The functions of the stock exchange. Development and structure of the stock exchange
The stock exchange is created and operates in the organizational and legal form of a company (except for a full, limited company and a company with additional liability) or a subsidiary of an association of securities traders, and operates in accordance with the Civil Code of Ukraine, laws governing education, activities and termination of legal entities, with the features defined by this Law.
The stock exchange is formed by at least twenty founders - securities dealers who have a license for the right to carry out professional activities in the stock market, or their association, numbering at least twenty securities dealers. The share of one securities trader cannot be more than 5 percent of the authorized capital of the stock exchange.
The size of the authorized capital of the stock exchange must be at least UAH 15,000,000. The equity capital of the stock exchange that carries out clearing and settlement must be at least UAH 25,000,000.
Each member of the stock exchange has equal rights to organize the activities of the stock exchange as an organizer of trade.
The activities of the stock exchange as a trade organizer are temporarily suspended by the National Commission for Securities and the Stock Market if the number of its members is less than 20, and if the stock exchange is formed as a subsidiary of an association of securities dealers - when the number of members of such an association is less than 20 If within six months the admission of new members has not occurred, the activities of the stock exchange
Members of the stock exchange can only be securities traders who are licensed to carry out professional activities in the stock market and have committed themselves to comply with all the rules, regulations and standards of the stock exchange.
Membership in the stock exchange is terminated in the event of cancellation of the license for the right to carry out professional activities in the stock market, issued to a securities trader.
Stock market requirements:
1. The stock exchange is obliged to publish and provide the National Securities and Stock Market Commission with information on:
List of securities traders admitted to the conclusion of contracts for the purchase and sale of securities on the stock exchange;
List of securities that have passed the listing procedure;
Listing - a set of procedures for including securities in the register of a trade organizer and monitoring compliance cinnamon x securities and the issuer to the conditions and requirements established in the rules of the trade organizer.
The volume of trading in securities (number of securities, total value of concluded agreements, the rate of securities for each issuer separately) for the period established by the National Commission on Securities and the Stock Market.
2. The National Securities and Stock Market Commission establishes the procedure and forms for presenting the information specified in part one of this article and exercises control over the disclosure of information by stock exchanges.
Organization of trading on the stock exchange. The stock exchange creates organizational conditions for the conclusion of contracts with securities by quoting securities on the basis of supply and demand data received from participants in trading on the stock exchange.
Members of the stock exchange and other persons have the right to participate in trading on the stock exchange in accordance with the law.
Trading on the stock exchange is carried out according to the rules of the stock exchange, approved by the stock exchange board and registered by the National Securities and Stock Market Commission.
Stock exchange rules:
Organization and conduct of exchange trading;
Listing and delisting of securities;
Delisting- procedure for exclusion of securities from the register of the trade organizer if they do not comply with the rules of the trade organizer, with the subsequent termination of their circulation on the trade organizer or transfer to the category of securities admitted to circulation without being included in the trade organizer's register
Admission of members of the stock exchange and other persons specified by law to exchange trading;
Quotes of securities and publication of their exchange rate;
Quotes- a mechanism for determining and / or fixing the market price of a valuable
Disclosure of information about the activities of the stock exchange and its disclosure;
Resolution of disputes between members of the stock exchange and other persons who have the right to participate in exchange trading in accordance with the law;
Control over compliance by members of the stock exchange and other persons who have the right to participate in exchange trading in accordance with the law, the rules of the stock exchange;
Imposition of sanctions for violation of the rules of the stock exchange.
The stock exchange performs the following features:
Provides access for enterprises to loan non-bank capital;
Coordinates the placement of government securities;
Provides the transfer of financial capital from one area of activity to another;
Orders market relations regarding the circulation of financial instruments.
The main participants of stock exchanges are:
Brokerage companies- these are companies that carry out 1 civil legal transactions with securities, which provide for the payment of securities against their delivery to a new owner on the basis of commission or commission agreements at the expense of their clients.
Dealer companies- these are companies that carry out civil law transactions with securities, which provide for the payment of securities against their delivery to a new owner on their own behalf and at their own expense for the purpose of resale.
Brokers- These are persons who act as intermediaries in the conclusion of transactions on the stock exchange.
