Document electrician for the repair of lifting mechanisms. Production instruction for a locksmith
MINISTRY OF LABOR AND SOCIAL DEVELOPMENT
RUSSIAN FEDERATION
APPROVED
Deputy Minister of Laborand social development
Russian Federation
Typical instruction
on labor protection for electricians
for the repair and maintenance of electrical equipment
lifting machines
TI R M-O16-2000
1. GENERAL SAFETY REQUIREMENTS
1.1. To carry out the work of an electrician for the repair and maintenance of electrical equipment of hoisting machines, workers are allowed at least 18 years of age who have passed a medical examination, trained according to the appropriate program and certified by the qualification commission, as well as who have received instructions on safe working methods directly at the workplace with registration in the Instruction Registration Log. 1.2. An electrician admitted to the repair and maintenance of hoisting machines must have an electrical safety group of at least III. 1.3. A certified electrician is issued a certificate for the right to repair and maintain electrical equipment of hoisting machines signed by the chairman of the commission, sealed with a stamp. 1.4. The admission to the work of an electrician for the repair and maintenance of hoisting machines is issued by order of the enterprise (workshop, section) after the issuance of a certificate and instructions on labor protection. 1.5. Re-testing the knowledge of an electrician who repairs and maintains hoisting machines is carried out: periodically, at least once every 12 months; when moving from one enterprise to another; at the request of an employee responsible for the supervision of hoisting machines at the enterprise, or an inspector of Gosgortekhnadzor. Knowledge is tested in the scope of the labor protection instructions, the relevant sections of the "Safety regulations for the operation of consumer electrical installations" and "Rules for the design and safe operation of cranes". 1.6. An electrician admitted to independent work on the repair and maintenance of electrical equipment of hoisting machines must know: labor protection instructions for electricians when servicing general production electrical equipment with voltage up to 1000V; basic provisions of general electrical engineering; purpose, arrangement and principle of operation of units, mechanisms and electrical equipment of hoisting machines; electrical circuits fixed for the maintenance of lifting machines; the relevant sections of the "Safety Rules for the Operation of Electrical Installations of Consumers" and "Rules for the Design and Safe Operation of Hoisting Cranes"; the main causes of damage and accidents on the electrical equipment of hoisting machines, be able to find and eliminate them. 1.7. The electrician is obliged to comply with the internal labor regulations of the enterprise. Smoking in production and auxiliary premises and on the territory of the enterprise is allowed only in places specially designated for this purpose. 1.8. During work, the electrician may be affected by the following hazardous and harmful production factors: noise and vibration from working mechanisms; electricity; industrial microclimate. 1.9. The electrician must be provided with personal protective equipment: cotton overalls; dielectric gloves; dielectric galoshes. 1.10. An electrician admitted to independent work on the repair and maintenance of electrical equipment of hoisting machines must: inspect and repair electrical equipment of hoisting machines; prepare the electrical equipment of hoisting machines for technical certification. 1.11. An electrician for the repair and maintenance of lifting machines must know and observe the rules of personal hygiene. 1.12. An electrician for the repair and maintenance of hoisting machines must be able to provide the victim with first (pre-medical) aid in case of an accident. 1.13. In case of any questions related to its safe performance in the course of work, it is necessary to contact the employee responsible for the safe performance of work. 1.14. A trained and certified electrician for the repair and maintenance of electrical equipment of lifting machines is fully responsible for violation of the requirements of this Instruction in accordance with applicable law.2. SAFETY REQUIREMENTS BEFORE WORKING START
2.1. Before starting work, the electrician must familiarize himself with the entries in the operational log, accept from the electrician who handed over the shift the technical documentation approved by the power engineer, safety protective equipment, make an entry on the acceptance of the shift in the operational log and sign. 2.2. Make sure the work area is adequately lit. 2.3. Tidy up the workplace, remove all items that may interfere with safe work. 2.4. Put on the appropriate overalls, prepare serviceable and tested personal protective equipment (dielectric gloves, galoshes). 2.5. Notify the foreman or supervisor of all noticed shortcomings in the workplace and do not start work until their instructions.3. SAFETY REQUIREMENTS DURING WORK
During maintenance between repairs 3.1. Work carried out to eliminate faults in the electrical equipment of hoisting machines at the request of drivers and non-electrical personnel, and inspections regarding the safety of their implementation are divided into: work performed in the order of current operation, with an entry in the operational log; for work performed by order of administrative and technical personnel with an electrical safety group of at least IV, with an entry in the operational log. In the order of current operation, the electrician on duty for servicing the electrical equipment of hoisting machines is allowed, in the presence of a driver (crane operator) who has an electrical safety group II, to perform the following work: inspection of electrical equipment; replacement of burnt-out lamps and fuse-links; repair and replacement of electric devices located in the cab of the driver (crane operator); checking the correct operation of safety instruments and devices, lighting, signaling and blocking, with the exception of signaling devices indicating the presence of voltage on the main trolleys. 3.2. The electrician, having received an application from the driver (crane operator), must make an entry in the operational log, indicating the date and time of receipt of the application, the name and position of the person who submitted the application, the content of the application and the start time of work. After eliminating the detected faults in the same journal, it is necessary to make a record of the content of the work performed and the time of their completion. At the same time, a record is made of troubleshooting in the logbook of the driver (crane operator). 3.3. If faults are found that are not related to the list of works performed in the order of current operation, the electrician on duty must report to the shift supervisor about the deficiencies found. 3.4. Work performed by order, with an entry in the operational log: replacement of burned-out electric motors; replacement of electromagnetic coils and brakes; adjustment of limit switches; conducting periodic inspections. 3.5. The execution of work according to the order should be carried out by two employees with an electrical safety group of at least III, with complete removal of voltage, with the implementation of the necessary organizational and technical measures in accordance with the requirements of the "Safety Rules" when operating consumer electrical installations with an entry in the operational log. 3.6. The employee giving the order must determine the composition of the team, the foreman and organize the admission of the team to work. 3.7. For all types of repairs and inspections of the electrical equipment of a crane located between two operating cranes, a work permit must be issued with entries in the watch logs of all cranes of this span. 3.8. Periodic inspection of the electrical equipment of hoisting machines is aimed at identifying and eliminating possible malfunctions in electrical equipment, safety devices and devices, in power circuits, control circuits, alarm circuits, checking the serviceability of safety protective equipment and fire extinguishing equipment and confirming in the journal of periodic inspections that the electrical equipment of hoisting machines is in good condition. 3.9. When inspecting the electrical equipment of cranes, the adjustment and activation of the mechanisms must be carried out at the signal of the person performing the inspection. 3.10. When moving the crane bridge, workers inspecting and troubleshooting the crane's electrical equipment should be in the cab or on the bridge deck, while avoiding touching the protruding parts of the ceiling, columns, fittings. When entering the flooring of the crane gallery, the knife switch in the driver's cab must be turned off and a poster "Do not turn on - people are working" is posted on its drive. Remove the poster only by order of operational personnel. 3.11. When inspecting and troubleshooting the electrical equipment of the crane, it is necessary to observe all precautions, use the necessary serviceable and tested protective equipment. 3.12. Upon completion of the repair and inspection, all removed guards on electrical equipment and on electrical appliances must be put in place and strengthened. 3.13. The results of the inspection for each crane separately must be recorded in the journal of periodic inspections indicating the date, time of the inspection, a summary of the identified and eliminated deficiencies, and there must be a signature of the personnel performing the repair. 3.14. When troubleshooting, adjusting and inspecting the electrical equipment of the crane, it is prohibited: to enter the crane and leave it while it is moving; go out onto the crane tracks, walk along the crane tracks, climb from one crane to another; to adjust the brake of the mechanism with a raised load, as well as to install devices for releasing the brake manually; leave tools, as well as loose equipment and parts on the gallery floor or on the trolley; dump tools, materials and spare parts from the crane. 3.15. For portable power tools and portable lamps, use a safe voltage not higher than 36 V. 3.16. When performing all work, the electrician must withdraw the key-mark from the crane operator in the manner established at the enterprise for the use of the key-brand system.During scheduled repairs
3.17. The withdrawal of the crane for repair should be carried out by the employee responsible for maintaining the lifting machines in good condition, in accordance with the scheduled repair schedule with the issuance of an order for work in electrical installations. The outfit is issued by representatives of the electrical personnel of the site, authorized by the order of the chief power engineer of the enterprise. In the lines of the “Separate instructions” order, additional safety measures are recorded related to working at height, to prevent running cranes from colliding with the one being repaired, the repair personnel entering the crane tracks of existing cranes, etc. The issued order is handed over to the employee responsible for the repair the day before the start of the repair. for the maintenance of lifting machines in good condition, which, by signature, allows work in the lines “Separate instructions” of the order and returns it to the employee who issued the order. The employee responsible for maintaining hoisting machines in good condition, prior to the start of repairs, is obliged to make the following entry in the watch log of the driver (crane operator) of the crane being repaired: “. date _________ of the month of _____ of the year, until __ h _____ min of ____ of the ____ of the month of _______ of the year” and sign. 3.18. The work order for work in electrical devices must indicate the composition of the team, the foreman who allows work, the worker issuing the work order; necessary technical measures to ensure the safety of work during the repair of electrical equipment of the crane; date and time of commencement of work, admission of the brigade and completion of work. 3.19. The admission of the brigade to the repair of the electrical equipment of the crane is carried out by an employee of the operational personnel on the basis of an order for work in electrical installations and the permission of the personnel responsible for maintaining the hoisting machines in good condition. The admitting person makes an entry in the operational log of the power engineering service with the design of the appropriate columns in the order and admits the brigade to the crane. 3.20. To ensure safety during the repair of the electrical equipment of the crane, it is necessary to put it on the repair site, make the necessary shutdowns, lock the knife switch drive, hang safety warning posters, install portable grounding and make a fence under the repair site. 3.21. Repair of the electrical equipment of the crane can be carried out by electricians who have a certificate for the right to repair and maintain hoisting machines; of these, at least two people must have an electrical safety group of at least III. 3.22. Do not allow strangers to the crane. It is forbidden to enter the crane tracks without obtaining a special permit. 3.23. Upon completion of the repair and closing of the order, the employee responsible for maintaining the hoisting machines in good condition checks the readiness of the crane for operation, makes an entry in the crane watch log: “I allow the crane to operate from ___ h _____ min ____ day ______ month ____ year” with his signature.
