Export factoring. Export factoring - a solution for small and medium-sized businesses
Post-export financing - factoring
International factoring is a means of financing international receivables by which a firm can request a factoring company (factor) to advance funds based on existing receivables. Currently, there is no universal definition of factoring. Factoring is defined differently in different countries. Back in 1988, it was defined that factoring is an agreement between a factor and its client, which includes at least two of the following services:
- ? financing;
- ? account management;
- ? receiving debts;
- ? credit risk protection.
In terms of its financial and economic content, any factoring is a trade and commission operation combined with lending to the client's working capital, including collection of his receivables, lending and a guarantee against credit and currency risks. The goal of factoring is to get the supplier to receive payment as soon as possible, but at a discount, on a certain date. The basis of a factoring operation is the assignment of outstanding payments to a factor (factoring company). This is done by the transfer (endorsement operation) of bills and invoices.
Factoring in international trade is of interest primarily to small and medium-sized businesses with an export orientation. Such companies often have prospects for expanding export production, but do not have a sufficient financial base, as they are burdened with receivables. The reason for this is the delay in payment for their export supplies by foreign buyers, which leads to a lack of own working capital [Pokrovskaya, 2009]. In an effort to increase the rate of capital turnover, they give up part of their trading margin to factors.
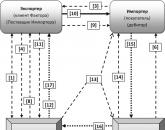
Thus, international factoring can be defined as an operation that provides settlements and services for financing international supplies of goods and services. International factoring, in contrast to trade finance transactions, is used to work on long-term or open-ended foreign economic contracts, characterized by regular deliveries and a tendency to increase turnover. International factoring is carried out according to two models: one-factor (Fig. 4.3) and two-factor (Fig. 4.4).
Rice. 4.3.
In order to better understand the role of the factor in the organization of continuous export flows by reducing the perceived risk of the exporter and the real risk for the exporter, we present a sequential course of events developing between the three main actors of export factoring, namely:
The Exporter enters into an agreement (agreement) with the Factor on export factoring;
The Exporter and the Importer enter into an agreement in which both one and (more often) several international deliveries can be made within a certain time (for example, a calendar year);
The Importer places an order with the Exporter for some product without prepayment (expecting to receive it as a "commodity credit");
The Exporter delivers the goods to the Importer under a foreign trade contract with such an invoice, according to which the payment must be transferred to the Factor, which de facto makes the Importer a debtor of the Factor or, in other words, the Exporter transfers the receivables to the Factor under the transaction with the Importer (the stages of transferring the goods to the carrier, as well as receiving the goods by the Importer are omitted in the scheme);
The Exporter sends an invoice for the delivery to the Factor;
The factor conducts advance financing of the Exporter (for example, 80-90% of the invoice value of the delivery under the contract). Interbank relations are not shown in the diagram;
The factor, in accordance with the invoice under the contract, issues an invoice to the Importer for payment and checks the execution if it does not receive payment on time;
The Importer pays the invoice according to the invoice in favor of the Factor;
The factor transfers funds for the final settlement with the Exporter.
The relationship of a factoring company (factor) with an exporter is based on the conclusion export factoring agreements, which primarily determines the conditions for the emergence and elimination of credit and currency risks. By signing the contract, the factor company buys from the exporter all commercial rights (invoices) arising from the moment the goods are delivered to the buyer. The exporter receives most of the amount (60-90%) as payment for the delivery immediately after shipment, and the remaining part (minus the commission) is paid by the factor company within the period specified in the contract. This payment is made regardless of the financial situation of the buyer.
A factoring operation involving the transfer of settlement functions from the main factor company to any branch is called mutual factoring. Export and import factoring imply the presence of elements of mutual factoring. Sometimes direct factoring may be present in the process of implementing a factoring agreement. With mutual factoring, the exporter signs a legal agreement only with the national factoring company serving him, without concluding an agreement with a company operating in the importer's market. At the same time, the exporter is aware of all the information and conditions on which the importer's company operates, so that the exporter can correctly assess the conditions for the assignment of his documents and rights to another factor company.
Export factoring is a financial scheme that combines financing of the exporter's working capital, credit protection, management of the foreign importer's receivables, and collection of payment. The factor itself can be represented by a bank or other financial institution that finances exports by purchasing invoices from the exporter or receivables from the importer.