Depending on the type of trading activity, members of the exchange are divided into four categories:
The broker-commission agent collects client requests from brokerage firms, delivers them to the exchange floor and is responsible for their implementation;
An exchange broker executes orders from other brokers;
An exchange trader carries out operations only at his own expense, according to the rules of the exchange. He is forbidden to carry out the orders of clients;
"specialist" performs three main functions: executes orders with certain groups of securities, acting as a broker; acts as a dealer, that is, buys and sells securities at his own expense; performs the task of maintaining stability in the market for certain securities by compensating for temporary imbalances in supply and demand. The specialist is the central figure in the stock exchange.
All operations on the stock exchange are divided into cash (spot) and urgent.
Cash transaction (spot)- Its peculiarity is that the securities are paid for and transferred to the buyer, as a rule, on the day of the transaction or within 1 C days. The market for such agreements is called cash (spot), and the cash (spot) price. These agreements provide for the initial placement of securities and their secondary resale. Securities that have been listed (examined) in the expert group of the exchange are accepted for initial placement through the exchange. Secondary resale of securities is as follows:
Transactions are carried out on securities that are quoted on the stock exchange;
Notation is compiled on the basis of real exchange prices of supply and demand;
Instructions to brokers to buy and sell securities are given in the form of an order.
Agreements that have the subject of delivery of an asset in the future are called urgent. Subject futures deals can be any asset. Forward transactions include: options, futures, warrants.
In terms of expiration dates, options are divided into:
american option, which can be completed any day before the expiration of the contract.
European option, which is carried out only on the day of the expiration of the contract.
The first stock exchanges in the world were the Amsterdam Stock Exchange (1602), the London Stock Exchange (1770), and the New York Stock Exchange (1792). At first, the development of exchanges was associated with an increase in public debt, since capital invested in bonded loans could be turned into money. After the first joint-stock companies appeared, shares become the object of exchange turnover. Today there are about 200 stock exchanges in the world, united in the International Federation of Stock Exchanges. The largest of them are the stock exchanges of New York, London and Tokyo - they account for up to 60% of the global volume of securities trading. Each country has its own international, historically established system of exchanges. Given the role played by stock exchanges in national financial and investment systems, it is possible to single out countries with mono- and polycentric organization of stock exchanges.
There are 10 stock exchanges on the Ukrainian securities market:
1. Public Joint Stock Company "Ukrainian Exchange", Kiev
2. Public Joint Stock Company "Eastern European Stock Exchange", Kiev
3. Public Joint Stock Company "Stock Exchange" PERSPECTIVE ", Dnepropetrovsk
4. Private Joint Stock Company "Ukrainian Interbank Currency Exchange", Kiev
5. Open Joint Stock Company "UKRAINIAN INTERNATIONAL STOCK EXCHANGE", Kiev
6. Public Joint Stock Company "Kyiv International Stock Exchange", Kiev
7. Public Joint Stock Company "PFTS Stock Exchange", Kiev
8. Private Joint Stock Company "Pridneprovsk Stock Exchange", Dnepropetrovsk
9. Open Joint Stock Company "Stock Exchange" SHNEKS ", ..
10. Open Joint Stock Company "Ukrainian Stock Exchange", Kiev PFTS (over-the-counter stock trading system) - the secondary market of the Central Bank their purpose - the creation and implementation of organizational and technical systems in Ukraine, which would make it possible to quickly and efficiently conclude and execute transactions purchase and sale of securities (Fig. 3.1).
Rice. 3.1 Dynamics of trading in securities on PJSC "Ukrainian Exchange" in 2014
The volume of trading on the Ukrainian Stock Exchange in June 2014 increased by 2% compared to May, but fell short of the successful April 2014 by 3%. As a result, in the first month of summer, investors "traded" securities for 661.85 million hryvnias.
Compared to the stock market, the futures market lost much less in 2013. Monthly volumes of transactions with futures instruments in total on two main floors - the Ukrainian Exchange and the stock exchange "Perspektiva" - almost did not change during the year. The maximum fell on March - 2.3 billion hryvnia, the minimum - on the festive May, 1.3 billion hryvnia (see Fig. 3.2).

Rice. 3.2. Dynamics of trading in the derivatives market in 2013
At the same time, the volume of transactions in December -2013 almost did not differ from January - 2013: 1.68 against 1.7 billion hryvnia in the amount for the month. However, the results of each stock market separately differed quite significantly. On the UX since March - 2013, the volume of transactions with term instruments has been decreasing, and by the end of the year amounted to about 120,000,000 hryvnia (against 918 in March - 2013). On the PSE, on the contrary, there was a slight increase: from 1.2 billion hryvnia in January - 2013 to 1.56 in December, while in April, July and September the volume of transactions in futures securities here reached 1.7 billion hryvnia.
