the date of the start of labor activity or internship. According to the existing legislation, which is taken into account by the business process, the employee must go through medical checkup, during which a complete diagnosis of his body will be made.
When getting a job, an employee must provide a whole package of important documents to HR specialists:
- copy of your passport;
- work book;
- SNILS;
- a copy of the diploma of higher education (with inserts);
- a photocopy of the military ID;
- several 3x4 photos (the number depends on the company);
- a photocopy of marriage and birth certificates of children who are under 18 years of age at the time the candidate is hired.
Sometimes employers as part of this business process require their employees to provide them with whole line additional documents: medical certificate on the passage of the examination, a copy of the driver's license, the first pages of the passport, etc. In some enterprises, this process is organized according to a principle different from others - it is there that additional documents are needed.
A new employee is invited to write an application with a request to hire him, it is endorsed by all higher managers, and then sent to the HR department, where the inspectors formalize the newcomer and form the appropriate order for the management to sign. The HR specialist will need to introduce the new employee to a lot of important documentation:
- an order of admission to the state;
- working conditions;
- labor contract;
- internal rules;
- job descriptions;
- provisions with the requirement to keep the organization's commercial secrets (if any).
Business Processes: Final Phases
As soon as the employee is on the staff of the enterprise, it may seem that this is the end of the business process for the selection, but this is not the case. Further, HR specialists should help the newcomer to adapt in the team and learn how to behave correctly. For this, trainings, seminars are held, where new employees are told about the enterprise, its functionality, career and personal growth opportunities within the enterprise.
Business processes in this case are decomposed into a large number of sequential stages, among which hiring is the most important. As soon as the employee begins to actively express himself, the management may invite him to attend trainings aimed at developing personal and professional qualities.
As part of the existing business process, new employees are actively involved in the life of the enterprise, they are invited to events, holidays, promotions, where they can either participate or watch them as spectators. In this case, it is best for an employee not to refuse, since the team is unlikely to find it appropriate. The HR specialist is obliged to explain to the new employee that there are cultural values and norms of behavior within the company, which should be observed. In some cases, this responsibility is assigned to the immediate supervisor of the new employee; it will also be necessary to explain to the newcomer some of the little things of a domestic nature.
Thanks to such a voluminous business process, no new employee is left without attention. This helps him to feel much more comfortable in the new workplace and to carry out the tasks assigned to him by the enterprise. Almost all large organizations have stopped seeing their people as easily replaceable parts in a machine tool. Some businesses even choose to “nurture” top-level executives within the company without opening those positions to outside applicants. The only thing that is required of a new employee in this case is an active desire to develop and work for the good of the enterprise. Then he will definitely be noticed by the management and begin to move up the career ladder.
COURSE WORK
Small business HR management
Introduction
The chosen topic of the course work is currently relevant, since the number of companies related to small businesses in Russia is constantly growing and for them, as well as for any modern enterprise personnel management is one of the most important steps to maintaining and prospering their activities. Firstly, this direction activity reduces the cost of finding new employees, their adaptation and training in the organization, which is of paramount importance for small business organizations. Secondly, it increases the efficiency of the organization's personnel due to the competent direction and arrangement of work. Thirdly, this topic helps to form shortcomings in the work of a personnel manager, whose functions in a small enterprise are usually performed by the main manager, to find ways to turn them into advantages, to rally the team for more efficient work, etc. The study of this topic is a mandatory task of the enterprise in order to ensure effective performance and keeping it at this high level.
The object of research of the course work is LLC "Dentalium", the subject is the process of personnel management in small business.
The aim of the work is to analyze the features of personnel management in small business and develop recommendations for improving personnel management in OOO Dentalium.
To achieve the goal, the following tasks are solved in the work:
determination of the place of personnel management in the management structure of the company;
Revealing the process of personnel management in small business;
analysis of the peculiarities of training, adaptation and recruitment of workers in small business;
Analysis of personnel management activities in LLC "Dentalium";
The first chapter discusses theoretical basis- the concept and essence of small business in Russian Federation, features of personnel management in small business organizations.
The second discusses in detail such important points personnel management, as training, adaptation, the relationship of personnel with the manager in relation to small organizations.