4. SAFETY REQUIREMENTS IN EMERGENCIES
4.1. In the event of an accident, the victim or an eyewitness who was at the same time is obliged to immediately notify the foreman or head of the site, who must organize the provision of first (pre-medical) aid to the victim and send him to a medical institution. In case of a severe accident, immediately call an ambulance and notify the administration. 4.2. Troubleshooting of electrical equipment of hoisting machines should be carried out only when the crane is disconnected from the mains.5. SAFETY REQUIREMENTS AFTER WORK IS COMPLETED
5.1. At the end of the shift or work, the electrician must: put the workplace in order; remove parts, materials, electrical equipment and tools; tidy up the wiring diagrams and other technical documentation; make an entry in the operational log on the technical condition of the electrical equipment of hoisting machines in the assigned area; hand over to the electrician accepting the shift the technical documentation approved by the power engineer of the shop (site), safety protective equipment, make an entry on the handover of the shift in the operational log and sign the handover of the shift.WORK SAFETY INSTRUCTION No. 10
FOR ELECTRICIANS FOR REPAIR AND MAINTENANCE OF ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT OF LOAD-LIFT MACHINES
Electricians for the repair and maintenance of electrical equipment of hoisting machines in the performance of work according to their qualifications are required to comply with the safety requirements set forth in the "Instructions on labor protection for workers in the construction, building materials industry and housing and communal services", this instruction, developed taking into account building codes and regulations Russian Federation, "Rules for the design and safe operation of cranes" Gosgortekhnadzor of Russia.
1. GENERAL SAFETY REQUIREMENTS
1.1. To perform the work of an electrician for the repair and maintenance of electrical equipment of hoisting machines, persons are allowed at least 18 years of age who have passed a medical examination, trained in the appropriate program and certified by the qualification commission, as well as who have received instructions on safe working methods directly at the workplace with registration in the instruction log.
1.2. An electrician authorized to repair and maintain hoisting machines must have an electrical safety group of at least III.
1.3. A certified electrician is issued a certificate for the right to repair and maintain electrical equipment of hoisting machines signed by the chairman of the commission, sealed with a stamp.
1.4. The admission to the work of an electrician for repairs is issued by an order for the enterprise (workshop, section) of the labor protection instruction.
1.5. Re-testing the knowledge of an electrician; carrying out repair and maintenance of hoisting machines, is carried out:
periodically, at least once every 12 months;
- when moving from one enterprise to another;
- at the request of the person responsible for the supervision of hoisting machines at the enterprise, or the inspector of Gosgortekhnadzor.
Knowledge is tested in the scope of the Labor Protection Instructions, the relevant sections of the Safety Rules for the Operation of Electrical Installations of Consumers and the Rules for the Design and Safe Operation of Hoisting Cranes.
1.6. An electrician admitted to independent work on the repair and maintenance of electrical equipment of hoisting machines must know:
- instructions on labor protection for electricians when servicing general-purpose electrical equipment with voltage up to 1000 V;
- the basic provisions of general electrical engineering;
- purpose, arrangement and principle of operation of units, mechanisms and electrical equipment of hoisting machines;
- electrical circuits fixed for the maintenance of lifting machines;
- the relevant sections of the Safety Rules for the operation of consumer electrical installations and the Rules for the Design and Safe Operation of Hoisting Cranes;
- the main causes of damage and accidents on the electrical equipment of hoisting machines, be able to find and eliminate them.
1.7. The electrician is obliged to comply with the internal labor regulations of the enterprise. Smoking in production and auxiliary premises and on the territory of the enterprise is allowed only in places specially designated for this purpose.
1.8. During work, the electrician may be exposed to the following hazardous and harmful production factors:
- noise and vibration from working mechanisms;
- electricity;
— industrial microclimate.
1.9. The electrician must be provided with personal protective equipment:
- cotton overalls;
- dielectric gloves;
- dielectric galoshes.
1.10. An electrician admitted to independent work on the repair and maintenance of electrical equipment of hoisting machines must:
- to inspect and repair electrical equipment of hoisting machines;
— prepare the electrical equipment of hoisting machines for technical certification.
1.11. An electrician for the repair and maintenance of lifting machines must know and observe the rules of personal hygiene.
1.12. An electrician for the repair and maintenance of hoisting machines must be able to provide the victim with first (pre-medical) aid in case of an accident.
1.13. If any questions arise during the work related to its safe performance, it is necessary to contact the person responsible for the safe performance of work.
1.14. A trained and certified electrician for the repair and maintenance of electrical equipment of lifting machines is fully responsible for violation of the requirements of this Instruction in accordance with applicable law.
2. SAFETY REQUIREMENTS BEFORE WORKING START
2.1. Before starting work, the electrician must familiarize himself with the entries in the operational log, accept from the electrician who handed over the shift the technical documentation approved by the power engineer, safety protective equipment, make an entry on the acceptance of the shift in the operational log and sign.
2.2. Make sure the work area is adequately lit.
2.3. Tidy up the workplace, remove all items that may interfere with safe work.
2.4. Put on the appropriate overalls, prepare serviceable and tested personal protective equipment (dielectric gloves, galoshes).
2.5 Notify the foreman or supervisor of all noticed shortcomings in the workplace and do not start work until their instructions.
3. SAFETY REQUIREMENTS BEFORE WORKING START
During maintenance between overhauls
3.1. Work carried out to eliminate faults in the electrical equipment of hoisting machines at the request of machinists and non-electrical personnel, and inspections regarding the safety of their implementation are divided into:
- work performed in the order of current operation, with an entry in the operational log;
- work performed by order of administrative and technical personnel with an electrical safety group of at least IV, with an entry in the operational log.
In the order of current operation, the electrician on duty for servicing the electrical equipment of hoisting machines is allowed, in the presence of a driver (crane operator) who has an electrical safety group II, to perform the following work:
- inspection of electrical equipment;
— replacement of burned-out lamps and fusible inserts;
— repair and replacement of electric devices located in the cab of the driver (crane operator);
– checking the correct operation of safety instruments and devices, lighting, signaling and blocking, with the exception of signaling devices indicating the presence of voltage on the main trolleys
3.2. The electrician, having received an application from the driver (crane operator), must make an entry in the operational log, indicating the date and time of receipt of the application, the name and position of the person who submitted the application, the content of the application and the start time of work.
After eliminating the detected faults in the same journal, it is necessary to make a record of the content of the work performed and the time of their completion. At the same time, a record is made of troubleshooting in the logbook of the driver (crane operator).
3.3. If faults are found that are not related to the list of works performed in the order of current operation, the electrician on duty must report to the shift supervisor about the deficiencies found.
3.4. Work performed by order, with an entry in the operational log:
— replacement of burned-out electric motors;
— replacement of electromagnetic coils and brakes;
— adjustment of limit switches;
- Carrying out periodic inspections.
3.5. The execution of work according to the order must be carried out by two persons who have an electrical safety group of at least III, with complete removal of voltage, with the implementation of the necessary organizational and technical measures in accordance with the requirements of the Safety Rules for the operation of consumer electrical installations with an entry in the operational log.
3.6. The person giving the order must determine the composition of the team, the foreman and organize the admission of the team to work.
3.7. For all types of repairs and inspections of the electrical equipment of a crane located between two operating cranes, a work permit must be issued with entries in the watch logs of all cranes of this span.
3.8. Periodic inspection of the electrical equipment of hoisting machines is aimed at identifying and eliminating possible malfunctions in electrical equipment, safety devices and devices, for power purposes, for control purposes, signaling, checking the serviceability of safety protective equipment and fire extinguishing equipment and confirming in the journal of periodic inspections that the electrical equipment of hoisting machines is in good condition.
3.9. When inspecting the electrical equipment of cranes, the adjustment and activation of the mechanisms must be carried out at the signal of the person performing the inspection.
3.10. When moving the crane bridge, persons inspecting and troubleshooting the crane's electrical equipment should be in the cab or on the bridge deck, while avoiding touching the protruding parts of the ceiling, columns, fittings.
3.11. When exiting to the deck of the crane gallery, the knife switch in the driver's cab must be turned off and a poster "Do not turn on - people are working" is posted on its drive. Take down the poster on order of operational personnel.
3.12. When inspecting and troubleshooting the electrical equipment of the crane, it is necessary to observe all precautions, use the necessary serviceable and tested protective equipment.
3.13. Upon completion of the repair and inspection, all removed guards on electrical equipment and on electrical appliances must be put in place and strengthened.
3.14. The results of the inspection for each crane separately must be recorded in the journal of periodic inspections indicating the date, time of the inspection, a summary of the identified and eliminated deficiencies, and there must be a signature of the person performing the repair.
3.15. When troubleshooting, adjusting and inspecting the electrical equipment of the crane, it is prohibited:
- enter the crane and get off it during its movement;
- go out on the crane tracks, walk on crane tracks, climb from one crane to another;
- adjust the brake of the mechanism with the load raised, as well as install devices for releasing the brake manually;
- leave tools, as well as loose equipment and parts on the gallery flooring or on the trolley;
- dump tools, materials and spare parts from the crane.
