Federal customs service fts rf. Federal Customs Servicefts rf Russian Customs Administration
The Federal Customs Service of Russia is the central executive body of the federal government, which directly manages the customs business in the Russian Federation. He leads, unites and directs the activities of the customs authorities. As a federal body of the FCS of Russia, it is responsible for the implementation of the customs policy of the Russian Federation; ensures compliance with customs legislation and other legislation, development, strengthening the unity of the entire system of customs authorities headed by him. The Federal Customs Service of Russia performs not only the functions of direct management of the customs business, but also coordinating and control functions in this area. In cases provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, as well as other acts of legislation, the FCS of Russia issues, within its competence, acts on customs matters that are binding on all customs authorities of the Russian Federation, enterprises, institutions, organizations, regardless of ownership, as well as officials and citizens.
The FCS of Russia, as a federal executive body, carries out its activities in cooperation with other federal executive bodies, executive bodies of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and local governments. In some cases, the FCS of Russia may enter into direct relations with officials of enterprises, institutions, organizations, as well as individuals (for example, when officials of the FCS of Russia conduct an inquiry into smuggling).
The legal status of the FCS of Russia, its tasks and functions, rights and obligations, structure are determined in the Labor Code of the Customs Union of the Russian Federation.
The FCS of Russia solves all the problems arising from the goals of the state customs policy of the Russian Federation.
The structure of the FCS includes:
8 main departments:
Main organizational and inspection department (office of the chairman of the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation);
General Directorate of Organization of Customs Control;
General Directorate for Combating Smuggling;
General Directorate of Commodity Nomenclature and Trade Restrictions;
Main Logistics Department;
Main Directorate of Federal Customs Revenues;
Main Financial and Economic Department;
Main Department of Information Technology.
11 controls:
Personnel Department;
Currency Control Department;
Department of Customs Cooperation;
Case Management;
Control and Audit Department;
legal management;
Management of own security;
Department of Customs Inspection;
Department of Customs Statistics and Analysis;
Department of Customs Investigations and Inquiries;
Office of the organization of power supply.
The Federal Customs Service is directly subordinate to the customs of central subordination: Vnukovo, Domodedovo, Sheremetyevskaya, Central Base, Central Energy, as well as specialized units: the Russian Customs Academy and the Canine Center of the Federal Customs Service of Russia.
The territorial subdivisions of the FCS are 7 RTUs:
Central Customs Administration (includes 28 local customs offices: Belgorod, Bryansk, Vladimir, Voronezh, Ivanovo, Kaluga, Kostroma, Kursk, Lipetsk, Moscow East, Moscow West, Moscow North, Moscow South, Noginsk, Oryol, Podolsk, Ryazan, Smolensk , Tambov, Tver, Tula, Shchelkovo, Yaroslavl, Central excise, Central operational and Central rear);
North-Western Customs Administration (includes 23 customs: Arkhangelsk, Bagrationovskaya, Baltic, Velikolukskaya, Vologda, Vyborgskaya, Kaliningradskaya, Kaliningradskaya operative, Kingiseppskaya, Kostomukskaya, Murmanskaya, Nemanskaya, Novgorodskaya, Petrozavodskaya, Pskovskaya, Pulkovo, St. Petersburg, Sebezhskaya , Sortavalsk, Syktyvkar, North-Western excise, North-Western operational, North-Western rear, as well as a specialized unit - the Canine Center of the North-Western Customs);
Southern Customs Administration (includes 20 customs offices: Adygei, Astrakhan, Volgograd, Dagestan, Ingush, Kabardino-Balkarian, Kalmyk, Karachay-Cherkess, Krasnodar, Millerovo, Mineralovodsk, Novorossiysk, Rostov, North Ossetian, Sochi, Stavropol, Taganrog, Tuapse, Chechen, Southern operational);
Privolzhsky customs administration (includes 16 customs offices: Bashkortostan, Kirov, Mari, Mordovia, Nizhny Novgorod, Orenburg, Penza, Perm, Samara, Saratov, Tatarstan, Togliatti, Udmurt, Ulyanovsk, Chuvash, Volga operational);
Ural customs administration (includes 10 customs offices: Yekaterinburg, Koltsov, Kurgan, Magnitogorsk, Nizhny Tagil, Tyumen, Khanty-Mansiysk, Chelyabinsk, Yamalo-Nenets, Ural operational);
Siberian customs administration (includes 19 customs offices: Altai, Bratsk, Buryat, Gorno-Altai, Trans-Baikal, Irkutsk, Kemerovo, Krasnoyarsk, Naushkinsk, Novosibirsk, Omsk, Tolmachevsk, Tomsk, Tuva, Khakass, Chita, East Siberian Operational, Siberian operational, Siberian rear);
Far Eastern Customs Administration (includes 16 customs offices: Amur, Birobidzhan, Blagoveshchensk, Vanino, Vladivostok, Grodekovo, Kamchatka, Magadan, Nakhodka, Sakhalin, Ussuri, Khabarovsk, Khasan, Chukotka, Yakutsk, Far Eastern operational).