The third chapter examines the practical application of personnel management activities in LLC "Dentalium", the current situation is analyzed, the organization, control and implementation of new techniques to improve the situation in the organization are described.
During the writing of the term paper, the literature and articles of the following authors were used: Grazhdankina E.V., Silevanov A.T., Kibanov A.Ya., Vesnin V.R. etc.
1. The theory of personnel management in small business organization
.1 Concept and essence of small business
staff adaptation management manager
An enterprise is an independent economic entity, formed as a result of the creation by an entrepreneur or an association of entrepreneurs for the production of products, performance of work and provision of services in order to meet social needs and make a profit.
The main features of an enterprise that make it an independent subject of market relations:
Organizational unity is the presence of a team at an enterprise, organized in a certain way, having its own internal structure and management procedure.
Industrial and technical unity is the union of economic resources by an enterprise for the production of goods and services (a certain set of means of production, capital, technology).
The presence of separate property that the company uses independently for certain purposes.
The enterprise bears full responsibility with its property for obligations arising in the course of its activities.
Operational, economic and economic independence - the enterprise itself carries out various kinds of transactions and operations, it itself makes a profit and bears losses.
V Civil Code RF is determined the main objective commercial enterprise- this is the achievement of a greater amount of profit or greater profitability, that is, the excess of results over costs. Also, the company has a whole range of multi-level goals that determine the strategy of activities and make up the tree of goals of the company.
Tasks solved by the enterprise in the course of its functioning:
Uninterrupted and rhythmic production of high quality products in accordance with the available production capabilities.
Satisfaction of public needs for products, comprehensive consideration of consumer requirements, the formation of an effective marketing policy.
Efficient use of production resources (fixed capital, material, financial and labor resources), increasing production efficiency.
Development of strategies and tactics for the behavior of the enterprise in the market.
Ensuring the competitiveness of the enterprise and its products, maintaining a high image and business reputation enterprises.
Improving the organization of production, labor and management; use of the latest achievements of scientific and technological progress in production.
Security social efficiency production (an increase in the qualifications and greater content of the work of workers, an increase in their standard of living, the creation of a favorable moral and psychological climate in the work collective).
Small business is a business based on the entrepreneurial activity of small firms, small enterprises that are not formally included in associations.
Entrepreneurial activity in small business can be carried out both with education legal entity, and without this procedure, associated with a certain cost of money and time. Very often, those wishing to become entrepreneurs do not need to create a legal entity, that is, an enterprise. The legislation of many countries provides an opportunity for citizens who are not limited in their legal capacity to register as an entrepreneur without forming a legal entity, that is, to become an individual entrepreneur.
The share of small and medium-sized companies is about 20% of the GDP of the Russian Federation, and so far only a quarter of working Russians are employed in them. The share of small business in the GDP of the Russian Federation relative to others developed countries is given in table 1.1.
Table 1.1. Share of small business in GDP in developed countries
Country Small business share Japan 65-70% Italy 55-60% France 50-55% Germany 60-65% USA 55-60% Great Britain 50-55% Russia 20-25%
In accordance with Federal law dated July 24, 2007 No. 209-FZ "On the development of small and medium-sized businesses in the Russian Federation" (Article 4), micro-enterprises (legal entities) include consumer cooperatives entered in the unified state register of legal entities and commercial organizations(excluding state and municipal unitary enterprises) corresponding to the following conditions:
) the total share of participation of the Russian Federation, constituent entities of the Russian Federation, municipalities, foreign legal entities, foreign citizens, public and religious organizations(associations), charitable and other funds in the authorized (joint-stock) capital (mutual fund) of the specified legal entities should not exceed twenty-five percent (except for the assets of joint-stock investment funds and closed-end mutual investment funds), the share of participation belonging to one or several legal entities that are not small and medium-sized businesses should not exceed twenty-five percent (this limitation does not apply to business entities whose activities are in the practical application (implementation) of the results of intellectual activity (programs for electronic computers, databases, inventions, utility models , industrial designs, breeding achievements, topologies integrated circuits, production secrets (know-how), the exclusive rights to which belong to the founders (participants) of such business entities - budgetary scientific institutions or scientific institutions created by state academies of sciences or budgetary educational institutions higher vocational education or educational institutions of higher professional education created by state academies of sciences);
) the average number of employees for the previous calendar year should not exceed 15 people;
) proceeds from the sale of goods (works, services) excluding value added tax or the book value of assets (residual value of fixed assets and intangible assets) for the previous calendar year should not exceed 60 million rubles (established by the decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of July 22, 2008 No. 556 "On the limit values of proceeds from the sale of goods (works, services) for each category of small and medium-sized businesses").