3.16. For portable power tools and portable lamps, use a safe voltage not higher than 36 V.
3.17. When performing all work, the electrician must withdraw the key-brand from the crane operator in the manner established at the enterprise for the use of the key-brand system.
During scheduled repairs
3.18. The withdrawal of the crane for repair should be carried out by the person responsible for maintaining the hoisting machines in good condition, in accordance with the scheduled repair schedule, with the execution of an order for work in electrical installations. The outfit is issued by persons of the electrical personnel of the site, authorized by the order of the chief power engineer of the enterprise.
In the lines of the “Separate instructions” order, additional safety measures are recorded related to working at height, to prevent running cranes from colliding with the one being repaired, the repair personnel entering the crane tracks of existing cranes, etc. The completed order is handed over to the person in charge the day before the start of the repair. for the maintenance of hoisting machines in good condition, which, with a signature, allows the work of the order in the lines "Separate instructions" and returns it to the person who issued the order.
The person responsible for maintaining the hoisting machines in good condition, before the start of the repair, is obliged to make an entry in the logbook of the driver (crane operator) of the crane under repair with the following content:
“I allow the foreman of work comrade ____ to produce
repair of electrical equipment of the crane No. __ by ____ type of repair
from ___ h ___ min ___ day ___ month ____ year,
until __h __min__day of the month-year” and sign.
3.19. The order for work in electrical devices must indicate the composition of the team, the foreman who allows work, the person issuing the order; necessary technical measures to ensure the safety of work during the repair of electrical equipment of the crane; date and time of commencement of work, admission of the brigade and completion of work.
3.20. The admission of the brigade to the repair of the electrical equipment of the crane is made by the person of the operating personnel on the basis of an order for work in electrical installations and the permission of the person responsible for maintaining the lifting machines in good condition. The admitting person makes an entry in the operational log of the power engineering service with the design of the appropriate columns in the order and admits the brigade to the crane.
3.21. To ensure safety during the repair of the electrical equipment of the crane, it is necessary to put it on the repair site, make the necessary shutdowns, lock the knife switch drive, hang safety warning posters, install portable grounding and make a fence under the repair site.
3.22. Repair of the electrical equipment of the crane can be carried out by electricians who have a certificate for the right to repair and maintain hoisting machines, at least two people with an electrical safety group of at least III.
3.23. Keep unauthorized persons away from the crane. It is forbidden to enter the crane tracks without obtaining a special permit.
3.24. Upon completion of the repair and closing of the order, the person responsible for maintaining the hoisting machines in good condition checks the readiness of the crane for operation, makes an entry in the crane watch log:
“I authorize the operation of the crane from ___ h ____ min ___ day ____ month ___ year” with my signature.
4. SAFETY REQUIREMENTS IN EMERGENCIES
4.1. In the event of an accident, the victim or an eyewitness who was at the same time is obliged to immediately notify the foreman or head of the site, who must organize the provision of first (pre-medical) aid to the victim and send him to a medical institution. In case of a severe accident, immediately call an ambulance and notify the administration.
4.2. Troubleshooting of electrical equipment of hoisting machines should be carried out only when the crane is disconnected from the mains.
5. SAFETY REQUIREMENTS AFTER WORK IS COMPLETED
5.1. At the end of a shift or work, the electrician must:
- tidy up the workplace;
- remove parts, materials, electrical equipment and tools;
- put in order the wiring diagrams and other technical documentation;
- make an entry in the operational log on the technical condition of the electrical equipment of hoisting machines in the assigned area;
- to hand over to the electrician accepting the shift the technical documentation approved by the power engineer of the workshop (site), safety protective equipment, make an entry on the handover of the shift in the operational log and sign the handover of the shift.
Safe operation oversight structure
lifting machines at the enterprise.
Chief Engineer
Engineering and technical staff for supervision of safe operation of load-lifting cranes
Engineer responsible for the maintenance of cranes in good condition
Person responsible for the safe operation of cranes
1. Locksmiths;
2. Electricians;
3. Instrument fitters
crane operators
1. Slingers;
2. Signalmen
To oversee the safe operation of cranes, the owner must appoint engineering and technical workers after training and testing their knowledge of these Rules, job descriptions for responsible specialists and production instructions for service personnel by an examination committee with the participation of an inspector of the State Gortekhnadzor and issuing them an appropriate certificate.
To ensure that the cranes are kept in good condition, the owner must appoint an engineering and technical worker of the appropriate qualification after training and testing his knowledge of these Rules by an examination committee with the participation of an inspector of the State Mining and Technical Supervision and issuing him an appropriate certificate and job description.
In each workshop, at the construction site or other site of crane work in each shift, a person responsible for the safe performance of work by cranes must be appointed by order from among the foremen, foremen, heads of workshops, sections. At warehouses of materials and other areas of work, warehouse managers and foremen can be appointed as persons responsible for the safe performance of work by cranes, in agreement with the state mining supervision authorities. The appointment of these employees as persons responsible for the safe performance of work by cranes should be made after training and testing their knowledge of the relevant sections of these Rules, job descriptions, production instructions for crane operators and slingers. The knowledge test is carried out by an examination committee with the participation of an inspector of the State Mining and Technical Supervision. Persons who have passed the knowledge test are issued a certificate and job description. (9.4.4).
To control and maintain cranes, the owner is obliged to appoint crane operators, locksmiths and adjusters of safety devices, and for servicing cranes with electric drive, in addition, electricians. (9.4.8).
Specially trained workers may be appointed to perform the duties of a crane operator, locksmith, electrician, adjuster of safety devices, slinger. (9.4.14).
Crane operators, other maintenance and repair personnel, before being assigned to work, must undergo a medical examination to determine whether their physical condition meets the requirements for workers in these professions. (9.4.15).
Training and certification of crane operators, slingers, locksmiths, electricians and adjusters of safety devices should be carried out in vocational schools, as well as in courses and technical schools for training workers in these specialties, created in organizations that have a basis for theoretical and industrial training and have permission (license) of Gosgortekhnadzor bodies. The training of workers in these specialties should be carried out according to programs developed by training centers and agreed with the Gosgortekhnadzor of Russia. (9.4.16).
Re-testing the knowledge of service personnel (crane operators, mechanics, electricians, adjusters of safety devices and slingers) by the qualification commission should be carried out:
A) periodically, at least once every 12 months;
B) when an employee moves to another place of work;
C) at the request of an engineering and technical worker for supervision of the safe operation of load-lifting cranes or an inspector of the State Gortekhnadzor.
Re-testing of knowledge should be carried out in the scope of the production instruction. Participation of the Gosgortekhnadzor inspector in the re-examination of the knowledge of the service personnel is not necessary. (9.4.19).
The results of certification and periodic testing of the knowledge of the service personnel must be documented in a protocol with a mark in the certificate. (9.4.20).
Participation of a representative of the Gosgortechnadzor in the work of the qualification commission during the initial certification of crane operators, adjusters of safety devices and slingers is mandatory. Certification of other workers servicing cranes can be carried out without the participation of the inspector of the State Gortekhnadzor, by the qualification commission of the organization that conducted the training. (9.4.21).
Persons who have passed the exams are issued appropriate certificates signed by the chairman of the qualification commission, and crane operators, their assistants, adjusters of safety devices and slingers - signed by the chairman of the qualification commission and a representative of the state technical supervision. The crane operator's license must indicate the types of cranes he is authorized to operate. A photo card must be pasted into the certificate of the crane operator and slinger. They must carry this ID while working. (9.4.22).
Admission to the work of crane operators, their assistants, locksmiths, electricians, adjusters of safety devices and slingers must be issued by order (instruction) for the organization. (9.4.23).
For proper maintenance of cranes, the owner is obliged to provide crane operators, their assistants, mechanics, electricians, adjusters of safety devices and slingers with production instructions that define their duties, safe work procedures and responsibilities. Production instructions for maintenance personnel must be issued against receipt before they are allowed to work. (9.4.26).
Registration of load-lifting cranes in the bodies of state technical supervision
Before being put into operation, cranes of all types listed in Art. 1.3 of these Rules, with the exception of those specified in Art. 9.1.3.
The following cranes are not subject to registration with the state technical supervision bodies:
A) bridge-type cranes and jib cranes with a lifting capacity of up to 10 tons inclusive, controlled from the floor by means of a push-button device suspended on the crane, or from a stationary console;
B) boom-type cranes with lifting capacity up to 1 ton inclusive;
C) boom-type cranes with a constant reach or not equipped with a turning mechanism;
D) adjustable cranes for mounting masts, towers, pipes installed on the structure being mounted;
E) bridge-type cranes and tower cranes used for educational purposes at the training grounds of educational institutions;
f) cranes installed on excavators, crushing and handling units, spreaders and other technological machines, used only for the repair of these machines;
G) electric hoists.
Permission to put into operation a load-lifting crane from the state technical supervision authorities
Permission to put into operation a crane subject to registration with the state technical supervision bodies must be obtained from these bodies in the following cases:
A) before putting into operation a newly registered crane;
B) after installation caused by the installation of a crane in a new location (except for jib and quick-erect tower cranes);
C) after the reconstruction of the crane;
D) after repair with the replacement of design elements or components of the crane metal structures using welding;
E) after installing a new load limiter on the crane.
Accounting and commissioning of cranes that are not subject to registration with the state mining supervision authorities.
Cranes that are not subject to registration with the state technical supervision authorities, as well as removable load-handling devices, are provided with an individual number and under this number are registered by their owner in the register of cranes and load-handling devices.
Permission to put into operation cranes subject to registration with the state technical supervision bodies is recorded in their passport by the inspector of the state technical supervision, and other cranes - by an engineering and technical worker for supervision of the safe operation of cranes. The permit for the operation of load-handling devices and containers is recorded in a special accounting and inspection log by the person responsible for the safe performance of work by cranes.