So, the Ukrainian stock market is ready for growth. And as soon as there are positive signals from the outside, the market will immediately revive. At the same time, new instruments are also needed to activate the market - for example, currency futures. Market participants hope that with the change in the policy of the NBU, which is now taking place, the regulator will agree on such instruments, and they will be able to enter the market.
Buying securities is a progressive way to use cash capital, with the help of which you can both increase your investments and insure against unplanned losses.
The main volume of all transactions with paper assets takes place on the stock market, which is a kind of organizer of the trading process. In order for transactions between participants to take place honestly, there are numerous stock exchange functions, the main ones of which will be discussed below.
1. Informing members of the financial exchange about accepted quotes
This is the key task of any stock market, the essence of which is to study the existing demand and response offers for traded securities. After the data has been analyzed, it will be available in the form of up-to-date quotation rates. To achieve this goal, all exchanges have a Quotation Commission, endowed with the following powers:
- Approval of price rates adopted in accordance with the Rules for Admission of Securities to Circulation on the Stock Exchange.
- Exclusion from circulation of assets issued in violation of standardized market norms.
- Creation and publication of the exchange bulletin.
- Formation of a comparative characteristic of the stock market instrument included in the subject of exchange transactions with similar assets of other stock markets.
- Maintaining the rating of issuers and exchange assets used by them.
- Publishing the results of the past trading day and resolving other similar issues.
It is important to note that it is the Quotation Commission that takes into account all, without exception, transactions carried out within the framework of a trading session. Therefore, on the basis of its decisions, the minimum technical parameters of transactions are established, taken into account during the formation of quotations, and prices are fixed, which no one can dispute later (the permissible deviation rate is determined). Next, consider other, no less significant functions of the stock exchange.
2. Registration and publication of prevailing price rates
The significance of stock quotes will differ depending on the type of transactions being carried out. So, if a market participant aims to carry out a cash transaction that will be completed within three days, then the information on quotations will be of a reference nature for him with a possible prospect of purchasing exchange-traded assets. However, if a transaction of an urgent nature is planned, then without reliable information about the listed assets and the degree of their liquidity, it is impossible to make an informed decision.
In order to implement any of the above tasks, the Quotation Commission of each exchange structure has an electronic journal of meetings, in which all quoted transactions are recorded. The generalized results are transferred to the quotation list, which is subsequently subject to publication. This happens in the exchange bulletin, which is displayed for public demonstration no later than the next exchange day.
3. Accumulation of financial resources
This function of the stock exchange should be reported separately. Issuers of securities and interested participants in exchange for their financial obligations can receive from the stock exchange the necessary investment amounts to support and (or) develop their own business.
This opportunity arises due to the accumulation in the stock market of temporarily unused funds received from constantly attracted investors. To this end, the entire management program of the exchange is aimed at maintaining and increasing the inflow of accumulated resources for their subsequent distribution among participants.
4. Reallocation of financial reserves
The implementation of the mechanism for redirecting funds forms a turnover on the market, due to which the increase in investor capital takes place. At the same time, not only the redistribution process itself is important for the subjects of the exchange floor, but also the existing vector of free resources. This is how the demand and the most profitable areas of application of funds are identified.
5. Market liquidity support
This process cannot but be included in the main functions of the stock exchange. The term "" itself means that sellers, buyers and investment values in demand are constantly present in the financial market. A highly liquid exchange will be one where transactions with tradable assets take place regularly and in sufficient volumes. In order to maintain such a state, the management of the stock exchange, together with issuers, performs a set of various measures:
- Creates a wide circulation market through the initial placement of securities among all potential investors.
- It includes paper assets in the exchange list, simplifies the procedures for conducting transactions and establishes guaranteed protection against fraudulent activities.
- Makes repo transactions available.
- Provides an opportunity to invest, both on and on the market.
- Includes market makers who ensure the formation of two-way market quotes.
- Performs other similar actions.
The concept of the stock exchange and their activities. stock is a free market for stocks, bonds and other securities (funds). In the stock market, the owners of securities make purchase and sale transactions with the help of members of the exchange (playing the role of intermediaries).
