What is the difference between public and non-public types of joint stock companies, partnerships and cooperatives?
The variety of commercial companies, partnerships and cooperatives can be confusing. Many people do not understand why they need to create so many different forms of organizing activities. It is worth understanding their differences. This will allow you to choose the best option. So, let's find out how a general partnership differs from a limited partnership, what is the difference between a public and non-public joint-stock company.
What is the difference between a public joint-stock company and a non-public one?
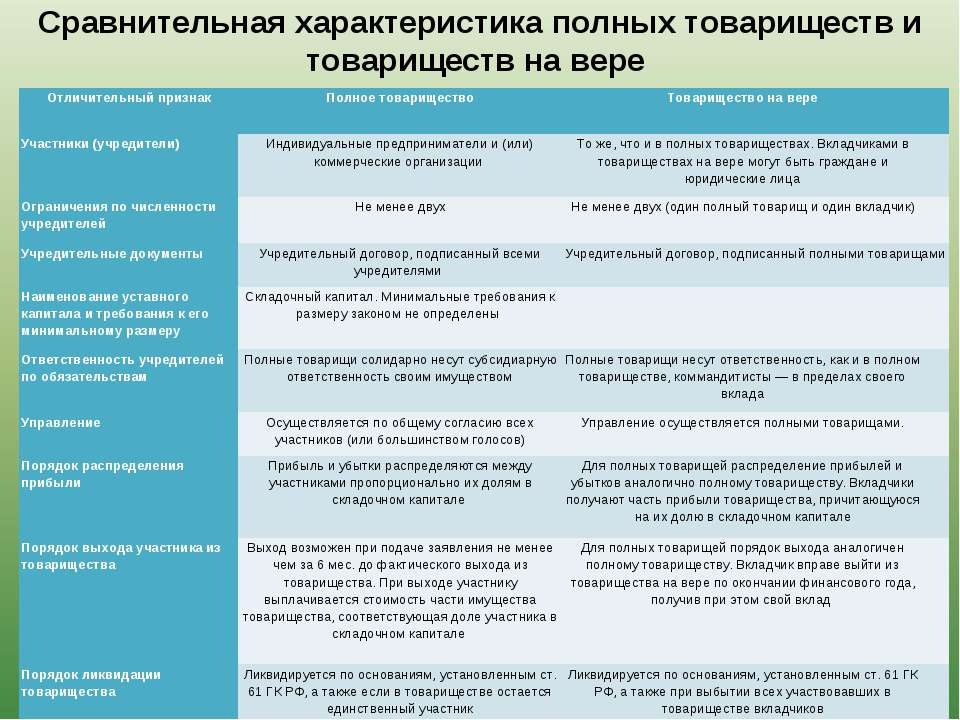
To begin with, let's subject a comparative characteristic of public and non-public joint stock companies. The first thing that distinguishes all types of joint-stock companies is the procedure for the formation of its capital. Such companies are characterized by the issue of shares, but the conditions for their acquisition are different. There are also differences in the composition of the participants, the size of the authorized capital and the obligation of public reporting.
- One of the signs is the free distribution of shares. Any purchaser of shares can become a member of such a company. The number of participants in a PJSC can be very large, and management is carried out in 4 different types. At the same time, PJSC is obliged to publish open reports annually, and the authorized capital cannot be less than 100,000 rubles.
- For the general manager, the meeting of the founders is the link. Only they have the right to own shares, their free distribution is unacceptable. The number of NAO participants cannot exceed 50 people. Exceeding this number requires a change in the form of activity. When one of the members of the NAO leaves, the right to purchase its shares is assigned to the rest of the participants. This form of organization does not require the publication of statements, and the authorized capital is minimal - 10,000 rubles.
Below is a table comparing the characteristics and differences between a public and non-public joint stock company.
Differences between public and non-public joint stock companies
Now let's talk about the difference between a full partnership and a limited partnership.
Even more useful information about public and non-public JSCs is contained in this video:
Comparison of a full partnership versus a limited partnership
These two types of partnerships differ in the form of management and the responsibility of the participants. Also, the types of partnerships have two types of members. In every type of such an organization there are general comrades. In the PT only they are present, and in a limited partnership there are also limited partners. The latter cannot take part in the management of the partnership, as well as be responsible for its debts in excess of the amount of their contribution. Companions of both varieties are responsible for all their property, regardless of the size of the share in the organization.
- A general partnership implies equal rights and obligations for all participants. There cannot be less than two of them, while they must be or. Each partner has 1 vote, and decisions are made unanimously or by a majority of the participants, depending on the instructions in the memorandum of association. The comrades are fully responsible for all their property.
- There are 2 types of participants. Some of them do not take on a role in management and bear minimal responsibility - these are fellow limited partners. They do not have the right to vote in decision-making and are responsible for the partnership's debts only by the amount of their contribution. The second type of participants is general comrades. They are the ones who manage the organization in accordance with the features prescribed in, and also bear full responsibility for the debt obligations that have arisen.
Comparison of a full partnership and a limited partnership
This video compares general and limited partnerships in terms of contributions:
Differences between business partnerships and production cooperatives
There are important differences between these two forms of organization. They apply to the responsibility of the participants, and to their number, and even to the form of contribution.
Cooperatives are more often organized for a specific purpose and a certain type, partnerships are founded for profit.
Signs of HT
Depending on, a different number of participants is allowed. Full and partial liability for debt obligations is possible. Full comrades answer with personal property, and limited partners only by the amount of their contribution. The choice of the form depends on the participants themselves, while the general comrades must issue an individual entrepreneur or legal entity.
Mostly HT of any type implies the pooling of capital and experience, without requiring personal labor input from the participants. , in which there is only one member left, must be renamed into a society.
PC features
Individuals who are unable to deposit funds can become members. As a share, personal property or labor contribution is permissible. The number of members in a cooperative cannot be less than five, and their responsibility, although subsidiary, has certain features. If the number of participants decreases to less than 5, the cooperative is obliged to change the form of organization or take an additional member with his voluntary consent.
According to the charter, liability can be limited to a certain amount. The law allows its value to be tied to the size of the share. In this case, the share itself from each participant may differ in size. For members of the cooperative, there is no need for everyone
Popular
- The bull and the bear on the stock exchange: the beastly face of the stock market
- Stages of opening a private dental office
- How to open your own store - step by step instructions for beginners + real life example
- Sales revenue - formula and concepts
- What is the difference between margin and profit - calculation formulas
- Advice 1: How to switch from simplified to a system with VAT payment
- Car depreciation - what is it?
- Yesterday's business: 7 main problems of modern realtors :: Opinions :: RBC Real Estate
- What is the difference between public and non-public types of joint stock companies, partnerships and cooperatives?
- Simple business - private household plots (personal subsidiary plots)