Permission to put into operation a load-lifting crane by an engineering and technical worker for supervision
Permission to put into operation crawler and pneumatic wheel cranes after moving them to a new facility is issued by an engineering and technical worker for supervision of the safe operation of load-lifting cranes based on the results of checking the condition of the crane and ensuring safe conditions for its operation with an entry in the logbook. (9.2.4) .
The technical examination of the crane must be carried out by an engineering and technical worker for supervision of the safe operation of cranes with the participation of an engineering and technical worker responsible for maintaining the cranes in good condition. (9.3.5) .
The results of the technical examination of the crane are recorded in its passport by the engineering and technical worker for supervision of the safe operation of load-lifting cranes, who conducted the examination, indicating the date of the next examination.
An entry in the passport of an operating crane subjected to periodic technical inspection must confirm that the crane meets the requirements of these Rules, is in good condition and has passed the tests. Permission for the further operation of the crane in this case is issued by an engineering and technical worker in charge of supervising the safe operation of cranes. (9.3.20) .
Permission to put into operation cranes that are not subject to registration with the state technical supervision authorities is issued by an engineering and technical worker for supervision of the safe operation of cranes based on the manufacturer's documentation and the results of a technical examination. (9.2.6) .
Technical
examination


Extraordinary full
A) installation caused by the installation of a crane at a new location;
b) crane reconstruction;
c) repair of the calculated elements of the crane metal structures with the replacement of elements or assemblies using welding;
d) installing interchangeable boom equipment or replacing the boom;
e) overhaul or replacement of a cargo or boom winch;
e) replacement of the hook or hook block (only static tests are carried out);
g) replacement of load-bearing or cable-stayed ropes of cable-type cranes.
Primary
periodic

Complete
At least once every 3 years
Partial
At least once every 12 months


Inspection
Static test
25% more load than rated load capacity
Dynamic test
10% more load than rated load capacity
The technical examination is intended to establish that:
A) the crane and its installation comply with these Rules, passport data and documentation submitted for registration;
b) the crane is in a condition that ensures its safe operation. (9.3.7).
Static test of a crane.
Static tests of the crane are carried out with a load that is 25% higher than its nameplate load capacity. (9.3.10).
Static testing of an overhead crane is carried out as follows. The crane is installed over the supports of the crane runway, and its trolley (carts) - in a position corresponding to the greatest deflection of the bridge. The control load is lifted by a crane to a height of 100-200 mm and kept in this position for 10 minutes.
After 10 minutes, the load is lowered, after which the absence of residual deformation of the crane bridge is checked. In the presence of residual deformation, which was the result of testing the crane with a load, the crane should not be allowed to work until a specialized organization clarifies the causes of deformation and determines the possibility of further operation of the crane. (9.3.11).
Static tests of a jib-type crane having one or more load characteristics, during periodic or extraordinary technical examination, are carried out in a position corresponding to the highest crane capacity and / or the highest load moment. (9.3.12).
During static tests of boom-type cranes, the boom is installed relative to the running support part in a position corresponding to the lowest design stability of the crane, and the load is lifted to a height of 100-200 mm.
The crane is considered to have passed the static tests if the lifted load does not fall to the ground within 10 minutes, and no cracks, residual deformations and other damage to metal structures and mechanisms are detected. (9.3.13).
Dynamic test of a load-lifting crane.
Dynamic tests of the crane are carried out with a load, the mass of which is 10% higher than its passport load capacity, and are aimed at checking the operation of its mechanisms and brakes.
During dynamic testing of cranes (except for cable-type cranes), multiple (at least three times) lifting and lowering of the load are performed, as well as checking the operation of all other mechanisms when combining the working movements provided for in the crane operation manual. (9.3.14).
test questions
1. Who is allowed to perform the duties of an electrician for the repair and maintenance of electrical equipment of hoisting machines?
2. In what cases is a re-test of the knowledge of electricians on the repair and maintenance of hoisting machines.
3. Types of technical examination of hoisting machines and the timing of their implementation.
4. The structure of supervision over the safe operation of lifting machines in the organization.
5. The procedure for conducting a static test of a crane.
6. Procedure for conducting dynamic testing of a load-lifting crane.
7. The procedure for admission of repair personnel to cranes and crane tracks of overhead cranes.
Topic 4. Maintenance and repair of electrical equipment for lifting machines.
Operational documentation. Operational documentation of the crane includes a passport, technical description and operation manual, installation manual supplied by the manufacturer; crane log, log of acceptance and delivery of shifts by machinists, production instruction, protocols for measuring the insulation resistance of electrical wiring and grounding device, log of accounting and inspection of load handling devices and containers, work organization project (POR), order on the appointment of persons responsible for the safe production of work by cranes, a list of goods with an indication of their mass, a graphical representation of cargo slinging schemes provided by the operating organization.
Crane passport- PS - consists of two parts. In the first part, the manufacturer provides a complete description of the crane (with a drawing of the general view of the crane, kinematic diagrams of all mechanisms, rope reeving diagrams and electrical diagrams) and the crane runway, information about the crane tests; in the second, the forms used in the operation of the crane and filled in by the owner are attached (on the location of the crane, the person responsible for maintaining the crane in good condition, information about the repair, replacement of mechanisms, ropes and lifting hook; records of the results of the survey and registration of the crane). A drawing of the crane installation at the construction site is attached to the passport, indicating the main dimensions (work organization project), a certificate confirming that the crane track is designed for the load from this crane.
Passport sheets must be numbered and laced. The passport is kept in the technical department of the owners of the crane and transferred along with the crane to the new owner.
Technical description and maintenance manual- consists of two sections: technical description and operating rules. The first section contains: purpose, general arrangement and technical characteristics of the crane; composition, arrangement and operation of parts and mechanisms, including electrical equipment; instrumentation and safety devices; tool and accessories; in the second - general instructions; security measures; preparation of the crane for work; order of work on the crane; possible malfunctions and methods for their elimination; Maintenance; instructions for current repairs; rules for storage and conservation. The appendix to the TO contains electrical diagrams of the crane, drawings of reinforced concrete ballast and counterweight slabs, links of special crane tracks (if any), a lubrication map, permissible mechanical damage to the crane metal structures, wear tolerances for critical parts of mechanisms, a list of bearings and lip seals, a certificate of conservation.
TO is stored in the crane cabin in a locker.
IM installation guide- contains information about safety measures, preparation of the crane for installation and installation, commissioning, start-up, regulation and running-in; putting the crane into operation; dismantling, transportation, The appendix contains electrical diagrams of the crane, including installation, and a cabling log.
The IM manual can be stored both on the crane and in the department that relocates and installs the cranes.
crane magazine reflects everything related to the operation, maintenance and repair of the crane, and is a legal document. The journal contains a list of persons responsible for the technical condition of the crane and its operation, the location of the crane, information about repairs and inspections of the crane; take into account the operating time of the crane and its downtime; make records about the state of grounding and crane tracks, lifting devices and containers (if there is no special log for this).
The section of the journal "Remarks on the operation and technical condition of the crane" is filled in by the crane operator and persons controlling his work. Troubleshooting records are made by the person who fixed the problem.
The crane magazine is stored in the crane cabin along with the maintenance manual, and during major repairs they are transferred along with the passport to the repair organization.
Journal of acceptance and delivery of shifts (shift) contains records of the machinists of each shift on the results of the inspection of the crane before the shift and receipts for accepting the shift; comments on malfunctions, work carried out to eliminate and maintain them, and receipts for the shift at the end of work.
The log is stored in the driver's cab.
The production instruction contains the main provisions for the safe operation of the crane and safety precautions for the operation and maintenance of the crane. Instructions, tables of the mass of elements with which to work on a given construction site, and schemes for their slinging are hung in the crane cabin.
General information
In order to prevent accidents and ensure the efficient, trouble-free and safe operation of cranes, a clear preventive maintenance and repair (MRO) system should be developed, consisting of cyclically recurring maintenance work and repairs of cranes.
Maintenance- a set of operations or an operation to maintain the serviceability or performance of cranes when used for their intended purpose, waiting, storing and transporting. MOT is planned and unplanned. The scope of work and the procedure for maintenance and repairs are regulated by repair and regulatory documentation.
Repair– restoration of damaged, worn out or unusable for any reason components, crane safety devices with bringing the crane to a working condition.
Current repair- repairs performed to ensure or restore the crane's performance and consisting in the replacement and / or restoration of individual parts.
Overhaul- repairs performed within the lifetime of the crane to restore serviceability and complete or close to complete restoration of the crane resource with the replacement or restoration of any of its parts, including basic ones.
Taking into account the design, load capacity, certain conditions and modes of operation of cranes, provisions (instructions, recommendations, RD) should be developed for organizing and carrying out their maintenance and repair.
The regulation (instructions, RD) for the maintenance and repair of hoisting machines provides for:
Procedure for developing maintenance and repair plans;
Accounting and control of maintenance and repair;
Maintenance standards, repair cycle structures, duration of overhaul periods;
The composition and content of repair work for all machines, taking into account the conditions of their operation;
Application of perfect methods of maintenance and repair using mechanization;
The frequency and duration of scheduled repairs of machines;
The complexity of repair work;
Consumption of materials;
Spare parts fund;
Raising the qualifications and level of specialization of repair personnel.
Provisions for the maintenance and repair of cranes should be developed taking into account the unconditional fulfillment of the requirements set forth in the operating and repair documentation of manufacturers, as well as current state and industry standards and safety rules.