Exchanges, as a rule, have a joint-stock character, which determines their activities by the historically established traditions of using this type of business, the degree of dispersal of ownership of securities, the value of shares and bonds as an object of placement of funds. Exchange members (owners, holders, etc.) may be individual securities traders, as well as banks and other credit institutions.
The activities of stock exchanges are regulated by the law of the country and other regulations. In accordance with them, the Board of the exchange establishes the rules governing the very possibility of companies (whose securities are admitted to the exchange) to participate in its activities. The exchange must meet certain requirements-criteria in relation to the volume of securities sold, the amount of profit received, the market value of shares, etc.
Stock exchanges were designed to replace the cumbersome, costly and inefficient hierarchically built vertical system of sectoral redistribution of financial resources. The object of exchange trading are various types of securities that appeared in the course of securitization, i.е. in the process of registration of credit and financial relations with securities. The exchange acts as one of the main regulators of the financial market. The main role of the exchange is to serve the movement of financial and loan capital: accumulating and concentrating these capitals, on the one hand, lending and financing the state and various economic structures, on the other. The role of the stock exchange in the country's economy is determined primarily by the level of "maturity" of trade, economic and financial relations on the basis of the capitalist market, the degree of development of the securities market as a whole.
Functions of stock exchanges
The main functions of the stock exchange are:
- mobilization and concentration of free cash capital and savings through the sale of securities;
- lending and financing of the state and other economic organizations through the purchase of their securities;
- ensuring a high level of liquidity of investments in securities.
The stock exchange makes it possible to ensure the concentration of supply and demand for securities, their balance on the basis of exchange pricing, which really reflects the level of efficiency of the share capital.
Exchange auction. The first stage of an exchange transaction is an application. After the appropriate execution (filling in), the applications are entered into the exchange trading system. Depending on the type of exchange (open, closed), as well as the state of the market of the traded asset, primarily its liquidity, there are various forms of holding an exchange auction or trading. With a small volume of supply or demand, trading is carried out in the form of a simple auction. There are three types of simple auction:
- English;
- Dutch;
- correspondence.
In modern international practice, the state of the foreign exchange market and the securities market is characterized by high liquidity. This predetermines the choice of the form of a double auction. There are two forms of double auctions: on-call; continuous.
In an on-call auction, an exchange agent concentrates buy and sell orders and then sets a price that maximizes exchange turnover. Thus, a clearing price is established at which sellers and buyers enter into transactions. After some time, as a sufficient number of applications are received, the authorized exchange again sets the price that maximizes the exchange turnover. As a result, each "volley" clears the market from the largest number of orders; the largest of these "volley" markets are the stock exchanges of Austria, Belgium and Germany, which indicates the presence of a constant supply and demand for the traded asset, the liquidity of the market and allows you to move to a continuous auction.
Transactions on stock exchanges. Exchange transactions, or exchange transactions with securities, are understood as trading transactions aimed at establishing, terminating or changing the rights and obligations of participants in transactions in respect of securities admitted to quotation and circulation, concluded in the exchange premises during the established hours of the exchange. Under the wording "in relation to securities admitted to quotation and circulation" understood procedure listing- inclusion in the list of traded securities. Each company must enter its securities in the list (list) of the relevant exchange, which is a prerequisite for admission to trading.
Listing is a market support system that creates favorable conditions for an organized market, allows you to identify the most reliable and high-quality securities and helps to increase their liquidity. The listing requirements of the New York Stock Exchange are considered the most stringent. To be listed on it, a company must meet the following requirements:
- have a profit before taxes for the last year of at least $2.5 million;
- have a profit for the previous two years of at least $2 million;
- own a net worth of tangible assets of at least $18 million;
- have a number of shares in public ownership of at least $1.1 million;
- control a block of shares worth at least $18 million;
- have a minimum number of shareholders owning 100 shares or more, not less than 2,000 people;
- the average monthly trading volume of this issuer's shares must be at least $100,000 during the last six months.
These requirements actually mean that only a small number of the largest corporations can meet such high standards. The object of exchange relations with securities can be: shares, bonds (state, municipal, corporate), bills (state, municipal, corporate), certificates of deposit, American depository receipts, derivative securities (futures and options on securities), warrants.
Futures transactions are transactions on the commodity and stock exchanges in which a share must be transferred and money paid within a specified period, usually within a month. They were discussed in detail in paragraph 10.8.