RTUs manage the customs business in their region, which is determined by the Federal Customs Service of Russia. The tasks of the RTU include the organization of customs affairs, ensuring the timely transfer of customs payments to the federal budget, generalization and analysis of customs practice, development and implementation, within its competence, of measures aimed at ensuring the unity of the customs territory of Russia, its economic security in the part related to customs business , the fight against smuggling and other customs offenses, organizational, logistical, financial, personnel, social and other support for its activities and the activities of subordinate bodies. Customs is directly subordinate to RTU. There are customs directly subordinate to the FCS. The tasks of customs include the implementation of customs activities in their region, including customs clearance of goods, placing them under a certain customs regime, performing customs procedures, collecting customs payments, and customs control. Customs are law enforcement agencies that ensure, within their competence, the implementation of legislation on criminal and administrative proceedings. Customs carry out its activities through customs posts. The structure, staffing of customs officers are determined by the RTU.
Unlike the FCS, RTU and customs, customs posts are not a legal entity (with the exception of special cases determined by special orders of the FCS). The tasks of the customs post include the direct implementation of customs affairs, customs clearance and customs control in the entrusted area, the fight against administrative offenses in the field of customs affairs. The structure, number of employees, the head of the customs post are determined by the higher customs. Customs law. Textbook for high schools. / Ed. A.A. Bogomolova - M: Yurayt Publishing Group - M-2011.
The main tasks of the FCS of Russia are: determination of the most effective methods for the implementation of tasks in the field of customs in accordance with international standards and the legislation of the Russian Federation. The achievement of this goal is ensured by solving the following tasks:
improving the quality of customs regulation, contributing to the creation of conditions for attracting investments into the Russian economy, revenues to the federal budget, protecting domestic producers, protecting intellectual property, and maximizing the promotion of foreign trade activities;
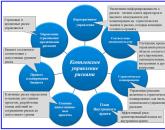
improvement of customs administration, including the development of a risk management system based on the implementation of customs procedures in accordance with international standards based on the latest achievements in the field of information and management technologies;
strengthening cooperation with Russian, foreign and international bodies and organizations in the fight against terrorism, smuggling of weapons, drugs and counterfeit products, as well as in ensuring economic, environmental and radiation safety.
The implementation of these tasks involves ensuring a stable legal regime for foreign trade throughout the Russian Federation, based on the following international principles approved by the World Customs Organization: standardization and improvement of customs legislation, development of norms, rules and procedures taking into account international standards; transparency and predictability.
Customs legislation, norms, rules and procedures in the field of customs are applied consistently; they are unified, well-known and brought to the attention of all interested parties in an accessible form; minimal intervention.
The customs authorities, to the maximum extent possible, observe the principles of selectivity and sufficiency of customs control, apply a risk management system;
consumer orientation. Customs administration is aimed at improving the quality of customs procedures in relation to legal entities and individuals as participants in foreign trade activities;
cooperation and partnership. The activities of the customs authorities provide for the development of cooperation with all participants in the foreign trade process, including government agencies, the business community, customs services of other states;
balance in terms of the relationship between customs control in the field of security and trade facilitation measures.
As a basis for the activities of the customs authorities of the Russian Federation, new principles will be used, defined in the framework standards for ensuring the security and facilitation of world trade, adopted by the World Customs Organization and approved by the Federal Customs Service.