The average number of employees of a micro-enterprise for a calendar year is determined taking into account all its employees, including employees working under civil law contracts or part-time, taking into account the actual hours of work of employees of representative offices, branches and others. separate subdivisions microenterprises.
The procedure for conducting sample surveys of microenterprises is established by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated February 16, 2008 No. 79 "On the procedure for conducting sample statistical observations for the activities of small and medium-sized businesses ".
Individual entrepreneurs form the simplest form of small business organization, preparing the basis for other, more complex formations - partnerships (general and limited partnerships), production cooperatives and business companies in the form of limited (additional) liability companies and closed and open joint stock companies. Let's consider the above forms of organizing a small business in more detail.
An individual entrepreneur is a person who conducts business at his own expense, independently makes decisions and bears full financial and financial responsibility according to their obligations. His reward is the resulting commercial activities profit and a sense of moral satisfaction that he experiences from engaging in free enterprise.
An individual entrepreneur can fully devote himself to business, working only in the field of entrepreneurship, or he can combine entrepreneurial activity with employment or study.
Taking into account the Russian specifics of doing business without forming a legal entity, we can also note that an individual entrepreneur has the right to hire employees. In the small business system, this organizational and legal form is very mobile and in fact does not have a clear divide between an individual and a legal entity.
Individual entrepreneurs act on the market on a par with enterprises as producers of goods and services in equal rights. An entrepreneur may have an account in commercial bank, my trade mark, has the right to use a bank loan. This form of entrepreneurial activity is associated with the simplest financial and tax accounting.
Individual entrepreneurial activity is typical for small producers of goods and services, as well as for trade.
A general partnership is a partnership, the participants of which (general partners), in accordance with the agreement concluded between them, are engaged in entrepreneurial activities on behalf of the partnership and are responsible for its obligations with property belonging to them.
The firm name of a full partnership must contain either the names (names) of all participants and the word "full partnership", or the name (name) of one or more participants with the addition of the words both "company" and "full partnership". The management of the activities of a full partnership is carried out by the general agreement of all participants. Each participant in a full partnership has one vote, unless the memorandum of association provides for a different procedure for determining the number of votes of its participants. The profits and losses of a full partnership are distributed among its participants in proportion to their shares in the contributed capital, unless otherwise provided by the memorandum of association or other agreement of the participants.
A limited partnership is a type of full partnership. Compared to a general partnership, it has the following features: it consists of two groups of participants:
) general partners - carry out entrepreneurial activities on behalf of the partnership itself and bear unlimited and joint liability for the partnership's obligations;
) contributors (limited partners) - only make contributions to the property of the partnership, but do not answer with their personal property for its obligations.
A limited liability company (LLC) is a company founded by one or more persons, the authorized capital of which is divided into shares determined by the constituent documents; members of a limited liability company are not liable for its obligations and bear the risk of losses associated with the activities of the company, within the value of their contributions.
Additional liability company (ALC) - such a company is a type of LLC, however, a distinctive feature of an ALC is that if the property of this company is insufficient to satisfy the claims of its creditors, the members of the company can be held liable, and jointly with each other. However, the amount of this liability is limited - it does not concern all of their personal property, which is typical for general comrades, but only for a part of it - the same multiple size and amount of contributions for all. From this point of view, such a society occupies an intermediate place between societies and partnerships.
Although small businesses practically do not use closed and open joint stock companies that are more suitable for medium and large enterprises, consider them.
Joint-stock company (JSC) is a company, the authorized capital of which is divided into a certain number of shares. The members of the JSC are not liable for its obligations and bear the risk of losses associated with the activities of the company, within the value of the shares they own. A JSC, whose members can alienate their shares without the consent of other shareholders, is recognized as an open JSC (JSC). A JSC, whose shares are distributed only among the founders or other predetermined circle of persons, is recognized as a closed JSC (CJSC).