The maintenance and repair system for cranes should be based on the planned preparation and implementation of the appropriate types of maintenance and repair for each crane in operation, with a given sequence and frequency. During the operation of cranes carry out:
Every shift maintenance (EO) performed before, during or after the work shift;
Scheduled maintenance (TO), performed in a planned manner after a certain time set by manufacturers;
Seasonal maintenance (TS) carried out twice a year when preparing the crane for operation in the next season (summer or winter).
The types and frequency of maintenance and repair for cranes are determined by the design organization or the manufacturer, taking into account the improvement of design solutions and improvement of reliability indicators. Types, frequency, volume and procedure for performing maintenance and repair of cranes are regulated by the operating instructions.
Maintenance cycle - these are the smallest recurring time intervals or operating hours of the crane, during which all established types of periodic maintenance are performed in a certain sequence in accordance with the requirements of regulatory documentation. The number of maintenance in one cycle depends on the design of the crane and its operating conditions.
Repair cycle - these are the smallest repeating time intervals or operating hours of a crane, during which all established types of repairs are performed in a certain sequence in accordance with the requirements of regulatory documentation. It is installed for each type of crane, depending on its design. The repair cycle is calculated in such a way that each stop of the crane for repair corresponds to the time to reach the wear limit of a certain group of parts.
The frequency of maintenance and repairs is set in hours of operation, and for cranes operating in ports, the frequency can also be set according to the number of lifted loads in tons.
Taking into account that different regulatory documents adopt different systems for recording the crane operation time, for the convenience of drawing up maintenance plans, it is recommended to use the table of the frequency of maintenance and repair of cranes in machine and dress time (see table). Under the elegant operating time of the crane is meant the operating time taken into account by the shift report, under the machine time - the time when at least one mechanism is working on the crane.
Frequency of maintenance and repair of tower cranes,
expressed in engine hours and hours of dress time
Organization of repair of cranes
Enterprises that have cranes on their balance sheet must ensure that maintenance and repairs are carried out in accordance with the approved annual quarterly or monthly schedules.
The annual maintenance and repair plan determines the number of scheduled maintenance and repairs for each crane. The annual plan is the basis for calculating the need for materials and labor resources. The initial data for the development of the annual plan are:
The actual operating time of the crane in hours before the beginning of the planned year from the time of the corresponding type of maintenance, repair or from the start of operation;
Planned operating time of the crane for a year in hours;
Number of maintenance and repairs. The annual maintenance and repair plan for lifting thefts is approved by the chief engineer (chief mechanic) or a higher organization.
The quarterly or monthly schedule for the maintenance and repair of cranes sets the date for stopping each crane for maintenance or repair and the duration of its downtime in days. The quarterly (monthly) schedule is approved by the chief engineer (chief mechanic) of the enterprise for which it was developed
The operating time of cranes equipped with hour meters is determined by the readings of meters that do not have meters - according to shift time accounting data, adjusted by the intra-shift utilization factor.
Maintenance of tower crane KB-474.
1. Crane maintenance is divided into:
Shift maintenance (EO);
Periodic maintenance (TO-1 and TO-2);
Seasonal maintenance (SO).
2. Frequency of types of maintenance.
Shift maintenance is performed daily at the beginning of the work shift.
Periodic maintenance is carried out in a planned manner through certain operating hours:
TO-1 after 200 machine hours of crane operation;
TO-2 after 600 machine hours of crane operation;
Elements of electrical equipment after 100 machine hours of crane operation, but at least once a month.
Seasonal maintenance is carried out 2 times a year during the transition from summer to winter and vice versa.
The control of the tightening of the power pins of the joints of the tower sections of a free-standing crane, as well as the joints of the upper hinged section fixed to the building (structure) under construction and all joints of the tower sections located above it, should be carried out using a special device in accordance with a schedule drawn up in such a way that each hairpin was inspected at least once every two weeks.
Average standards for maintenance and repair of the crane are shown in the table.
| Types of maintenance and repair | Periodicity of maintenance and repairs, engine hours | Number of maintenance and repairs during the period of operation | Labor intensity of one maintenance and repair, man-hour |
| TO-1 | 200 | 55 | 10 |
| TO-2 | 600 | 14 | 30 |
| SO | 2 times per year | 14 |
|
| T | 1200 | 13 | 345 |
| where - T - current repair. |
|||
List of works for various types of maintenance.
| The content of the work and the methodology for their implementation | Technical requirements | Devices, tools, fixtures and materials necessary for the performance of work |
| Shift maintenance (EO) |
||
| 1. Inspect and check the condition of the faucet ground wire. Check the availability of a free approach to the crane, the absence of foreign objects on the transitional platforms. In winter, the approaches to the crane must be cleared of snow. | No damage to the grounding elements. Free access to the crane. | Wrench, shovel |
| 3. Check the condition of the power cable and its terminal connections. | Absence of damage (sharp bends, gusts, etc.). Terminal connections must have tight contact. | |
| 5. Check the serviceability of lighting, emergency switch, sound signal. | No failures. | Check by turning them on. |
| 6. Check operation of safety devices and limit switches. | In accordance with section 2.2.3 of this manual. Failure is not allowed. | |
| 8. During breaks in work, check the degree of heating of electric motors, bearings, resistances, brake electromagnets. | Overheating is not allowed. | hand. |
| Periodic maintenance TO-1. |
||
| 1. Perform shift maintenance work. | ||
| 2. Check the fastening of the power cable. | There should be no sharp bends, gusts. | |
| 3. Check the integrity of the insulation of electrical wires in the places of approach to electrical devices. | There should be no cracks, open cores, loose seals in the glands and in the inputs to the devices and junction boxes. | |
| 4. Check brushes for contact with slip rings and, if necessary, clean motor slip rings. | The surface of the rings must be free of carbon deposits, oxides and dirt, the brushes must fit snugly against the rings. | Sandpaper, solvent. |
| 5. Check the tightness of the contacts of the contactors, clean the contacts of the contactors, relays and limit switches. | The contacts should be free of soot and dirt. When pressed, the failure of the contact bridge should be no more than 3 + 0.55 mm and the withdrawal of contacts 13 + 3 mm. | Screwdriver, wrenches, velvet file, ruler, caliper. |
| 6. Clean the terminal sets from dust and dirt and check the tightness and reliability of the contacts. | Contact tightness must be ensured. The presence of dust and dirt is not allowed. | Screwdriver, keys, rags. |
| 7. Inspect the limit switches and check: | ||
| - the presence of lubrication | According to the lubrication table (see appendix B). | Wrenches, screwdrivers, lubricants. |
| - tightening tightness of all screw connections | The screws must be tightly tightened. | Screwdriver. |
| - clear operation of the return mechanism by hand | ||
| - failure of the closing contact | In direct action switches (VP-15E) not less than 1.5 mm. In switches of the VU type, the failure of the contact bridge should be 2l mm. The lever must be locked with a pawl. In the case when the roller of the closing washer is located against the ledge of the lever, the dip should be 4.5 ± 1 mm. | Calipers. |
| - contact wear | Silver contacts are considered worn if their thickness has reached 0.5 mm. | Calipers. |
| - contact surface condition | With strong soot, it is recommended to clean the silver contacts with a file with a fine ("velvet") notch. | File with a small ("velvet") notch |
| - insulation resistance | Not less than 0.5 MΩ, at a lower value, dry the switch. | Megaohmmeter 500 - 1000V. |
| Periodic maintenance TO-2. |
||
| 1. Perform periodic maintenance work TO-1. | ||
| 2. Measure the resistance of the grounding device and record the measurement result in a log. | Resistance should be no more than 4 ohms. | Grounding meter. |
| 3. Inspect all electric motors. Make sure there are no mechanical damages. Check the tightness and integrity of the bolts securing the end shields to the motor stator housings. | The connection must be tight with all bolts and spring washers present. | Spanners. |
| 4. Check the insulation resistance of the electrical wiring of the control circuits (after disconnecting the tap from the external network). | The insulation resistance of the control circuits must be at least 0.5 MΩ. | Megaohmmeter500-1000V. |
| 5. Check tightness of connections of all wires and cables. | The contact screws must be tightly tightened. | Screwdriver |
| 6. Check the tightness of contactor cams. | With open cams, the distance between the main contacts must be at least 7 10 mm, between the auxiliary 13 - 20 mm. | hand. |
| 7. Check the mechanical serviceability of the movable magnetic system and the tightness of the auxiliary contacts of all relays and starters. | hand. |
|
| 8. Conduct an external inspection of the motor brushes by raising the lever with the brushes. | The maximum allowable height of a worn brush for electric motors 4 - 5 dimensions - 20 mm. | Ruler. |
| 9. Measure the insulation resistance of electric motors. | The resistance of the stator winding must be at least 0.5 MΩ at a temperature of + 10 - 30 °C. | Megaohmmeter on 1000 W. |
| 10. Check the possibility of condensate leakage through the holes in the lower part of the motor housings. | Holes must be free of dirt. | |
| Seasonal maintenance (SO) |
||
| 1. Perform maintenance work TO-2. | ||
| 2. Carry out an oil change in the gearboxes during the transition to the autumn-winter and spring-summer periods. | Oil grade according to the lubrication table in accordance with Appendix B. | Keys, screwdriver, oiler, watering can, lubricants. |
Checking the technical condition of electric motors.
Check the reliability of fastening of electric motors and current-carrying wires.
Check the condition of the insulation.
Check the insulation resistance of the stator windings, which must be at least 0.5 MΩ at a temperature of plus 10 ... 30 ° C.
Check the amount of movement of the fingers of the brush holders and the tightness of the brushes to the contact rings.
Check the gaps between the rotor and the stator through the holes in the motor fan cover. The gap must be within the following limits:
For turning mechanisms, trolley winch, auxiliary winch - 0.4 0.6 mm;
Clean motor parts.