On the one hand, new approaches to customs administration will be formed, which involve ensuring its high efficiency with external simplicity and speed of clearance of goods and vehicles moved by individuals and legal entities, and on the other hand, these approaches will help solve the problems associated with understating there
The main functions of the FCS of Russia: The FCS of the Russian Federation performs the following main functions:
participate in the development of the customs policy of the Russian Federation and implement this policy;
ensure compliance with the legislation, the control over the implementation of which is entrusted to the customs authorities of the Russian Federation, take measures to protect the rights and interests of citizens, enterprises, institutions and organizations in the implementation of customs affairs;
ensure, within their competence, the economic security of the Russian Federation, which is the economic basis of the sovereignty of the Russian Federation;
protect the economic interests of the Russian Federation;
apply means of customs regulation of trade and economic relations;
collect customs duties, taxes and other customs payments;
participate in the development of economic policy measures in relation to goods transported across the customs border of the Russian Federation, implement these measures;
ensure compliance with the permit procedure for the movement of goods and vehicles across the customs border of the Russian Federation;
fight against smuggling, violations of customs rules and tax legislation related to goods transported across the customs border of the Russian Federation, stop illegal trafficking across the customs border of the Russian Federation of drugs, weapons, objects of artistic, historical and archaeological heritage of the peoples of the Russian Federation and foreign countries, objects of intellectual property , endangered species of animals and plants, their parts and derivatives, other goods, as well as assist in the fight against international terrorism and the suppression of unlawful interference at Russian airports in the activities of international civil aviation;
carry out and improve customs control and customs clearance, create conditions conducive to the acceleration of trade across the customs border of the Russian Federation;
keep customs statistics of foreign trade and special customs statistics of the Russian Federation;
maintain the Commodity nomenclature of foreign economic activity;
contribute to the development of foreign economic relations of the republics within the Russian Federation, the autonomous region, autonomous districts, territories, regions, cities of Moscow and St. Petersburg, as well as enterprises, institutions, organizations and citizens;
promote the implementation of measures to protect state security, public order, the morality of the population, human life and health, the protection of animals and plants, the protection of the natural environment, and the protection of the interests of Russian consumers of imported goods;
exercise control over the export of strategic and other materials vital for the interests of the Russian Federation;
carry out currency control within their competence;
ensure the fulfillment of the international obligations of the Russian Federation in the part related to the customs business; participate in the development of international treaties of the Russian Federation affecting the customs business; carry out cooperation with customs and other competent authorities of foreign states, international organizations dealing with customs matters;
carry out research work and consulting in the field of customs; carry out training, retraining and advanced training of specialists in this field for state bodies, enterprises, institutions and organizations;
provide, in accordance with the established procedure, the President of the Russian Federation and the Government of the Russian Federation, other state bodies, enterprises, institutions, organizations and citizens with information on customs issues;
implement a unified financial and economic policy, develop the material, technical and social base of customs authorities, create the necessary working conditions for employees of these bodies.
The FCS RF carries out its activities in cooperation with other federal executive authorities, executive authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and public associations. RF. State bodies and their officials are obliged to assist the customs authorities of the Russian Federation in solving the tasks assigned to them, including by creating appropriate conditions for this.
The Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation is directly subordinated to regional customs departments, as well as specialized customs offices (eg Central Energy Customs, Sheremetyevo Customs, Domodedovo Customs, etc.).
Organizational structure of the FCS of Russia. Tasks and functions, i.e. the main activities of the customs authorities determine the internal structure of the FCS of Russia. The organizational structure of the FCS of Russia consists of the following elements: the leadership of the FCS of Russia, the apparatus of the FCS of Russia, consisting of departments and departments.
Among the structural elements, the leading role belongs to the leadership, which includes: the chairman, his deputies, the collegium of the FCS of Russia.
The FCS of Russia is headed by a chairman who is appointed and dismissed by the President of the Russian Federation. The Chairman of the Federal Customs Service of Russia carries out general management of the system of customs authorities. He has deputies who are appointed and dismissed on his recommendation by the Government of the Russian Federation. Responsibilities between the deputies are distributed by the chairman of the FCS of Russia.
Chairman of the FCS of Russia: At the moment, Andrei Belyaninov is in charge of the activities of the FCS of Russia on the principles of unity of command; bears personal responsibility for the fulfillment of the tasks and functions assigned to the FCS of Russia; represents the FCS of Russia and ensures its interaction with other state bodies of the Russian Federation; appoints and dismisses senior officials of the Federal Customs Service of Russia, heads of regional customs departments and customs offices of the Russian Federation, heads of subordinate enterprises, organizations, institutions; establishes the powers of the subordinate customs bodies of the Russian Federation to independently resolve organizational, personnel, financial and other issues; performs other functions and enjoys other rights in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation.