Export factoring is carried out under an agreement between the exporter and the factor, under which the factor buys short-term receivables held by the exporter, paying for it in cash at a certain discount. Thus, the factor assumes the risk of non-payment by the importer and the need to conduct operations to receive this debt from the importer. As a result, by virtually eliminating the risk of non-payment by foreign importers, the factoring scheme allows the exporter to offer payment terms from an open account, thereby increasing liquidity in the exporter's financial performance and ultimately increasing its competitiveness in the international market.
International factoring of foreign receivables is a real alternative to export credit insurance, long-term bank financing of exports, the use of expensive intermediate short-term loans such as bridge loan and other types of borrowing that create debt in the exporting company's balance sheet. There are two main export financing schemes using factoring:
Discount factoring (discount factoring) - the factor advances funds against the receivables of the exporter before the funds are received from the importer. Transaction costs in this case turn out to be variable and depend on the time frame for receiving funds from the importer and on the exchange rate of the currency in which they will be received.
Collection factoring (collection factoring ) - the factor makes the payment to the exporter minus commissions for receivables that are due for payment, regardless of the financial capacity of the importer to pay. Transaction costs are fixed and typically range from 1-4% depending on the country, the size of the transaction and the amount of paperwork.
Export factoring restrictions:
- ? used only in those countries that have legislation that regulates the sale and purchase of receivables;
- ? usually not suitable for foreign receivables with a maturity of more than 180 days;
- ? may not be suitable for exporters who expect meager profits.
Natural for the case of international factoring, when the seller and the buyer are in different countries, has become two-factor factoring (see Fig. 4.4), which allows sharing responsibility between two factoring companies.
export factor ( export-factor ) finances the seller and provides receivables management. Import factor (Import-Factor) provides credit coverage and reclaims unpaid invoices. Such a scheme is very convenient and effective in cases where there are significant economic, legal and especially linguistic differences between the marketing environments of the countries of the seller and the buyer.

Rice. 4.4.
A step-by-step procedure for international two-factor factoring with a full range of services from four factoring actors can be represented as follows:
The Exporter (in terms of factoring - the client) enters into an international factoring agreement with the Export Factor, in which the agreed buyers (Importers) are often specified in advance;
The export factor and the import factor enter into an interfactorial agreement on cooperation, within the framework of which the agreed buyers (Importers) are specified in advance;
The Importer places an order for the purchase of goods from the Exporter;
The Exporter, using a pro forma invoice drawn up on the basis of the Importer's order, requests the Export Factor about the maximum allowable total value of the foreign trade contract corresponding to the Importer's order;
The Export Factor, in turn, agrees on the maximum allowable total value of the Importer's planned foreign trade contract with the Import Factor;
The import factor checks the current state (solvency, financial history) of the Importer;
The import factor in case of a positive result of the check of the status of the Importer, gives the export factor approval for the size of the foreign trade transaction;
The Export Factor gives approval to the Exporter for the deal in question;
The Exporter concludes a foreign trade contract with one of the Importers specified in the steps;
The Exporter, on the basis of a foreign trade contract concluded in accordance with the order of the Importer, delivers the goods to the Importer in accordance with the specified proforma invoice. Transport operations and customs formalities are not shown on the diagram;
The Exporter transfers to the Export Factor the invoice of the foreign trade contract and other documents necessary for the transfer of the Importer's receivables (assuming the form of payment from an open account);
The export factor transfers to the Exporter the funds agreed in their factoring agreement (usually not more than 90% of the total contract value);
The export factor sends documents on the foreign trade transaction to the Import factor and the Importer;
Upon the due date of payment (in accordance with the terms of the contract and the relevant invoice issued by the Exporter), the Import Factor makes a presentation to the Importer;
The Importer, in accordance with the submission, makes payment in favor of the Import Factor;
The import factor, in turn, transfers the appropriate funds under the interfactor agreement to the export factor.
The export factor transfers (taking into account its own compensation under the agreement) the balance of funds to the Exporter, thereby making the final settlement of the Exporter's invoice, taking into account the advance payment previously made by the Export factor.
Mutual, or two-factor, factoring is a factoring operation in which a factoring company will act in its country on behalf (on behalf of) a foreign factoring company in transactions involving these two countries. In fact, two-factor factoring is the most reliable means of integrating the cross-border section of the supply chain (network) and, in addition, can be interpreted as a tool for international logistical risk management (Table 4.3).