Troubleshoot electric motors.
Lubricate motor bearings.
Adjust the amount of movement of the fingers of the brush holders and the tightness of the brushes to the contact rings.
Dry the motors (if necessary).
Checking the technical condition of electrical equipment.
Check the condition of contactors, relays, magnetic starters:
The size of the gap in the contacts;
Ease of movement of moving parts:
Degrees of pressing force of contacts of contactors, relays and magnetic starters;
Reliability of fastening of conclusions, anchors, coils;
State of isolation.
Check the condition of the brake resistor units, electric heaters, sound signals and lighting fixtures.
Check the condition of the insulation of all cables, wires of the electrical circuits of the crane and the reliability of their fastening to the terminal sets.
Check the condition of all limiters. If it is necessary to repair the load limiter, it must be dismantled and sent to a specialized instrument repair shop.
Tighten the contact connections in the terminal sets and devices (if necessary).
Clean contacts and moving parts, contactors, relays, magnetic starters and limiters (if necessary).
Replace contacts, auxiliary contacts, coils and other parts (if necessary).
Troubleshoot contactors, magnetic starters, relays, switches, cables, wires and terminal sets (if necessary).
Troubleshoot limit switches.
Lubricate the moving parts of the force sensor, angle sensor and wind speed sensor.
Adjust the hook lift, swivel, hook block lower position and additional hook block upper position limiter, capacity limiter.
Troubleshooting electrical equipment
Electrical failures can result from electrical or mechanical damage. To electrical damage wear, sparking of brushes, burning and breaking of contacts, short circuit, cracks in insulators, weakening of the bandage. Mechanical damage- wear of bearings, bending of the rotor shaft, development of keyways, wear and tear of threads, destruction of fastening tabs, cracks.
Consider typical malfunctions of the main electrical equipment.
Electric motors. A shortclosurein windingrotor. A symptom of a malfunction - the engine is turned on jerkily, the engine speed does not depend on the position of the controller. To check, disconnect the motor rotor from the ballast. If the motor runs when the stator is turned on, the rotor winding is short-circuited.
Short circuit instator winding. A symptom of a malfunction - the engine does not rotate when turned on, the maximum protection is activated.
The break of one ofstator phasesatconnectionenginestar. Signs of malfunction - the motor does not create torque, and therefore the mechanism does not turn.
cliffinchainsonerotor phase. Symptom - Motor spins at half speed and hums loudly. In the event of a phase failure of the stator or rotor at the motor of the cargo and boom winches, the load (boom) may fall, regardless of the direction the controller is turned on.
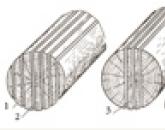
Wear of the commutator and brushes. The malfunction occurs due to incorrectly selected brush pressure; at high pressure, their wear is accelerated, at low pressure, vibration of the brushes, sparking occurs, which also contributes to wear. The brush pressure can be checked with a dynamometer. Springs that have lost their elasticity are replaced (when worn more than 2/3 of the height or when chips appear). Worn brushes can be cleaned with sandpaper. A contaminated collector (with slight wear) is cleaned with a fine-grained sandpaper. Collectors with a loose mount on the shaft, loose plates and with a short circuit between the plates or to the housing are replaced. Winding insulation is checked with an ohmmeter. A short circuit is detected either also with an ohmmeter or with the instrument shown in fig. The device works like this. If probes 1 connected to the collector and the neck of the shaft or to the soldering points of the two turns being checked, the lamp 2 In case of a short circuit, it lights up; in case of a break, it goes out.

The electrical circuit of the device for detecting a short circuit or open coils:
I - probes, 2 - lamp,
3 - connection to power supply
Controllers. Symptoms of a malfunction are increased sparking, overheating of contacts, sticking or lack of fixation of contacts. To troubleshoot, the contacts are checked for jaw fit, pressing force, gap, and failure. The fit of the sponges is controlled using carbon paper. If the contact area of the jaws is less than 80% of the rolling area, they are machined to fit the template, and when worn above the norm, they are welded and machined. The pressure of the sponges is checked with a dynamometer (by the force at which thin tissue paper can be pulled out from under the sponges without damaging it). The pressure is adjusted using screws that change the preload of the springs. The solution or opening of contacts is checked using templates from a metal ruler. The failure of the contactor is the movement of the movable jaw with the fixed jaw removed, due to which the contactor works reliably even when the jaws are worn. Replace damaged contactor insulation.
Magnetic switch. A symptom of a malfunction is a hum emitted by the starter. Repair of magnetic starters consists in correcting the insulation of the turns (with mica or asbestos gaskets), soldering broken wires, and tightening the contacts.
Breakers and switches. A symptom of a malfunction is increased heating of the contacts. This fault occurs during operation, especially during overloads, which increases the resistance and causes heating of the contacts. This defect is eliminated by cleaning the contacts. If the switch is under load for a long time, then due to overheating, the contacts may burn and the spring properties of the contact jaws may decrease. The contacts are cleaned and wiped with a cloth moistened with gasoline. Contact sponges that have lost elasticity are replaced.
Control buttons. A symptom of a malfunction is jamming, lack of a clear contact. Since it is not economically feasible to restore broken and worn parts of control buttons, they are replaced.
Contact connections. Symptoms of a malfunction - increased heating, lack of a clear inclusion. Contact connections are subject to constant monitoring. At the same time, they are checked and, if necessary, tightened. It is especially important to prevent self-loosening of nuts and screws.
Fuses. The symptom is a blown fuse. Since the reliable and safe operation of electrical equipment is more dependent on the state of protection, it is necessary to regularly check the fuses and change them in a timely manner. Fuses are selected depending on the operating conditions of electrical equipment.
Time relay. Symptoms of a malfunction - discrepancy between the time delay and the set value. The relay is checked with a stopwatch. The time delay is regulated in two ways: by changing the spring tension or the gap in the magnetic system of the relay. Increasing the tension of the spring decreases the dwell time, and decreasing the tension increases it. The gap in the magnetic system of the relay is changed using diamagnetic gaskets with a thickness of 0.1; 0.25; 0.35 and 0.5 mm. The thicker the gasket, the larger the gap in the magnetic system with the armature stretched, the faster the flux decline and the shorter (with the same spring tightening) the relay time delay, and vice versa. The time delay is regulated by gaskets only on newly installed relays.
Overcurrent relay. Symptoms of a malfunction - a discrepancy between the operation current (setpoint) and the passport data of the motor. Typically, the pickup current is 200-225% of the rated motor current. The relay is adjusted using the adjusting screw, controlling the setting current on the scale. After adjusting the current setting, the operation of the relay is checked by starting the mechanism several times with full load.
Brake electromagnets MO. Symptoms of a malfunction are loud noise and insufficient braking force. When monitoring the state of the electromagnet, pay attention to the state of the mechanical part of the magnet, check the clearance in the hinges of the armature axis, as well as the state of the transverse bar against which the rod rests. If the gap in the axle supports is more than 1 ... 1.5 mm, the electromagnet is replaced.
The reason for the strong noise is the breakage of the short-circuited coil or the distortion of the magnet. If the short-circuited coil is in order, then to eliminate the noise, loosen all the bolts securing the magnet to the brake lever. If at the same time the noise disappears, then the bolts are sequentially tightened and the moment of noise occurrence is observed. A gasket is placed at the attachment point, the deformation of which causes noise.
Wiring. Symptoms of a malfunction are the presence of bare wires, their short circuit, breakage.
When replacing electrical wiring, the following rules are followed. According to the metal structure of the crane, the wires are laid in pipes or metal hoses; on such parts of the metal structure, where mechanical damage to the wire is excluded, as well as the ingress of oil and water onto it. All wires of a three-phase network are placed in one pipe if the current in them is equal to or greater than 25 A; it is not allowed to solder the wires inside the pipe or metal hose; it is allowed to use wires, the insulation of which is designed for a voltage of at least 500 V.
Insulated wires are connected by welding, soldering and crimping or twisting.