A production cooperative (PC) is a voluntary association of citizens for joint activities in such areas as production, processing, marketing, trade, consumer services, medical services, etc. The firm name of a cooperative must contain its name and the words "production cooperative" or "artel". The property of a PC is formed on a share basis at the expense of contributions of its members, made in cash and material forms. Founding document PC is its charter. The number of members of the cooperative must be at least 5 people. The property owned by the PC is divided into shares of its members in accordance with the charter of the cooperative. The profit of the cooperative is distributed among its members in accordance with their labor participation unless a different procedure is provided for by the charter of the cooperative. A PC can be voluntarily reorganized into a business partnership or society by a single decision of its members, or liquidated. The PC is not entitled to issue shares.
Limitation on the number of employees in small business - up to 100 employees.
Revenue limit:
Since January 1, 2008, in accordance with the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated July 22, 2008 No. 556, limit values of proceeds from the sale of goods (works, services) for the previous year, excluding value added tax, have been established for the following categories of small and medium-sized businesses: small enterprises - 400 million rubles.
Summing up, we can conclude that the level of development of small and micro-businesses in the Russian Federation is significantly lower than in many countries with developed market economies. Those. in countries with developed market economies, the percentage of small and micro-enterprises, their contribution to GDP is greater than in the Russian Federation.
1.2 Personnel management in a small business organization: modern tendencies
Since 1991, Russia has been implementing a reform program for the transition to a socially oriented market economy, free enterprise, a new model labor relations.
The scientific approach to the formation of personnel management implies the need to take into account the requirements of physiology and psychology to the organization of labor activities of workers.
Knowledge of the basics of psychology and physiology of labor is necessary already when organizing the recruitment and hiring of employees, conducting labor expertise, professional selection, and vocational guidance.
The experience of developed countries testifies to the necessity and expediency of creating a developed nationwide system of vocational guidance, starting from school, about the need for a link between education and production.
Based on the basic provisions of psychophysiological work, a rational regime of work and rest is developed in each organization.
One of the important tasks of the organization is to establish the optimal labor intensity at which physiological costs are required from workers that do not go beyond the limits that threaten their health.
The unfavorable working conditions of workers are of particular concern. Organizations, in order to survive in difficult conditions, cut costs intended to improve working conditions, and workers, out of fear of losing their jobs, agree to work in difficult conditions. Scientists have proposed a "Hygienic classification of labor", on the basis of which the organization conducts certification of workplaces, with the help of a point assessment, an integral indicator of working conditions is calculated and the amount of compensation required for unfavorable working conditions is established.
The scientific approach to the formation and functioning of the personnel management system, along with psychophysiological problems, involves the solution of social problems.
The sociology of labor serves as a methodological basis for the study of these problems and the development of recommendations for their implementation.
Sociology of labor studies labor activity as a social process, explores social factors that increase labor efficiency, the impact of technical, technological and social conditions on attitudes towards work.
In conditions market economy a special role is acquired by research aimed at finding ways to optimally realize the employee's labor potential.
Sociology considers the development of collective forms of labor organization, the transfer of the functions of operational planning and management, determination of the number and placement of personnel by the primary labor collective as one of the main directions in work to increase the content and attractiveness of labor.
In any labor process there is a combination of two factors of production: personal and social.
Personnel management is considered as an organizational and economic mechanism of subordination and the use of hired labor in the economic system.
The transition to a personnel management policy in modern conditions is associated with the formation of a new normative culture, focused on a person and providing for the maximum involvement of employees in the affairs of the organization and self-discipline.
The peculiarities of a small business require managers to be highly professional in the field of personnel management. The general features of personnel management of a small enterprise, regardless of the form of ownership and the field of activity of the organization, include a number of characteristics:
The complex nature of activities and flexible organization of work. The lack of a clear functional separation between administrative and production personnel helps to reduce the distance between personnel, but does not eliminate social differences(for example, in wages). Employees of a small enterprise have to perform functions that are not characteristic of their positions, therefore, they do not need narrow professionals, but universal workers who are able to combine positions and perform different kinds works. One of strengths small business - freedom in determining the scope of responsibilities and the ability to quickly change.