Table 4.3
Brief characteristics of export factoring
For business
All articlesExport factoring
Which type of export factoring is right for you?
Export international factoring services are provided according to two schemes.
- Export factoring with recourse. This is the most popular payment format. The presence of recourse gives the financial company in case of non-payment of funds by the debtor and refusal to supply the right to demand them from the supplier after a certain time. The factor assumes liquidity risk. Credit at the same time remains with the supplier.
- Export factoring without recourse. In this case, the financial institution assumes all responsibility. This leads to the fact that factoring services without recourse require a thorough check of debtors for solvency. If the client fails to pay the funds in full, the factor will incur losses.
More about export factoring
Export factoring is a set of services for regulating mutual settlements between suppliers and buyers from different countries. Factors provides clients with the following services:
- Financing without delay;
- Providing long-term deferrals at favorable interest rates;
- Consultations and information support;
- Preparation of reconciliation acts;
- Debt control, etc.
The benefits are obvious. Export international factoring services significantly speed up and simplify the organization of deliveries abroad.
Advantages of export factoring
Export factoring gives counterparties a large number of advantages.
Buyers.
- Importers receive deferrals to pay for deliveries.
- Working capital is replenished without the transfer of property as collateral.
- The range is expanding.
- There is an opportunity to enter new markets.
- Interest rates on factoring loans are lower than the rates offered by banks.
Suppliers.
- Exporters receive most of the money immediately.
- Sales are increasing.
- There are no strong cash gaps.
- The risk of buyers not paying for orders is greatly reduced.
- Would you like to order export factoring services? Contact. We will assess the solvency of the company and offer a suitable option for mutually beneficial cooperation.
Export factoring without recourse- the type of international factoring operation most demanded by Russian companies, in which the Export factor fully assumes the risk of non-payment of the export delivery by the non-resident buyer. As a rule, this type of international factoring is implemented according to a two-factor model.
Algorithm for the implementation of export factoring without the right of recourse, two-factor model:
At the same time, the Export Factor sends a request to the Import Factors in the country of the non-resident buyer through the FCI or IFG information system in order to guarantee the return of proceeds and assess the solvency of the non-resident buyer.
2. After passing the underwriting and receiving confirmation from the Import Factor, an export factoring agreement is concluded without the right of recourse (General agreement on general conditions for factoring services for export deliveries). The non-resident buyer is sent a notification of its conclusion and an instruction to make payments.
3. The exporter delivers, in accordance with the export factoring agreement, without the right of recourse, transfers the shipping documents to the Export factor (as a rule, the original invoice (invoice), the original or a copy of the consignment note (bill of lading), a copy of the state customs declaration (CCD)) , the transfer of the monetary claim (the right to receive proceeds) to the Export factor is completed.
4. The export factor, having verified the delivery, provides the exporter with financing in the amount of 70 to 100% of the invoice (delivery) amount. Financing is paid in the currency of the Russian Federation. The Export Factor commission is paid by deducting a percentage of the financing amount, or by a separate account.
5. The exporter returns the financing to the Export Factor after receiving the proceeds from the non-resident buyer. In case of delay in payment or refusal to pay for the delivery, the import factor transfers the amount of proceeds to the exporter.
Export factoring with the right of recourse- the most popular type of export factoring in Russia, characterized by a low commission for risk, since the range of services does not include protection against non-payment by a non-resident buyer. This type of international factoring is used to increase the volume of export deliveries to reliable counterparties abroad, as well as to prevent cash gaps in case of long delays in payment. Export factoring with the right of recourse is more often implemented according to a one-factor model.
Algorithm for the implementation of export factoring with the right of recourse, two-factor model:
1. To conclude an international factoring agreement, it is necessary to provide the Export Factor with information for the analysis of the financial, economic and production activities of the exporter (see the list of documents in the “Factor Profile” section).
The exporter indicates the countries and companies with which foreign economic activity is carried out, provides copies of foreign trade contracts for supplies with deferred payment.
The term for consideration of documents and risk assessment (underwriting) can be from 7 to 30 days.
2. After passing underwriting, an export factoring agreement is concluded with the right of recourse (General agreement on general conditions for factoring services for export deliveries). The non-resident buyer is sent a notification of its conclusion and an instruction to make payments. According to the payment instruction, the proceeds must be sent by the non-resident buyer to the factoring account of the exporter in the bank of the Export Factor.