The Chairman of the FCS of Russia has the right to delegate certain powers granted to him to subordinate officials.
Members of the board of the FCS of Russia (except for persons included in its composition ex officio) are approved by the Government of the Russian Federation on the proposal of the chairman of the FCS of Russia.
The Collegium, at its regularly held meetings, considers the most important issues related to the activities of the FCS of Russia. At meetings of the board, reports are heard from the heads of the central office of the Federal Customs Service of Russia, other customs authorities, subordinate enterprises, organizations and institutions. Customs law. Training and metodology complex. / Ed. CM. Stepanenko M., 2012.
FCS emblem The Federal Customs Service (FCS of Russia) is a federal executive body that, in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, exercises control and supervision functions in the field of customs, as well as functions ... ... Wikipedia
Federal Customs Service (FCS of Russia)- 1. The Federal Customs Service (FTS of Russia) is an authorized federal executive body that, in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, carries out the functions of developing state policy and regulatory ... ... Official terminology
Federal Customs Service of Russia- a federal executive body that performs the functions of developing state policy and regulatory legal regulation, control and supervision in the field of customs, as well as the functions of a currency control agent and special ... ... Customs law. Glossary
- (FMS of Russia) Emblem of the FMS ... Wikipedia
The Federal Tax Service (FTS of Russia) is a federal executive body that exercises control and supervision over compliance with the legislation of the Russian Federation on taxes and fees, over the correct calculation, ... ... Wikipedia
"FAS" redirects here. See also other meanings. Emblem of the FAS Flag of the FAS of Russia, 2004 The Federal Antimonopoly Service (FAS of Russia) is a federal executive body that exercises control and supervision functions ... ... Wikipedia
Heraldic sign emblem of Rosregistration Flag of Rosregistration Federal Service for State Registration, Cadastre and Cartography (Rosreestr) (until 12/30/2008 Federal Registration Service (Rosregistration)) federal executive body ... Wikipedia
Requests "Rosarchiv" and "Federal Archival Service of Russia" are redirected here. The Federal Archival Agency of Russia (Rosarchiv) is a federal executive body under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Culture. Carries out the functions ... ... Wikipedia
Emblem of the FMS Flag of the FMS of Russia The Federal Migration Service (FMS of Russia) is a federal executive body that implements state policy in the field of migration and performs law enforcement functions, functions of control, supervision and ... ... Wikipedia
The customs business belongs to the federal authorities. And the FCS is a service that exercises control and supervision in the Russian Federation in accordance with the legislation of the country.
Definition

The customs territory of the state consists of:
- Land space.
- airspace.
- Territorial and internal waters.
Direction of activity
The head of the FCS and the service as a whole follow in their work:
- constitutional laws.
- Federal laws, orders and decrees.
- Decrees and orders of the government of the state.
- international treaties.
- Legal acts of the Ministry of Economic Development and Trade, and the Central Bank of the Russian Federation.
According to legislative norms, the FCS is an authority that performs the following functions:
- Ensuring the maintenance and publication of the nomenclature of goods of foreign economic activity.
- Preparation, approval, publication of decisions on clarification of the nomenclature of goods.
- Issuance of qualification certificates to customs clearance specialists.
- Metrological support of customs activities.
Powers

The main powers of the customs service of the Russian Federation include:
- Implementation of the collection of customs duties and taxes, various duties.
- Control of the correctness of the calculation and timely payment of fees and taxes, approval of measures for the forced collection of taxes and duties.
- Compliance with prohibitions and restrictions on the import of goods into the country.
- Ensuring the correct application of customs legislation.
- Implementation of customs clearance and control.
- Approval of decisions on the systematization of goods.
- Ensuring the protection of intellectual property (within the competence of the service).
- Maintaining a list of citizens and organizations that carry out customs business.
- Maintenance of customs statistics.
- Free informing of participants of foreign economic activity on customs issues.
- Execution of currency control.
- Implementation of operational-search activities, inquiry and production of investigative actions.