Lack of a multilevel organizational structure. This leads staff to understand careers as extensions and complications. functional responsibilities, the growth of professionalism, an increase in wages, and not a promotion.
Relatively higher awareness of employees. It is difficult for a plant manager to hide information about working methods and relationships with clients from the staff and government agencies... This awareness puts the employer in some dependence on the employee and thereby forces them to search for personnel among relatives, personal acquaintances or on the recommendation of trusted people.
Less bureaucracy in work. Small businesses lack many regulatory guidance documents personnel work, but there is a system of unofficial installations. This disposes to an individual approach to each situation and the employee, however, it leads to the emergence of conflicts, the expression of personal sympathies and antipathies of the manager to the employees.
There is practically no organizational learning. This is explained by a number of reasons: the manager's underestimation of the need for training, lack of funds, uncertainty of the company's prospects.
A small business places high demands on the personal qualities of an employee. A small team will quickly get rid of workers whose qualities do not correspond to the accepted norms and values of the given enterprise.
The principles of personnel selection are sometimes focused not on direct, but on indirect evidence of professional suitability. Recommendations for small businesses are actually confirmation that the candidate has acquaintances and colleagues who are ready to answer with their reputation for the actions of the employee. In other words, it is not only the content of the recommendation that is important, but the personality (position) of the person who gives it. The principles of personnel selection are focused not on direct, but on indirect evidence of the candidate's professional competence. The company receives an employee with specific capital in the form of personal acquaintances, official contacts and informal connections, which in the future can bring additional orders and proposals to the company.
One of the most important problems of small business workers is social insecurity. The well-being of staff depends on the manager. There is a weak formalization of labor relations: often preference is given to oral employment contracts, labor protection is rarely guaranteed, flexible forms of forcing employees to work without paying sick leave are widely practiced. annual leave... Practically all small enterprises lack collective agreements or trade unions that could put pressure on the administration to protect the interests of workers.
A significant difference in the starting conditions of enterprises. The former state-owned enterprises already had premises, equipment, and an established system of economic ties. This gives them the opportunity to develop and improve the social sphere and invest in personnel training and development. However, the orientation towards the traditional organization of labor does not allow them to provide sufficient flexibility to operate in a market environment, which is reflected in lower profitability compared to new enterprises.
In addition to the listed aspects in organizing the activities of small enterprises, a number of points can be distinguished that are used to motivate highly qualified workers and employees:
the place of work is not far from home;
employees are often impressed by the speed of decision-making and communication processes;
close business relationship between the employer and the staff make it easier to solve problems;
employee achievements are recognized and rewarded more quickly;
the personnel of the enterprise have more opportunities for career growth;
employees can take part in the decision-making process;
wages can be comparable to the wages paid in large enterprises;
small businesses are not constrained by numerous regulations;
participation in the income of the enterprise;
employees can become shareholders or partners.
Not all of these opportunities are available to every small business, but many can be part of a workforce management plan.
In general, personnel management of a small enterprise is a poorly systematized procedure. However, the complex nature of the activities of employees and the subordination of all functions to one person create the prerequisites for the emergence of a systematic approach to personnel management.
2. Specificity of personnel management in small business
.1 Features of selection and adaptation of personnel
Personnel selection is the process by which an enterprise selects from a list of applicants the person or persons best suited to the criteria for a vacancy.
The selection of personnel in small businesses is not very different from the selection in large firms. The main difference lies in the limited finances and, as a result, the impossibility of carrying out such expensive analytical operations as, for example, graphological and physiognomic examinations in the selection of applicants, as well as the universalization of the employee (combining several posts by him or simply conducting side work, not provided for by him. position).
A small business HR manager is usually the only resource for a small business firm to review the applicant's application documents and evaluate their performance during the trial period.
To begin with, the HR manager in a small business is invited to think about the questions, answering which you can get information that allows you to write a job description and more efficiently select the appropriate employee.
what is the name of the work?
where should this work be done?
what is the purpose of the work, who is responsible for the employee?
what is the employee responsible for?
Who does the employee deal with in the course of the work?
what are the main tasks of the work, how are these tasks performed?
what working standards are expected?
what skills, knowledge and experience are needed to do this job?
does this work require physical and / or mental labor?
which tasks are simple, which tasks are difficult?