3. The exporter delivers, in accordance with the export factoring agreement with the right of recourse, transfers the shipping documents to the Export factor (as a rule, the original invoice (invoice), the original or a copy of the consignment note (bill of lading), a copy of the state customs declaration (CCD)) , the transfer of a monetary claim (the right to receive proceeds for a specific supply) to the Export factor is completed.
4. The export factor, having verified the delivery, provides the exporter with financing in the amount of 70 to 100% of the invoice (delivery) amount. Financing is paid in the currency of the Russian Federation. The factoring commission is paid by deducting a percentage of the financing amount, or by deducting after receipt of proceeds from a non-resident buyer.
5. In case of non-receipt of proceeds from a non-resident buyer, the Export Factor updates the waiting period - the period during which a set of measures is taken to pay off the debt that has arisen. If it is not possible to receive proceeds from the non-resident buyer, the Export Factor sends the exporter a notice of recourse and a request for the return of previously paid financing for the unpaid delivery by the non-resident buyer.
Import factoring- the largest type of international factoring in Russia. A distinctive feature of import factoring is that the Russian importing company does not incur direct financial costs: with a two-factor model, the commission for the service and financing is paid by the non-resident supplier. Import factoring under the two-factor model does not imply the right of recourse.
The algorithm of import factoring without the right of recourse according to the two-factor model is a "mirror reflection" of the algorithm of export factoring without the right of recourse.
In Russia, a recourse import factoring scheme is also used, in which the Russian Import Factor issues a guarantee to the non-resident supplier's bank, which removes the risk of non-payment for the delivery.
Export factoring is one of the most effective financial mechanisms that allows both experienced companies and beginners in foreign trade to solve a significant number of complex problems associated with the implementation of export deliveries.
Export factoring allows suppliers to carry out settlements on the terms of deferred payment without a significant diversion of working capital. It is often difficult to check the reliability of foreign counterparties due to the peculiarities of legislation and business transactions abroad. The factor undertakes to check the creditworthiness of foreign buyers, covers a number of financial risks, incl. the risk of insolvency of buyers (credit risk), the risk of delay in payment (liquidity risk).
The factor takes responsibility for the collection of receivables, which significantly frees up time and reduces the supplier's costs associated with monitoring the status of receivables, their collection and work with overdue payments. At the same time, highly professional market participants - factoring companies - members of IFG can also join the process of collecting receivables.
The factor can provide services of both direct export factoring and factoring under a two-factor scheme (Fig. 2.1 and 2.2, respectively).
Exporters of goods and services from Russia, working with buyers from one or more countries at the same time, can immediately receive financing from the deliveries made, insure themselves against a number of financial risks, and simplify work with their debtors through export factoring services. The guarantee of payment from the factor greatly simplifies cross-border trade with foreign counterparties.
Figure 2.1 - Direct export factoring
Figure 2.1 shows the scheme of direct export factoring, while the numbers indicate:
- · Conclusion of a factoring agreement.
- · Establishing a financing limit for the exporter.
- · Shipment of goods.
- · Assignment of receivables and provision of shipping documents.
- · Early payment (up to 90% of the delivery amount).
- · Payment for delivery by a foreign importer.
- · Sale of foreign exchange earnings.
- · Crediting the ruble amount of proceeds to the factoring account.
- · Crediting the balance of the amount to the account of the Exporter.
Membership in IFG and FCI allowed the factor to get the opportunity of direct cooperation with international factoring companies and banks from different countries, united by an international electronic system for the transfer of financial information, as well as access to a unique database on the solvency of foreign debtors, the latest developments and technologies in the field of international factoring.

Figure 2.2 - Two-factor export factoring
Figure 2.2 shows the scheme of two-factor export factoring, while the numbers indicate:
- 1. Export factoring agreement.
- 2. Approval of the creditworthiness of the foreign debtor.
- 3. Contract of sale.
- 4. Delivery of goods.
- 5. Providing shipping documents.
- 6. Financing in the amount of up to 90% of the delivery amount.
- 7. Notification of a foreign factoring company (Import Factor) about the delivery.
- 8. Payment in favor of the Exporter in the amount of 100% of export earnings.