- Implementation of other powers that are provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
Rights
The FCS is which, in order to exercise the above powers, has the right to:
- Creation, reorganization, liquidation of customs posts, specialized bodies, whose power is limited by individual powers.
- Determination of the area of activity of customs authorities and approval of regulations on customs authorities.
- Organization of examinations, tests, evaluations and analyses.
- Request for information related directly to the customs business.
- Implementation of control over the customs authorities of the Russian Federation located abroad.
- Application of measures of a restrictive, preventive or coercive nature to suppress violations.
- Development and approval of samples of service certificates and uniforms.
The customs service in its field does not have the right to legal regulation, as well as the management of state property and the provision of paid services, in addition to those cases that are established by federal law, decrees of the President of the country, and decisions of the government of the country.

The powers and rights vested in the customs service determine the internal structure.
Russia performs a number of functions related to the regulation and observance of customs law, is responsible for exports and imports, and forms the amount of duties at the federal and local levels. The list of tasks is huge, therefore the structure of the FCS is branched and has several levels for the effective work of each official.
From the history of the customs service in Russia
The first organization of the customs service and duties in Russia can be attributed to the X century. Merchants supplying consumer goods by water and land routes were obliged to pay myt at the outposts (current customs points) - the most common tax of that time on goods. The collection was carried out by mytniks. Three centuries later, the Tatar-Mongols who came introduced the tamga, which was charged for the seal of the governor when the goods went on sale. From the word "tamga" came the modern term "customs".
In tsarist Russia, tax collection was done by free-working heads and kissers. They received a premium for increasing income from customs duties, or they themselves paid a shortfall when revenues to the treasury decreased. Abuse of official position, financial transactions of the tsarist "customs officers" were severely punished, up to and including the death penalty.
Over the entire period of formation, management underwent many reforms under Peter the Great and Catherine the Second. By the 19th century, smuggling became widespread for the first time - a way of illegally importing luggage. On the borders with Russia, criminals are sometimes caught with a very large consignment of goods hidden from customs officers. It was only in 1921 that a law was passed to combat smuggling. The period fell on the years of "war communism" - this is the time of shortage and surplus appropriation. In 1924, the first codified charter of customs authorities was adopted, mainly controlling the export and import of goods. The State Customs Committee of Russia was established by decree of the President of the RSFSR in October 1991, and the decree "On the Federal Customs Service" - in 2004.
What is the FCS for the state?
The FCS is the central executive body that controls the import and export of goods, the legality of transportation and establishes duties, and also monitors compliance with the regulatory framework relating to customs. The Federal Customs Service stands for the protection of the economic interests of the country, protecting consumers from counterfeit, smuggling, things that pose a danger to people.
Main tasks and functions of the FCS of Russia
The tasks of the Federal Customs Service are:
- continuous improvement of the conditions of customs regulations on the territory of the Russian Federation to attract foreign investment;
- interaction with international representative offices of customs services for the joint fight against terrorism, smuggling and counterfeiting;
- development in customs administration, the introduction of Western software developments in the Russian service;
- assistance in the development of foreign economic relations with Russia.
The functions of the customs service are:
- development of customs policy and its application;
- establishment of customs duties;
- protection of the economic interests of the country;
- compliance with the rules and regulations for the movement of goods across the customs border;
- suppression of the actions of smugglers and illegal imported and exported goods.
Legislative framework governing the activities of the FCS
The main legislative document that reflects the functions, tasks, structure of the FCS of Russia is the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and the Regulations on State Customs Control. Customs policy is formulated in Article 2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Additions and changes are recorded in additional regulatory documents. A separate article on customs offenses and the competence of the customs authorities is in the Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation.

Also, the customs service relies on the Constitution of the Russian Federation, federal laws, international agreements, legal acts of the Central Bank of Russia.
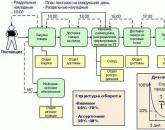
FCS structure
The FCS has the following hierarchy:
- Federal Customs Service.
- Regional customs structures and customs houses of direct subordination. They report directly to the FCS.
- Customs.
- customs posts
- Departments of technical control and maintenance, departments and costs, department of currency control. They are at every customs post.
Organizational structure of the FCS: leadership
The organizational structure of the FCS is represented by the leadership and staff of the FCS. The head of the service is the head Bulavin V. I. His right hand and the second person in the composition and structure of the central office of the FCS was appointed the first deputy head Davydov R. V.