Internal source - employees who are already employed in the organization and have the desire, opportunity (or need) and competencies to fill the opened vacancy.
External source - applicants for a vacancy with appropriate education and professional skills, but employed in other enterprises; temporarily not working or being in the status of graduates of educational institutions of various ranks.
Small business is characterized by the choice of an external source of attracting candidates.
Thus, having compiled a general picture of the position of a future employee, the HR manager places advertisements for the search for an employee on various Internet and print resources, contacts recruiting agencies (options for finding an employee depend on his future position and the required qualifications).
V modern Russia not only in large companies, but even in a small business, a resume is first required from an applicant -
a standard form of presentation of professional and personal data. The resume is as complete and at the same time concisely presents the employer with the image of a candidate for a vacant position. Further, the HR manager invites applicants with the most interested resume for an interview. In large companies, before the interview, it makes sense to conduct a survey, in small business, due to the specific "tightness" of the team, it is preferable to immediately conduct an interview. To achieve the desired results, the manager must know how to prepare, conduct, and evaluate the interview. He can also test a prospective candidate. After completing the above procedures, a discussion of the candidate takes place, which can also be carried out during the interview. The specifics of small business presupposes a mandatory set of qualities in the hired employee: "Universality", since often in small enterprises there is a need to replace an employee and part of his duties is assumed by an employee who carries out other activities; willingness to compromise due to the "tightness" of the team; the motivation of the future employee can be social, material, economic needs, but not the need for promotion. After hiring a new employee, the HR manager's job is to provide quality training and onboarding for the new employee. The small business adaptation program includes the following questions: ) a general idea of the company (history of the organization; traditions; products (services) and its consumers; organizational structure; information about the manual); ) policy and review of procedures (granting vacations; areas of training and advanced training; rules for the protection of commercial secrets); ) wages (form of payment; pay for work on weekends; overtime; terms and form of payment (through the cashier, ATM); taxes; revision of wages; bonuses; cost reimbursement); ) additional benefits (types of insurance; availability of discounts on products; other company services for its employees); ) labor protection and safety measures; ) rules, regulations in force in the organization (standards appearance; standards business correspondence and telephone conversations, etc.). The optimal time frame for general orientation, starting with the hiring procedure, is the first week of work, but no later than the first month of work. ) job duties and the responsibility of the employee (a detailed description of the current work and expected results; an explanation of why this particular work is important, possible problems and solutions; weekend work, overtime; additional appointments (for example, replacing an absent employee); ) required reporting (reporting form; timing); ) rules, regulations (rules typical only for this type of work; informing about accidents and dangers; hygiene requirements; security and theft problems; workplace negotiations; taking things out of the unit; use of the phone and the Internet for personal purposes). The new employee is usually more serious about the job than the others. The HR manager's job is to maintain that attitude and get him out of his typical new employee state of stress. You need to treat the employee as if he is the only person on earth who is able to do this job. Then the adaptation will be successful, and the new employee will decide that our organization is the one he dreamed of working for. The process of training an employee in a small business is also important. Since employees are selected, as a rule, universal, training should affect not only the direct responsibilities of the employee, but also indirect ones. For example, in private medical clinics, in addition to their direct duties - caring for patients, helping a doctor - nurses should also be trained in the methods of sterilization with the device, sanitary duties - in case the workers responsible for these operations, for some reason, cannot perform my job. Small businesses tend to employ on-the-job rather than off-site training methods. Some of them: briefing - explanation and demonstration of work techniques; change of workplace (rotation) - allows you to expand the experience of an employee by systematically moving him from one job to another; mentoring - specially selected and trained employees (mentors) give instructions and advice to help the "protégé" attached to them to develop in their profession; method of delegating part of functions and responsibilities; training in project teams created to solve specific problems. The main benefits of on-the-job training are lower cost; great adaptability of the content and training time to the needs of the organization; great opportunities for individualization of training. The main disadvantage of this method is the heavy load on the specialists conducting the training. Lectures and self-training of an employee can be considered an off-the-job training method used in small business organizations, as other methods are used, as a rule, in large organizations. Staff training, as well as its adaptation in a new place of work, are extremely important tools for the effective operation of an organization; in a small business, these tools are of paramount importance, since “Closeness” and versatility of workplaces presuppose close contact between workers. 2.2 Features of interaction between the head of a small business and the staff