Futures transactions are an important tool for dealing with price uncertainty. In the West, there are organized markets for the future supply of many goods and values, such as wheat, corn, other grains, coffee, sugar, honey, fuel oil, plywood, cash, treasury notes, certain types of bonds, etc. Their prices are subject to significant fluctuations. Therefore, special futures markets have been formed, allowing interested individuals and organizations to reduce the level of risk associated with the uncertainty of future sale and purchase prices.
In the futures market, the price for the supply of, for example, wheat in the future (up to a year and a half) is announced in advance. The standard contract (agreement) for the supply of wheat determines its quantity and the date of future delivery. With few exceptions, obligations in futures transactions are settled by paying or receiving the difference in price, and not by delivering the actual commodity.
Under exchange transactions, or exchange transactions with currency values, understand trading transactions of purchase and sale of currencies traded on the exchange, concluded in the exchange premises during the established hours of the exchange. We also discussed these transactions in paragraph 10.8.
In world practice, settlements on cash exchange currency transactions are usually carried out exclusively on a "spot" basis.
Second the type of currency transactions is a forward, or forward, transaction. The need for such transactions is caused by the desire of its participants to establish in advance the rate at which settlements on foreign exchange transactions will take place in the future. The term (forward) rate is based on the rate of cash transactions that prevailed at the time of the conclusion of the forward transaction, as well as premiums (report, agio) or discounts (deport, desagio). The size of the report or deport depends not only on the volume of forward transactions, but also on the difference in interest rates for individual currencies. These premiums and discounts are referred to as "swap" rates. The exchange rate for a futures transaction is determined as the ratio of supply and demand in the foreign exchange market at the time of the transaction, the difference in interest rates for individual currencies.
The forward rate is calculated using the following formula:
Forward rate = Spot rate (1 + % rate on deposits with leading national banks in hard currency) / (1 + % LIBOR rate level).
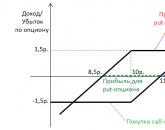
Option- a contract for the sale of an asset, according to which the buyer of an option acquires the right (not the obligation) to buy or sell this asset on or at a specified date in the future at a price agreed upon at the time of the transaction, with the payment of a certain amount for this right money called premium. The seller of the option is obliged to fulfill his specific obligations if the buyer (holder) of the option decides to exercise it. The buyer has the right to exercise the option, i.e. buy or sell an asset, only at a price that is fixed in the contract. The premium (option price) is always paid by the buyer to the seller.
Option types. From the point of view of expiration dates, the option is divided into two types:
- American - it can be executed on any day of the contract expiration date;
- European - this type can only be executed on the day the contract expires.
Options types. There are usually the following types of options:
- "call" (to buy) - gives the right to its holder to buy an asset;
- "put" (for sale) - gives the right to its holder to sell an asset.
Typical version of the options market. WITH formal point of view exists as exchange, so over-the-counter option market. The over-the-counter market in the last few decades, as the exchange market developed, has significantly decreased. The exchange technique of trading options is in many ways similar to futures trading. Like futures contracts, options are standardized contracts and the only variable is the price. The spread limits (the difference between the purchase and sale prices) are set by the exchanges themselves, depending on the option prices. Such a trading system ensures high liquidity of contracts, since at any time they can be bought or sold at a certain price.
Stock market. Loan capital is accumulated primarily in the stock markets (national, regional and global). It differs, for example, from bank loans in that financial resources are attracted through the issuance of securities (of various types and periods of use). In turn, this market is subdivided into markets for bond loans, commercial bills, shares and other securities. As a result of the transfer of one form of borrowing to another, a kind of transformation of the mechanism of lending operations takes place. In all developed countries of the world, this market has well-established institutions and is developing dynamically, carrying out numerous operations to regulate the movement of capital.
Types of specialists on the stock exchange. According to the rules of the exchange, there are four types of specialists:
- regular;
- auxiliary - they can take over the execution of the functions of regular ones in their absence;
- associates - they provide assistance to regular ones, but are not entitled to announce quotes and make transactions at their own expense. All their actions are possible only in the presence of a regular or auxiliary specialist;
- temporary - these specialists are appointed by the administration of the exchange in the event of an emergency, or when it is required by the increased volume of operations.