There are also 6 deputy heads who, in the structure of the FCS, are responsible for various areas of activity of the customs department.
The main tasks of the head of the customs service are:
- resolving issues related to the passage of the customs service in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation;
- making changes and personnel changes in the structure of the central office of the FCS of Russia;
- drawing up the budget of the customs service;
- approval of the state and salary fund in the structure of the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation, including at the regional level;
- distribution of duties between deputies;
- drafting and approval of decrees and regulations relating to the powers of the Federal Service;
- resolving issues of awards and badges of honor to customs officers who distinguished themselves in the service;
- approval of regulations on subdivisions in the structure of the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation.

The head is personally responsible for the activities of the entire system both at the federal and regional levels, and for all violations that are contrary to legal documents.
FCS apparatus
The management structure of the FCS is represented by the following bodies and departments:
- Main organizational and inspection department. This unit inspects the activities of organizations accountable to the FCS, performs methodological functions, controls the execution of decrees of the head of the customs service, organizes strategic planning and controls its implementation, is responsible for the main economic indicators of the service, and reports information in an analytical form about the work of the service to the management.
- Information Technology Department. This division is responsible for the information platform for the entire structure of the FCS. Its tasks also include the protection of databases and information technologies, informatization, setting up telecommunications, participation in the strategic planning of the entire service.
- Department of customs clearance and control. It develops a general procedure for customs operations when moving goods across the border, monitors the work of all departments of services, participates in the reform of customs policy, and makes proposals for improving the procedures for customs operations.
- Anti-smuggling department. It is engaged in intelligence in relation to persons violating customs legislation, protects the economic interests of Russia, carries out preventive work in relation to the legal import and export of goods, participates in search activities for violators, participates in the production of criminal cases in accordance with the competence of officials specified in the criminal procedure Code.
- Logistics Department. Conducting administrative and economic activities in the customs authorities, medical and social services for officials of the Federal Customs Service.
- Department of Tariff Regulation and Customs Revenues. It develops the tariff scale of duties in accordance with international agreements, regulates the accounting of all taxes paid and monitors their receipt by the treasury, monitors compliance with the payment of duties from regional authorities and the receipt of revenues in full.
- Financial and economic management. It draws up estimates, distributes budget funds according to the structure and composition of the Federal Customs Service of Russia, exercises control over the expenditure of targeted funds, and provides pensions to persons who served in customs.
- Control Control over compliance with the correctness of all customs procedures in relation to goods, assistance in protecting the interests of declarants.
- Department of customs inquiry and investigation. It conducts cases on administrative violations relating to the customs service, monitors compliance with the procedure for the arrest of goods.
- Legal management. It participates in the preparation of federal laws and international agreements.
- Office of Trade Restrictions, Currency and Protecting the economic interests of Russia, monitoring compliance by the parties with international agreements, tracking all foreign exchange transactions.
- Case management. Ensures proper paperwork.
- Civil service and personnel management. Here, the implementation of personnel policy, staffing, organization of service in the customs authorities is carried out.
- Public Relations Management. Interaction with the mass media.
- Office for Combating Corruption. Preventive measures, detection of violations among customs officers of a corrupt nature.
- Department of Customs Cooperation. The task of the FCS is the participation of Russia in the international arena in the field of customs interests, the preparation and submission of proposals for a joint mutually beneficial agreement with other countries.
- Management of customs statistics. The duties of this department include calculation, analysis of indicators of economic activity of customs authorities for the past period, comparative analysis between regional divisions of customs.
- Control and audit department. Carries out the work of an independent audit in relation to the divisions of the customs service.
- Control It is engaged in monitoring the observance of commodity nomenclatures and classification in accordance with these nomenclatures.
- Analytical management. The division analyzes the activities of customs when moving goods across the border of the Eurasian Economic Union, improves the risk management system, controls the export and import of goods, including the movement of excisable goods, evaluates the efficiency of work within the management structure of the Federal Customs Service of Russia.
Central Customs Administration (CTU)
The FCS activity platform is the Central Customs Administration, which is located, like the FCS, in Moscow. The department of CTU has the most important and largest customs authorities of regional importance, customs, customs posts. 18 regions, 13 customs houses and 91 customs points are subordinated to CTU.