- 8a. In case of non-payment by the importer, the Import Factor pays 100% of the export proceeds.
- 9. Repayment of financing and payment of factoring commissions
A foreign factoring company has complete information about the market of its country, which allows it to objectively assess the reliability of buyers. In addition, a foreign factoring company - a partner assumes the risk of insolvency of a foreign buyer, thereby guaranteeing a full return of funds. Thus, the exporter will not face unforeseen risks that could cause significant damage to his financial position.
Two years have passed since the launch of the Smart Factoring project at Priorbank OJSC, which provided an opportunity to implement the most successful factoring business experience borrowed from the banks of the Raiffeisen International group and adapted for Belarus in the business situation of the Republic of Belarus. Alexander Leonidovich Klochko, Executive Director of Priorbank OJSC, spoke about a new initiative to develop export factoring within the framework of the Smart Factoring project.
Alexander Leonidovich, why did the bank begin to actively develop export factoring?
Today, the demand from entrepreneurs for an open, comfortable business environment, technological financial services and services is huge and, no doubt, justified.
The year 2011, with its vicissitudes in the global financial markets, uncertainty and difficult macroeconomic situation, clearly demonstrated that export today is important not only for the state in terms of the successful implementation of the country's export-oriented policy, but also for the business entities themselves from the standpoint of maintaining profitability , business development opportunities and adequate management of foreign exchange risks in their own country.
In the context of the creation of the Customs Union and the Common Economic Space and taking into account the open nature of the Belarusian economy, in my opinion, financial instruments to support export-import operations, as well as the speedy implementation of the positive international experience of their application, already developed over the past decades, are becoming increasingly important.
One of such tools is export factoring, offered by Priorbank OJSC as part of the ongoing development of our project “Business Completion”.
It should be noted that mature financial markets are also characterized by activity in the field of import factoring, but Priorbank, for a number of reasons, decided to start with export factoring.
What types of export factoring are offered in Belarus today?
The main definitions in theory and practice boil down to the fact that export factoring is financing against the assignment of a monetary claim to a debtor located outside the Republic of Belarus.
There are several types of export (or international) factoring. The simplest type of export factoring is direct export factoring. Within the framework of this product, three parties are involved: the exporter, the bank (export factor) and the debtor to whom the goods (services/works) are supplied, and monetary claims that are assigned to the bank. This product is most often offered on a recourse basis (that is, the risk of non-payment by the debtor is assumed by the exporter) and with notification of the debtor of the assignment (open factoring). In addition, depending on the debtors and the terms of the transaction, the bank may require the provision of additional security (pledge of goods in circulation, equipment, etc.).
A more attractive type of export factoring seems to us to be two-factor factoring. 4 parties are already involved here: in addition to those mentioned above, a new party enters the transaction - the import factor. A special interfactorial agreement is concluded between the import factor and the export factor. An import factor is a bank or factoring company that is located in the country of the debtor and assumes the risk of non-payment by this debtor, and also assumes the collection of unpaid debt. Thus, if your buyer has not paid within a certain period (as a rule, the term under the contract + 90 days of waiting), the import factor will pay off the debt for him. It is critically important in this scheme that the export factor and the import factor are necessarily members of the international association of factors (for example, IFG - International Factors Group, where the only representative from Belarus today is Priorbank OJSC), which allows them to cooperate within the framework of unified rules and procedures that clearly, to the smallest detail, regulate and accelerate the processes of interaction and exchange of information (an analogue of the well-known Uniform Rules of the International Chamber of Commerce on documentary letters of credit and guarantees). Despite the apparent complexity of the scheme, nothing actually changes for the exporter: he still concludes a factoring agreement with Priorbank and receives financing in foreign currency against the assignment of claims to his buyers abroad.
This scheme has proven itself, is transparent and understandable to partners and is widely used in international trade. To date, Priorbank has already entered into the first interfactorial agreements with Russian banks - this allows us today to serve export flows to Russia under a two-factor scheme. Documents with Western European financial institutions are under development.
Who can benefit from export factoring?
Export factoring is especially relevant for exporters (manufacturers or wholesale suppliers) who ship goods (works/services) to non-residents on a deferred payment basis and who intend to qualitatively improve the elements of a standard offer to their counterparties.
What are the benefits of export factoring for exporters?