The following functions are assigned to the exchange specialist:
- execution of limit orders, which are transferred to him by other members of the exchange, if the current market price is noticeably different from the price indicated in the orders. By executing these orders on behalf of other members of the exchange, when the market price matches the price of the order, the specialist enables the latter to engage in the execution of other orders;
- acting as a dealer or principal on its own account. The specialist should, as far as possible, support the market for the shares for which he is responsible. In the event of a temporary imbalance between supply and demand, the specialist is obliged to buy or sell "papers" at his own expense in order to prevent a sharp change in prices and give the market "depth". Thus, the specialist ensures the continuity and continuity of the dynamics of the stock price and increases the liquidity of the market.
Other current participants (members) of the exchange:
- floor brokers, or "two dollar" brokers. They carry out orders for commission brokers if they do not have time to fulfill orders;
- registered traders. In fact, these are the same dealers, but unlike specialists, they are not responsible for the results of the stock movement. These members of the exchange have the right to make transactions with any securities on their own behalf and at their own expense, however, they are prohibited from executing clients' orders.
Applications. There are several types of orders for the purchase and sale of securities on the exchanges:
- market / limited;
- stop orders;
- daily/open (no date specified).
Orders may contain special conditions for their execution: "Execute at the opening price", "Execute immediately" or "Cancel", etc.
The order execution procedure on the New York Stock Exchange (NSE) is as follows: clients of securities companies typically give instructions to "registered representatives" by telephone. The conditions of the application are entered on a card, from which the technical officer of the company enters all the necessary data into a special device, which transmits the order to the NSE through communication channels. The order, of course, is fixed, with specific consequences in the forms of execution (or non-execution, which happens extremely rarely). All small orders (up to 2000 shares) come from brokerage firms directly to the specialist's computer (Super DOT system), which independently executes them. The time between a client submitting an order to his broker and its execution is from 30 seconds to 1 minute. Usually 15-20% of all orders are executed at the opening of trading. All bids received before the start of trading are sorted to reveal the overall picture of supply and demand. The specialist's task is to determine the price of the "security" at the opening of trades on the basis of the available limit orders. All paired bids are satisfied at a single price - the opening price of trading.
Large orders, as a rule, come from brokerage firms to the exchange to their representatives. Having received the next order, the broker executes it, but only at the corresponding trading post. If the "order is market", and the stock market is currently active enough, it will be executed in the so-called "exchange crowd" (ie, in this case, the broker can take a "positive initiative").
A more complicated situation arises when the broker receives a "limit order". In this case, the broker entrusts the execution of the order to a specialist on a commission basis; the specialist enters this application in his so-called "notebook".
The considered trading mechanisms are usually used in cases of transactions with relatively small blocks of shares. When it comes to transactions with large blocks of shares, they are pre-worked out outside the trading floor of the stock exchange, but Necessarily executed on the trading floor - this is a key requirement of the market. Another requirement of the same market is that transactions with large stakes are carried out at prices that develop during the usual, so-called continuous, "double" auction. At the same time, the so-called "block" transactions currently in effect, i.e. transactions with large blocks of shares, account for more than half of the turnover of the NSE. The movement of the indicators of these latter fundamentally determines the entire "climate" of the exchange.
- Exchange activity / ed. A. G. Gryaznova, R. V. Korneeva, V. M. Galanova. M., 1996.
The stock exchange is a market organized in a certain way, in which the owners of securities make purchase and sale transactions through members of the exchange acting as intermediaries. The contingent of members of the exchange consists of individual securities traders and financial institutions.
The range of securities with which transactions are carried out is limited. Members of the exchange or the state body that controls their activities establish the rules for conducting exchange operations, the regime governing admission to the quotation. Together with the procedure for conducting transactions, they form the core of the exchange as a mechanism that serves the movement of securities. The stock exchange is, first of all, a place where the seller and buyer of securities find each other, where the prices for these securities are determined by the supply and demand for them, and the process of buying and selling is regulated by rules and regulations, i.e. it is a market organized in a certain way valuable papers.
Securities—shares, bonds, etc., act as commodities in this market, and the rates of these securities act as prices for these commodities. The stock exchange performs three main functions:
Intermediary - creates sufficient and comprehensive conditions for trading in securities for issuers, investors and financial intermediaries;
Indicative - assessment of the value and attractiveness of securities;
Regulatory - the organization of trading in securities.
The purpose of the control activity of the exchange is to ensure the reliability of the quotation of securities and the reliability of exchange trading.