test questions
1. What regulatory documents are guided by the maintenance and repair of cranes?
2. What is the frequency of technical maintenance and repairs of cranes?
3. What work is carried out during the maintenance of the electrical equipment of the hoisting machine?
4. The procedure for bringing cranes into repair and putting them into operation after the repair is completed.
5. What repair work on electrical equipment on a crane is carried out according to a work permit?
6. Signs of malfunctions of electric motors.
7. For what purpose and in what terms are periodic inspections of hoisting machines carried out?
8. What parts and assemblies of cranes must be fenced?
9. Types of technical maintenance of cranes and the timing of their implementation.
10. Types of repairs and maintenance of cranes.
MINISTRY OF LABOR AND SOCIAL DEVELOPMENT
RUSSIAN FEDERATION
APPROVED
Deputy Minister of Laborand social development
Russian Federation
Typical instruction
on labor protection for electricians
for the repair and maintenance of electrical equipment
lifting machines
TI R M-O16-2000
1. GENERAL SAFETY REQUIREMENTS
1.1. To carry out the work of an electrician for the repair and maintenance of electrical equipment of hoisting machines, workers are allowed at least 18 years of age who have passed a medical examination, trained according to the appropriate program and certified by the qualification commission, as well as who have received instructions on safe working methods directly at the workplace with registration in the Instruction Registration Log. 1.2. An electrician admitted to the repair and maintenance of hoisting machines must have an electrical safety group of at least III. 1.3. A certified electrician is issued a certificate for the right to repair and maintain electrical equipment of hoisting machines signed by the chairman of the commission, sealed with a stamp. 1.4. The admission to the work of an electrician for the repair and maintenance of hoisting machines is issued by order of the enterprise (workshop, section) after the issuance of a certificate and instructions on labor protection. 1.5. Re-testing the knowledge of an electrician who repairs and maintains hoisting machines is carried out: periodically, at least once every 12 months; when moving from one enterprise to another; at the request of an employee responsible for the supervision of hoisting machines at the enterprise, or an inspector of Gosgortekhnadzor. Knowledge is tested in the scope of the labor protection instructions, the relevant sections of the "Safety regulations for the operation of consumer electrical installations" and "Rules for the design and safe operation of cranes". 1.6. An electrician admitted to independent work on the repair and maintenance of electrical equipment of hoisting machines must know: labor protection instructions for electricians when servicing general production electrical equipment with voltage up to 1000V; basic provisions of general electrical engineering; purpose, arrangement and principle of operation of units, mechanisms and electrical equipment of hoisting machines; electrical circuits fixed for the maintenance of lifting machines; the relevant sections of the "Safety Rules for the Operation of Electrical Installations of Consumers" and "Rules for the Design and Safe Operation of Hoisting Cranes"; the main causes of damage and accidents on the electrical equipment of hoisting machines, be able to find and eliminate them. 1.7. The electrician is obliged to comply with the internal labor regulations of the enterprise. Smoking in production and auxiliary premises and on the territory of the enterprise is allowed only in places specially designated for this purpose. 1.8. During work, the electrician may be affected by the following hazardous and harmful production factors: noise and vibration from working mechanisms; electricity; industrial microclimate. 1.9. The electrician must be provided with personal protective equipment: cotton overalls; dielectric gloves; dielectric galoshes. 1.10. An electrician admitted to independent work on the repair and maintenance of electrical equipment of hoisting machines must: inspect and repair electrical equipment of hoisting machines; prepare the electrical equipment of hoisting machines for technical certification. 1.11. An electrician for the repair and maintenance of lifting machines must know and observe the rules of personal hygiene. 1.12. An electrician for the repair and maintenance of hoisting machines must be able to provide the victim with first (pre-medical) aid in case of an accident. 1.13. In case of any questions related to its safe performance in the course of work, it is necessary to contact the employee responsible for the safe performance of work. 1.14. A trained and certified electrician for the repair and maintenance of electrical equipment of lifting machines is fully responsible for violation of the requirements of this Instruction in accordance with applicable law.2. SAFETY REQUIREMENTS BEFORE WORKING START
2.1. Before starting work, the electrician must familiarize himself with the entries in the operational log, accept from the electrician who handed over the shift the technical documentation approved by the power engineer, safety protective equipment, make an entry on the acceptance of the shift in the operational log and sign. 2.2. Make sure the work area is adequately lit. 2.3. Tidy up the workplace, remove all items that may interfere with safe work. 2.4. Put on the appropriate overalls, prepare serviceable and tested personal protective equipment (dielectric gloves, galoshes). 2.5. Notify the foreman or supervisor of all noticed shortcomings in the workplace and do not start work until their instructions.3. SAFETY REQUIREMENTS DURING WORK
During maintenance between repairs 3.1. Work carried out to eliminate faults in the electrical equipment of hoisting machines at the request of drivers and non-electrical personnel, and inspections regarding the safety of their implementation are divided into: work performed in the order of current operation, with an entry in the operational log; for work performed by order of administrative and technical personnel with an electrical safety group of at least IV, with an entry in the operational log. In the order of current operation, the electrician on duty for servicing the electrical equipment of hoisting machines is allowed, in the presence of a driver (crane operator) who has an electrical safety group II, to perform the following work: inspection of electrical equipment; replacement of burnt-out lamps and fuse-links; repair and replacement of electric devices located in the cab of the driver (crane operator); checking the correct operation of safety instruments and devices, lighting, signaling and blocking, with the exception of signaling devices indicating the presence of voltage on the main trolleys. 3.2. The electrician, having received an application from the driver (crane operator), must make an entry in the operational log, indicating the date and time of receipt of the application, the name and position of the person who submitted the application, the content of the application and the start time of work. After eliminating the detected faults in the same journal, it is necessary to make a record of the content of the work performed and the time of their completion. At the same time, a record is made of troubleshooting in the logbook of the driver (crane operator). 3.3. If faults are found that are not related to the list of works performed in the order of current operation, the electrician on duty must report to the shift supervisor about the deficiencies found. 3.4. Work performed by order, with an entry in the operational log: replacement of burned-out electric motors; replacement of electromagnetic coils and brakes; adjustment of limit switches; conducting periodic inspections. 3.5. The execution of work according to the order should be carried out by two employees with an electrical safety group of at least III, with complete removal of voltage, with the implementation of the necessary organizational and technical measures in accordance with the requirements of the "Safety Rules" when operating consumer electrical installations with an entry in the operational log. 3.6. The employee giving the order must determine the composition of the team, the foreman and organize the admission of the team to work. 3.7. For all types of repairs and inspections of the electrical equipment of a crane located between two operating cranes, a work permit must be issued with entries in the watch logs of all cranes of this span. 3.8. Periodic inspection of the electrical equipment of hoisting machines is aimed at identifying and eliminating possible malfunctions in electrical equipment, safety devices and devices, in power circuits, control circuits, alarm circuits, checking the serviceability of safety protective equipment and fire extinguishing equipment and confirming in the journal of periodic inspections that the electrical equipment of hoisting machines is in good condition. 3.9. When inspecting the electrical equipment of cranes, the adjustment and activation of the mechanisms must be carried out at the signal of the person performing the inspection. 3.10. When moving the crane bridge, workers inspecting and troubleshooting the crane's electrical equipment should be in the cab or on the bridge deck, while avoiding touching the protruding parts of the ceiling, columns, fittings. When entering the flooring of the crane gallery, the knife switch in the driver's cab must be turned off and a poster "Do not turn on - people are working" is posted on its drive. Remove the poster only by order of operational personnel. 3.11. When inspecting and troubleshooting the electrical equipment of the crane, it is necessary to observe all precautions, use the necessary serviceable and tested protective equipment. 3.12. Upon completion of the repair and inspection, all removed guards on electrical equipment and on electrical appliances must be put in place and strengthened. 3.13. The results of the inspection for each crane separately must be recorded in the journal of periodic inspections indicating the date, time of the inspection, a summary of the identified and eliminated deficiencies, and there must be a signature of the personnel performing the repair. 3.14. When troubleshooting, adjusting and inspecting the electrical equipment of the crane, it is prohibited: to enter the crane and leave it while it is moving; go out onto the crane tracks, walk along the crane tracks, climb from one crane to another; to adjust the brake of the mechanism with a raised load, as well as to install devices for releasing the brake manually; leave tools, as well as loose equipment and parts on the gallery floor or on the trolley; dump tools, materials and spare parts from the crane. 3.15. For portable power tools and portable lamps, use a safe voltage not higher than 36 V. 3.16. When performing all work, the electrician must withdraw the key-mark from the crane operator in the manner established at the enterprise for the use of the key-brand system.During scheduled repairs
3.17. The withdrawal of the crane for repair should be carried out by the employee responsible for maintaining the lifting machines in good condition, in accordance with the scheduled repair schedule with the issuance of an order for work in electrical installations. The outfit is issued by representatives of the electrical personnel of the site, authorized by the order of the chief power engineer of the enterprise. In the lines of the “Separate instructions” order, additional safety measures are recorded related to working at height, to prevent running cranes from colliding with the one being repaired, the repair personnel entering the crane tracks of existing cranes, etc. The issued order is handed over to the employee responsible for the repair the day before the start of the repair. for the maintenance of lifting machines in good condition, which, by signature, allows work in the lines “Separate instructions” of the order and returns it to the employee who issued the order. The employee responsible for maintaining hoisting machines in good condition, prior to the start of repairs, is obliged to make the following entry in the watch log of the driver (crane operator) of the crane being repaired: “. date _________ of the month of _____ of the year, until __ h _____ min of ____ of the ____ of the month of _______ of the year” and sign. 3.18. The work order for work in electrical devices must indicate the composition of the team, the foreman who allows work, the worker issuing the work order; necessary technical measures to ensure the safety of work during the repair of electrical equipment of the crane; date and time of commencement of work, admission of the brigade and completion of work. 3.19. The admission of the brigade to the repair of the electrical equipment of the crane is carried out by an employee of the operational personnel on the basis of an order for work in electrical installations and the permission of the personnel responsible for maintaining the hoisting machines in good condition. The admitting person makes an entry in the operational log of the power engineering service with the design of the appropriate columns in the order and admits the brigade to the crane. 3.20. To ensure safety during the repair of the electrical equipment of the crane, it is necessary to put it on the repair site, make the necessary shutdowns, lock the knife switch drive, hang safety warning posters, install portable grounding and make a fence under the repair site. 3.21. Repair of the electrical equipment of the crane can be carried out by electricians who have a certificate for the right to repair and maintain hoisting machines; of these, at least two people must have an electrical safety group of at least III. 3.22. Do not allow strangers to the crane. It is forbidden to enter the crane tracks without obtaining a special permit. 3.23. Upon completion of the repair and closing of the order, the employee responsible for maintaining the hoisting machines in good condition checks the readiness of the crane for operation, makes an entry in the crane watch log: “I allow the crane to operate from ___ h _____ min ____ day ______ month ____ year” with his signature.