- - Financing of export operations in foreign currency.
- - Coverage of risks of non-payment by a non-resident buyer (in the case of using a two-factor scheme or a scheme with insurance coverage).
- - Efficient management of receivables outside the country.
- - The possibility of completing a foreign trade operation during export by obtaining financing through factoring (Decree of the President of the Republic of Belarus dated March 27, 2008 No. 178 "On the procedure for conducting and controlling foreign trade operations", clause 1.7, paragraph 5) - thanks to factoring, the exporter is relieved of the obligation to ensure the receipt proceeds from the export transaction immediately after receiving the amount of financing under the factoring agreement.
- - The possibility of concluding export contracts with a grace period of more than 90 days (no additional permission from the National Bank is required).
- - Entering new markets and expanding the client base: thanks to factoring, the exporter has the opportunity to offer buyers more favorable payment terms with deferred payment.
Undoubtedly, we are ready to discuss in more detail the positive aspects and new opportunities offered by export factoring in each specific case during negotiations with our clients.
What is the practice of working with deferred payment in international trade?
In international practice, deferred payment is classically viewed as a commodity credit provided by the seller to the buyer. That is, the seller, providing a deferred payment, in fact, credits the working capital of the buyer. This situation can be viewed from two sides. On the one hand, the seller is undoubtedly interested in increasing the purchasing power of his customers: from this point of view, lending to their working capital seems reasonable. However, on the other hand, logic dictates that any loan must be paid. After all, the provision of a deferment significantly increases the turnover of the working capital of the buyer, which directly affects its financial performance. In world practice, the situation is quite common when the “cost” of such a commodity loan is included in the final price of the goods (works/services): the longer the payment delay, the higher the final price.
Unfortunately, our exporters are not accustomed to considering the delay as a kind of service that you have to pay for, and as an additional advantage in negotiations with the buyer. But often the exporter can fully or largely compensate for the costs associated, for example, with factoring, if the export delivery is carried out on the terms of a long delay and is financed using this instrument, including them in the selling price.
Thus, on the one hand, the provision of deferred payment helps to expand the sales market and reach new customers. On the other hand, the use of factoring at the same time allows you to improve turnover ratios and avoid liquidity gaps that usually arise when granting a deferment - this is the practice that is widely used in world markets.
What would you like to say to your potential clients?
The desire for creativity and excellence unites Priorbank and most of our existing clients. Our new services are focused primarily on successful and growing companies, which I invite to support us in our efforts to jointly make the financial and banking services market more mature and bring it closer to the level of the best world standards.
I would like to note that our development specialists predict a serious interest in international factoring not only from large corporate clients, but also from small and medium-sized businesses. Our task is to ensure the growth of the factoring market not as a substitute for credit and a source of liabilities, but as a comprehensive service with a serious service component aimed at efficient and, most importantly, safe growth of the company. Already, our customers are demonstrating a huge demand for financial logistics solutions with high added value, combining a number of financial and commercial services (verification of deliveries, collection and management of receivables, insurance against delays and non-payments, consulting, etc.)
The program for launching and promoting the service to the market includes not only a standard set of tools (marketing, project administration, pricing, etc.), but also a number of new ones that are widely unknown in the country. We will encourage our clients.
Regarding our intentions: I have already noted in my previous interviews that this time, as in the case of our rapidly developing internal factoring, we intend to actively promote this service and take a dominant position in this segment in the market in the near future.
And in conclusion, the launch of this product on the market and the creation of a favorable environment for its successful promotion was preceded by serious joint work with the leaders and experts of the National Bank, the Ministry of Economy, and a number of other state bodies and institutions. Taking this opportunity, I would like to express my gratitude to them for prompt consideration and support of our undertakings.
Popular
- Summary of the lesson on familiarization with the surrounding children of the group preparatory to school “Who hatched from the egg?
- Summary of the lesson for the preparatory group “Who hatched from the egg?
- Turukhtan (Philomachus pugnax)
- Pygmy right whale (Caperea marginata)Eng
- The concept and features of corporate clients
- Why Phoenix. The symbol of the phoenix among the Slavs. Legends about the Phoenix in different religions
- How to make soap at home with your own hands
- We make fragrant soap with our own hands
- Composition and properties of laundry soap, household use Laundry soap household use
- How to use laundry soap in everyday life Household soap in medicine