As mentioned above, a feature of a small business is a very close interaction between management and personnel. All employers in small organizations want good business relationships with their staff. But to achieve this, you need constant business conversation with employees, their stimulation, solution of their problems, elimination of conflicts in the team. Also, in addition, from a leader in a small business, understanding and help is required not only in business matters life of staff, but also in personal problems. Small business communication: This should be a two-way process between the employer and his employees. The manager must provide employees with full information on the following issues: instructions for work, changes in terms and conditions, rules and procedures production process, in the development of the enterprise. At the same time, the manager must carefully listen to the messages of employees, their opinions, suggestions and complaints. Feedback will provide at the enterprise: normal business (and not only) relationships between employees and the employer; lack of rumors and complaints; team cohesion, trust in relationships; efficiency in solving problems of personnel and the organization as a whole. Communication in a small business is usually done through: dialogue: communicating with employees during informal conversations or formal discussions, the manager provides employees with complete information and uses an effective feedback mechanism. Such conversations and discussions allow us to discuss important issues and provide employees with the opportunity to ask the manager questions and express their views. Dialogue is the main way of communication in a small business .; message board: that's enough effective method transmission of messages to all personnel, provided that information is regularly updated on it; suggestion box: the leader must take into account the ideas of his employees. A suggestion box (or book) is one way for staff to voice their opinions. It is not always possible for an employee to express his opinion or a proposal to the manager orally due to the peculiarities of his character, physiology, etc. The manager can also give a written response to the employee to his proposal or comment. To achieve team cohesion, and, consequently, more effective team performance, the head of a small business must stimulate and motivate employees. Leader can use the following factors motivation: wages - an employee evaluates his contribution to the overall result in accordance with the amount of money he receives; working conditions - the employer must provide a safe work environment and comfortable working conditions. Employees should understand and appreciate that their manager seeks to create such conditions for them; social opportunities - providing company personnel with discounts on goods and services, assistance in paying for travel, interest-free or low interest loans for various purposes, health insurance, tuition fees and other social benefits are an incentive to improve the performance of personnel; granting autonomy - providing employees with greater independence and responsibility in their daily work is also an incentive to work (for example, entrusting work, leaving the employee the right to choose the way to perform it, or involving employees in setting goals and work tasks). The head of a small business should show interest in the work of each employee, setting individual goals and objectives for the week, month, quarter. Most workers have personal or work-related problems that often escalate into conflicts that can affect how they do the job. In a small business, the manager develops a very close working relationship with the staff. This makes it possible to identify difficulties and problems at an early stage. The employee should know that he can turn to the manager for help and advice. An important aspect in interaction with personnel is the ability to manage conflicts in the enterprise and select the right personnel. Among the duties of the employee listed in the employment contract with the employer, the most important are the duties of the manager to ensure healthy and safe environment labor, labor protection for all employees of his enterprise. The head of a small business must develop a health and safety program. In accordance with the legislation, the employer is obliged to ensure the safety of employees during the operation of buildings, equipment, as well as the raw materials and materials used, the use of personal and collective protective equipment for employees, the working conditions at each workplace that meet the labor protection requirements, etc. This list of the employer's obligations to ensure their labor safety is not exhaustive. It is complemented by appropriate job-specific occupational safety standards, other laws and regulations, as well as collective agreements and agreements, internal labor regulations. Effective workforce management in a small business can increase productivity and ensure business success. Searching, selecting, hiring and developing personnel requires knowledge of the needs of employees. To stimulate the personnel of a small enterprise, it is necessary to develop a system for assessing the effectiveness of its work. Assessment cannot be based on personal attitude towards a subordinate, otherwise it can develop into criticism, which in most cases causes a negative reaction. The results must be communicated to employees with a frequency determined by the effectiveness of their work. For the assessment, specific goals and standards should always be set. The main requirement for the evaluation system is objectivity on the part of the evaluator, in our case, the leader. The activity of assessing the qualifications of