4. SAFETY REQUIREMENTS IN EMERGENCIES
4.1. In the event of an accident, the victim or an eyewitness who was at the same time is obliged to immediately notify the foreman or head of the site, who must organize the provision of first (pre-medical) aid to the victim and send him to a medical institution. In case of a severe accident, immediately call an ambulance and notify the administration. 4.2. Troubleshooting of electrical equipment of hoisting machines should be carried out only when the crane is disconnected from the mains.5. SAFETY REQUIREMENTS AFTER WORK IS COMPLETED
5.1. At the end of the shift or work, the electrician must: put the workplace in order; remove parts, materials, electrical equipment and tools; tidy up the wiring diagrams and other technical documentation; make an entry in the operational log on the technical condition of the electrical equipment of hoisting machines in the assigned area; hand over to the electrician accepting the shift the technical documentation approved by the power engineer of the shop (site), safety protective equipment, make an entry on the handover of the shift in the operational log and sign the handover of the shift.1. General safety requirements
1.1. To work independently as an electrician for the repair and maintenance of electrical equipment of hoisting machines, persons are allowed at least 18 years of age who have passed a preliminary medical examination upon admission to work, as well as;
- induction training;
- fire safety briefing;
- initial briefing at the workplace;
- electrical safety training in the workplace
1.2. An electrician for the repair and maintenance of electrical equipment of lifting installations must;
- undergo repeated training on labor safety at the workplace at least every three months;
- undergo unscheduled and targeted briefings;
- pass a knowledge test on PEEP and PTB when servicing electrical equipment;
- pass a knowledge test on the rules for the design and safe operation of lifting mechanisms.
- undergo a sanitary medical examination in accordance with the order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 90 dated March 14, 1996.
- perform only the work that is part of his duties.
- .use safe work practices.
- comply with the requirements of prohibiting, warning, indicative and prescriptive signs and inscriptions and signals given by train compilers, vehicle drivers.
- be extremely careful in traffic areas.
1.3 An electrician for the repair and maintenance of electrical equipment of lifting installations must know:
- the impact on a person of dangerous and harmful production factors that arise during work;
- general arrangement of crane installations;
- rules for the design and safe operation of lifting mechanisms;
- requirements for industrial sanitation, electrical safety and fire safety;
- location of first aid kits;
- internal labor regulations established at the enterprise;
- the requirements of this instruction, instructions on fire safety measures, instructions on electrical safety;
- appointment of personal protective equipment; rules and regulations on labor protection, safety and industrial sanitation;
- be able to provide first aid to victims, use fire extinguishing equipment, call the fire brigade in the event of a fire.
1.4. An electrician for the repair and maintenance of electrical equipment of lifting installations must be guided by the requirements:
this instruction;
Rules for the design and safe operation of cranes.
1.5. During work, the electrician for the repair and maintenance of electrical equipment of lifting installations may be exposed to the following hazards:
Falling objects and tools;
The action of an electric current;
High or low temperature;
Increased humidity and air mobility of the working area;
Increased levels of noise and vibration;
Moving vehicles, mechanisms, rolling stock;
Insufficient lighting at night.
1.6. An electrician for the repair and maintenance of electrical equipment of lifting installations must use the following cotton PPE suit, combined gloves, boots. In winter additionally: insulated jacket,
1.7. An electrician for the repair and maintenance of electrical equipment of lifting installations must comply with the following fire safety requirements:
Smoking only in designated areas;
Do not approach with an open flame to a gas welding machine, gas cylinders of flammable liquids, gaseous liquids and spray booths;
Do not touch oxygen cylinders with hands contaminated with oil;
Know and be able to use primary fire extinguishing equipment.
1.8. Personal clothing and overalls must be stored separately in lockers and dressing rooms. It is prohibited to take work clothes outside the enterprise.
1.9. Eating should only be in canteens, buffets or specially designated rooms with appropriate equipment. Before eating, wash your hands thoroughly with soap
1.10. When on a railway track, an electrician must comply with the following requirements:
Railway tracks should pass only in the established places, marked with signs "Service Passage", pass along the track only along the side of the road;
Cross the tracks only at a right angle, after making sure that there is no locomotive moving at a dangerous distance in this place;
Cross the track occupied by the rolling stock only using the transitional platforms of the wagons;
Bypass groups of wagons no closer than 5 m from the automatic coupler;
Pass between uncoupled wagons if the distance between them is at least 10 m;
When leaving the car, hold on to the handrails and position yourself facing the car, having previously inspected the place of exit and made sure that the handrails and steps are in good condition, as well as that there is no rolling stock on the adjacent track;
Pay attention to traffic lights;
Do not cross paths in front of a moving train;
Do not sit on the steps of the wagons and do not get off them while moving;
Do not crawl under the wagons;
Do not step on electrical wires and cables;
Do not touch broken wires;
Do not climb onto the roof of the car under the contact wire;
Do not approach closer than 2 m to the current-carrying parts of the contact network.
1.11. When leaving the track from the heating room, as well as from buildings that impair the visibility of the track, you must first make sure that there is no train moving along it.
1.12. For non-compliance with the safety requirements set forth in this manual, the electrician is responsible in accordance with applicable law.
2. Safety requirements before starting work
2.1. Before starting work, an electrician for the repair and maintenance of electrical equipment of lifting installations must:
Put on overalls and special footwear according to the norms, put them in order;
Fill the loose ends of the clothes so that they do not hang down;
Set the sequence of operations;
Inspect your workplace, check the condition of electrical equipment;
Check the availability and serviceability of tools, measuring instruments, templates, as well as their presence on racks and repair installations of spare parts and materials;
Check the operation of lighting and the serviceability of lighting fixtures;
Check the availability of fire fighting equipment;
Check the serviceability of ladders, bridges, ensure their reliable installation;
When using a portable electric lamp, check the presence of a protective grid on the lamp, the serviceability of the cord and the insulating rubber tube, the voltage is not higher than 12 V
The conclusion of the crane for repair is carried out by the person responsible for the good condition of the lifting mechanisms in accordance with the repair schedule .;
A work permit is issued for the repair work of overhead and jib cranes.
3 .Safety requirements during work
3.1. Work on troubleshooting electrical equipment of hoisting machines at the request of crane operators is divided into:
- for work carried out in the order of current operation, with an entry in a special journal, performed by order of managers who have an electrical safety group of at least no lower;
- at the same time, the electrician can perform work on replacing lamps and fuses, repairing and replacing electrical appliances located in the crane operator's cab, and checking the correct operation of safety devices.
3.2. An electrician who has received an application from a crane operator is obliged to make an entry in a special journal, indicating the content of the application.
3.3. After troubleshooting, make an entry in a special log.
3.4. If faults are found that are not related to the list of works performed in the order of current operation, the electrician must report to the master for the need to eliminate the deficiencies.
3.5. These works include:
Replacement of burned-out electric motors, electromagnetic coils;
Adjustment of limit switches;
Conducting periodic inspections.
3.6. These works must be carried out by 2 electricians with an electrical safety group of at least 3.
3.7. Periodic inspection of the electrical equipment of cranes is carried out according to the schedule and by order with an entry in a special journal.
3.8. If it is necessary to reach the deck of the crane gallery, the knife switch in the driver's cab must be turned off and a poster “do not turn on - people are working” should be hung on its drive.
3.9. Upon completion of the repair and inspection, all removed guards on electrical equipment must be put in place and secured.
3.10.. Repair and maintenance of electrical equipment of lifting installations must be carried out in accordance with the requirements of the current repair and maintenance documentation of the manufacturer, as well as in accordance with the scheduled preventive maintenance schedule.
3.11. When inspecting the electrical equipment of the lifting installation, portable lamps with a voltage of 12 volts or electric storage lamps should be used.
3.12.. When working with a blowtorch, observe the following rules:
Do not pour fuel into a working lamp;
Do not pump air into the lamp more than the allowable pressure.
The lamp plug must be fully screwed on.
3.13 When using a portable electrified tool, use dielectric gloves and rubber mats.
3.14. When removing or installing parts and assemblies of electrical equipment of a lifting installation, use the tools and devices provided for this type of work.
3.15.. Workplaces and passages to them should be kept clean, not allowing them to be cluttered with spare parts removed from the compressor.
3.16. Cleaning material must be stored in metal boxes with tight-fitting lids.
3.17..Before using the ladders, check for the presence of an inventory number on their bowstrings, the date of the next test, the presence of tips and ties, and the absence of chips.
3.18.. When working on a ladder, there must be a second worker in a protective helmet below, insuring the worker on the ladder.
4. Safety requirements in emergency situations
4.1. In the event of an emergency, the electrician is obliged to stop work, immediately inform the master and then follow his commands.
4.2.. When eliminating an emergency, it is necessary to act in accordance with the approved plan for eliminating accidents.
4.3. In the event of a fire that could lead to an explosion, it is necessary;
Notify the fire department immediately
Proceed to put out the fire.
Organize the evacuation of people.
Arrange a fire department meeting.
4.4. When electrical equipment catches fire, use only carbon dioxide fire extinguishers. or powder.
4.5. In case of injury or illness, an electrician for the repair of technological installations must stop working, notify the master and contact the first-aid post.
5. Safety requirements at the end of work
5.1. At the end of the work, the electrician must;
Tidy up your workspace.
Fold the tool, inventory and fixtures in a specially designated place.
Collect used cleaning material in metal boxes with tight-fitting lids.
Take off your overalls and put them in the dressing room closet.
5.2. If necessary, hand over the contaminated overalls for washing.
5.3. After work or in cases of contamination of body parts, take a shower.
5.4. The electrician must inform the foreman about all violations of the production process.
Popular
- How to choose a CNC milling machine (milling cutter) for wood with your own hands
- The easiest way to transfer any image to fabric or wood How to paint on plywood with acrylic paints
- Order on the provision of one free day from work per week to prepare for writing a thesis
- CNC milling machine for the manufacture of straight and curved facades
- Underground greenhouse - a new trend or a forgotten technology
- Decoupage of caskets: master classes and ideas for decoration Decorating wooden caskets with your own hands
- How band saws are welded
- When and how did the first zoos appear?
- Organization and holding of the graduation party
- Winter patterns on glass painted with frost What are the names of patterns on windows in winter