Here they prepare new developments of customs procedures, test and implement software and technologies. Over the years of its existence, the CTU has become one of the significant divisions of the FCS. On its customs territories, 4 departments have been created to control the customs border with Ukraine and Belarus. The share of management accounts for the bulk of the income of customs activities.
Regional Customs Administrations (RTU)
The Federal Customs Service includes regional customs departments that are accountable to the FCS. The following subordinate departments are distinguished:
- Northwestern RTU;
- Far East;
- North Caucasian;
- Volga;
- East Siberian;
- West Siberian;
- Tatar;
- Ural;
- Kaliningrad;
- Western;
- Moscow;
- Dagestan;
- Bashkir.
RTUs implement the customs policy in the regions, protect the economic interests of Russia, make proposals for the region, and ensure the coordinated work of the entire FCS. All tasks are performed according to the competence of the regional customs authority. The RTU performs the functions of monitoring compliance with regulatory and legal aspects, tracking the movement of goods in the region, currency movements, and is engaged in personnel policy in the regional administration.
RTU structure
The RTU hierarchy is similar to the organizational structure of the FCS of Russia. There is also a chief, who is appointed only by the Chairman of the central office. His deputies and the chief accountant are also appointed and dismissed upon submission of information from the regional head. Personnel changes at other levels are carried out by the decision of the chief, based on the regulation on customs services. The tasks of the head of the RTU are to manage the regional division on the principles of one-man management, to monitor compliance with and implement all assigned tasks.

The head interacts with the central customs body, submits a report on the work done, and exercises control over operational-search activities. On the financial side, the head of the RTU is responsible for the distribution of budgetary funds allocated by the FCS and provides a rationale for their intended use.
The chief has deputies who perform approximately the same role as the deputies of the head of the FCS, but at the regional level.
Customs as a reporting organization of the FCS and RTS
The customs of the Russian Federation are part of the customs system of Russia and are subordinate to the federal service and the regional administration to which they belong. Sometimes, by decision of the central office, some customs offices may be exclusively subordinate to the FCS. Customs are divided into border and internal. Border customs are located on the state border in the area of large transport hubs, and internal customs controls import and export within the country between regions. There is also a specialized customs office that conducts customs operations with special cargoes: oil, gas, electricity. The activity of customs is regulated by normative acts.
The tasks of customs are:
- ensuring the unity of the customs borders of the state;
- implementation of customs policy;
- implementation of customs procedures;
- detection of violations of cargo transportation;
- application of customs tariffs and goods registration system;
- providing own activities with financial, material and human resources.
customs posts
One of the links of the customs system is It is accountable to customs, or may report directly to the RTS. Separate posts function under the leadership of the federal service.
The creation and reorganization of the customs post lies on the "shoulders" of the RTS; if the post has the exclusive status of a legal entity, then it is handled by the FCS. Usually the customs post does not take such an organizational form. But if the FCS decides to give the post the status of a legal entity, then it will have its own balance sheet, charter, and bank accounts. Such a post may administer property assigned to federal bodies.

The functions of the customs post consist in the implementation and conduct of all customs operations, control over the legality and legality of procedures, the implementation of adopted resolutions of federal and regional significance.
Department of customs procedures and customs control (OTP and TC)
OTP and TC are subordinate to customs and build a work plan in coordination with customs, RTS and FCS of Russia. The plan is approved by the first deputy head for customs control. Appointment to a leadership position is carried out by the head of customs, who in turn approves the candidate with the regional service. The head of the department also has deputies. The management of the OTP and the TC approve the number of personnel, job descriptions prescribed in the FCS distribute job responsibilities. The department of procedures and control faces the tasks of complying with customs regulations, implementing customs policy, interacting with other persons involved in customs processes: declarants, temporary storage warehouses. The department keeps records of special goods that have passed customs procedures, interacts with tax authorities in international transportation, and coordinates simplified customs procedures with the RTS. OTP and TC participate in the analytical collection of information on the effectiveness of the work of customs authorities, develop a strategy and preventive measures for risks. The department takes part in the inspection of the customs authorities on the issue of compliance with the normative documents of the customs policy. He also decides on the processing and disposal, or the arrest of illegal products.