Thanks to the exchange, investors get the opportunity to easily turn securities into money, this makes it possible to invest in securities not only for long-term savings, but also for temporarily free funds.
The liquidity of these securities, which are traded on the stock exchange, creates the conditions for their widespread use to secure bank loans, makes it possible for investors to buy securities of new issues by selling the existing papers on the stock exchange.
Exchanges can be established by the state as public institutions. In France, Italy and a number of other countries, stock exchanges are considered public institutions. This is expressed in the fact that the state provides premises for exchange operations. Exchange traders are considered representatives of the state, but act as private entrepreneurs, at their own expense.
The general management of the exchange is carried out by the board of directors. In his activities, he is guided by the charter of the exchange, which determines the procedure for managing the exchange, the composition of its members, the conditions for their admission, the procedure for the formation and functions of exchange bodies.
For the day-to-day management of the exchange and its administrative apparatus, the council appoints a president and a vice-president. In addition, all aspects of the exchange's activities are supervised by committees formed by its members, for example, audit, budget, systems, stock indices, options.
The tasks of the stock exchange:
1. Creation of a permanent securities market.
2. Determination of the exchange price for securities, terms of their circulation and dissemination of information on financial instruments.
3. Mobilization of temporarily free financial resources and funds and facilitation of the transfer of property rights.
4. Ensuring liquidity and guarantees for the execution of agreements concluded on the exchange.
5. Conducting an analysis of the economic situation in the domestic and foreign capital markets, determining the prospects for their development.
The Exchange assists in the entry and development of national capital to the foreign market. For the formation and development of securities, the exchange builds its activities on the following principles:
Personal trust between broker and client;
Publicity;
.
strict regulation by the administration of the exchange and auditors of the activities of dealer firms by establishing rules for trading and accounting;It develops cooperation with financial and credit institutions within the state and abroad.
The structure of the securities market.
The structure of the securities market in Russia is characterized by the presence of primary and secondary markets, as well as markets by types of stock instruments and transactions. Primary placement and secondary circulation of a few types of securities in the initial period of development of the stock market of the Russian Federation took place mainly on stock and commodity exchanges. The emergence of the primary over-the-counter market is associated with the issuance of a state privatization check (voucher) in 1992.
Currently, the primary OTC placement of shares and corporate bonds is carried out either directly by the issuer or with the help of an intermediary firm (agent) - a professional participant in the securities market.
Primary over-the-counter placement of stock instruments, in accordance with the legislation of the country, can also be carried out through the formation of an emission syndicate (consortium). Members of syndics distinguish in their structure a firm-manager, an underwriter and commercial agents. However, this practice is currently poorly developed in the Russian market.
In addition, the country is quite well organized and carried out the initial exchange placement of securities at auctions through the Moscow Interbank Currency Exchange (MICEX).
The secondary securities market of the Russian Federation is also divided into over-the-counter and exchange markets. Until recently, the main secondary OTC market of the country was the non-commercial partnership established in 1995 - the Russian Trading System (RTS).
A stock exchange is an organized market for trading in standard financial instruments, created by professional participants in the stock market for mutual wholesale transactions. The stock exchange acts as a trading, professional and technological core of the securities market. Signs of a classic stock exchange: It is a centralized market with a fixed trading place, i.e. the presence of a trading platform; · in this market there is a procedure for selecting the best goods (securities) that meet certain requirements (financial stability and large size of the issuer, the mass character of the security as a homogeneous and standard product, the mass character of demand, clearly expressed price volatility, etc. .); Existence of a procedure for selecting the best market operators as exchange members; Availability of temporary regulations for trading in securities and standard trading procedures; Centralization of registration of transactions and settlements on them; Establishment of official (exchange) quotations; Supervision of exchange members ( in terms of their financial stability, safe business conduct and compliance with the ethics of the stock market). From the point of view of the legal status in the world, there are three types of stock exchanges: · public-law; · private; · mixed.
Popular
- How to make money on the stock exchange: examples Is it possible to get rich on the stock exchange
- Event marketing: types, tools and examples
- How to start earning in the game Farm Neighbors?
- Rewriting for a beginner: a memo to a beginner How to learn rewriting
- How to make money on Facebook: Facebook page monetization schemes without investments
- How does Facebook and VKontakte make money
- Step-by-step registration instructions
- Earnings on VKontakte likes
- Vktarget - earnings in social
- Golden tie with money withdrawal