employees of an enterprise is called certification. Personnel certification is a comprehensive assessment of the activities and performance of employees. In a small business, the leader is constantly in contact with all his employees and has the ability to quickly identify strengths and weaknesses employee. At the same time, periodic certification allows us to identify some of the shortcomings and positive aspects of employees. In a small business, the best way to qualify is through an all-inclusive interview. professional activity employee. It is recommended that managers of small enterprises conduct a personnel assessment to identify the employee's suitability for the position held, personal characteristics that affect labor results, to form a talent pool, and the need for training. In a small business, you should establish HR administration, which will ensure the "transparency" of compliance with the executive discipline of employees and thereby increase the degree of their responsibility. Summing up, we can say: in order to achieve normal business relationships between the management of a small enterprise and personnel, you need constant business communication with employees, their stimulation, solving their problems, eliminating conflicts in the team. Conflict resolution in a small business largely depends on the level professional competence leader, his ability to interact with employees, which is not least determined by his general culture and charisma. 2.3 Analysis of HR management activities in the organization
Analysis of personnel management activities in a small business organization can be carried out according to various criteria, this paper will describe the main ones. ) Analysis of the composition and structure of personnel. The characteristics of the composition and structure of personnel are given in terms of indicators such as: gender, age, education (general secondary, specialized secondary, specialist, bachelor, master), time of work in a given organization; information for analysis can be collected in the statistical documents of the organization, from the personal files of employees. An assessment of the changes that have occurred in the personnel structure for the analyzed period (as a rule, 1-5 years) is given. Diagrams are built, reflecting the structure of personnel in reporting period and their analysis is carried out. ) Analysis of the use of labor potential. To analyze the use of the labor potential of the enterprise, indicators of a comprehensive assessment of employees, obtained as a result of certification, are used. The purpose of the analysis is to identify the compliance or inconsistency of the actual level of labor potential with the required one and the degree of use of labor potential. It is possible to construct diagrams for each indicator (for example, skill level) that characterize the labor potential of workers, as well as a diagram that characterizes the use of the labor potential of workers for all indicators. Skill levels of employees may meet the requirements of their position, be in excess of job requirements, greatly exceeding, as well as whose qualification level is insufficient to perform official duties. Variants of the ratio of the labor potential of the employee (or the team itself), the actual use and the level of labor potential required by production conditions. The quality of the labor potential of the enterprise is determined by the characteristics of the main part of the personnel. Best (ideal) ratio: Potential = Its actual use = Labor potential The available labor potential in the organization, i.e. all the capabilities of workers as carriers work force are used completely, and this corresponds to the needs of production. In practice, the following option is often encountered: Potential> Its actual use = Labor potential Such a ratio indicates that the existing labor potential is not fully used, but the level of its actual use meets the needs of production. For this reason, the labor potential reserve cannot be used, since there is no direct need. Underutilization of the available labor potential of employees may result in underutilization of the working time fund through the fault of employees, poor motivation of employees for high-performance work, dissatisfaction with work due to lack of opportunities for professional growth, low level of labor intensity, etc. The situation when the underutilization of the available labor potential becomes too great, i.e. Potential> Actual use< Трудовой потенциал, свидетельствует о том, что фактический уровень использования имеющегося потенциала уже настолько низок, что из-за этого страдает производство и остро стоит проблема реализации имеющихся резервов рабочей силы. The following option is also possible: Potential = Actual use of it< Трудовой потенциал. It testifies to the fact that, despite the full use of the available labor potential, the needs for labor, both in terms of quantity and quality, are not fully satisfied. Indicators of this situation can be: a shortage of labor, a large number of overtime work, low quality of their implementation, etc. In these conditions management decisions should be aimed at building up labor potential, changing its quantitative and qualitative characteristics.
Popular
- Preventive maintenance and its role in production
- Planned preventive maintenance of equipment
- On the procedure for placing non-stationary objects of seasonal trade
- Provisions on the placement of non-stationary shopping facilities
- Decorative painting in kindergarten "magic curl" is a joint activity of the teacher and
- Synopsis of the organization and conduct of classes on cognitive development in the second junior group "Bird feeder
- New professions Where to get information about the right specialists
- Plasticine diplodocus. Sculpting lesson. How to easily make basic shapes from plasticine: a ball, cone, cylinder, plait, brick How to make a cylinder from plasticine
- Rating of recruiting agencies
- Rating of recruiting agencies