Russian customs- a state control body that carries out the movement of goods, cargo, cars, motorcycles, and other things across the border. The customs office establishes customs procedures for the passage of goods and collects customs payments, if any. Our section Russian customs will provide you with detailed information about the work of the customs of the Russian Federation, customs duties of the customs of Russia, addresses and contact numbers of the customs of Russia in your city or region of the country. Here you can find all the information about the customs of Russia.
Customs of Russia - official site, contact numbers, addresses.
Russian Customs (FCS) represented by regional customs departments, regional customs services, customs posts, customs of central subordination (customs of Moscow airports, etc.).
Customs of the Russian Federation establishes the procedure for customs clearance, establishes the classification of goods (commodity nomenclature of foreign economic activity) and vehicles that cross the border of the customs control of Russia, and also carries out customs control and law enforcement activities within the framework of the customs sphere. The Russian customs maintains a register of persons included in the field of customs office work (they are customs brokers, objects of intellectual property, etc.) The FCS also issues certificates for the right to operate in certain areas of customs (customs brokers, etc.)
Customs of the Russian Federation also provides consultations for participants of foreign economic activity (foreign economic activity).
Customs of Russia - official site, contact numbers, addresses.
Official website of Russian customs(Federal Customs Service of Russia) - http://www.customs.ru/
Russian customs website for individuals Section of the official website of the Russian customs for individuals - http://fl.customs.ru/
Official websites of customs are often inconvenient to use and full of news articles or regulations that are difficult to find or understand for a simple user who is not a customs specialist. For your convenience, we have collected detailed information for each country in a separate section, customs of Russia, customs of Ukraine, customs of Belarus, customs of Kazakhstan other. You can select the country you are interested in and the relevant section to easily find the customs information you need.Customs clearance
customs clearance is the procedure necessary to perform when moving goods or vehicles across the Russian border. Customs clearance involves the following steps customs clearance, payment of customs duties.
Preparation of documents required for customs clearance- produced by the consignor or Customs Broker on his behalf (if there are no relevant customs specialists in the staff of the consignor's company). The customs broker or consignor prepares a list of documents required for his category of goods or cargo. Such documents can be a completed customs cargo declaration, certificates, transport and shipping documents, a product license (if necessary, for certain categories of goods), a certificate of conformity (if necessary, for certain categories of goods), etc.
Cost of customs clearance depends on which group your product or cargo belongs to. This cost may also include the cost of services of a customs broker for customs clearance if you used a broker for the customs clearance procedure
More details about the amount of customs duties and the procedure for their payment will be discussed below.
Russian customs duties
The amount of customs payments:
Import and export of currency through the customs of Russia:
The customs of Russia allows you to import and export from Russia any foreign currency, the amount of which in cash does not exceed 10 thousand US dollars in equivalent. The same applies to the import and export of traveler's and bank checks from Russia.
Import and export of goods through the customs of Russia:
Customs value of goods- the value of the goods, which is determined in accordance with the agreement between the customs union of Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan dated 25.01.2008 "On determining the customs value of goods transported across the customs border of the Customs Union". This indicator is used to set the customs duty.
Duty-free import and export: The import of goods into Russia is allowed for personal use and non-commercial purposes. When transporting goods by air to Russia, the total value of goods must not exceed 10,000 euros, and the maximum weight must be 50 kilograms. When transporting goods by rail, road, sea transport, the total customs value of goods should not exceed 1.5 thousand euros, and the total weight should be less than 50 kg.
The amount of duties for the import and export of goods to Russia: If the total cost or weight is more than the specified limits, but not more than 650 thousand rubles. and 200 kg., customs charges a customs duty in the amount of 30% of the customs price of goods. If the total cost and weight are above 650 thousand rubles. and 200 kg. accordingly, customs duties are classified as for commercial activities.
Russian customs duties:
The amount and procedure for calculating customs duties in Russia is established by the Law of the Russian Federation "About the customs tariff" and is registered in the customs code of Russia, respectively. In accordance with the customs law of Russia "On the customs tariff" (Article 4), it is established 3 types of customs rates: customs duty No. 1 - ad valorem rate; customs duty No. 2 - specific rate; customs duty No. 3 - combined rate.
The customs of Russia has established a duty-free import of goods for a month, the total customs value for which is not higher than 1000 euros (in equivalent), and the total weight of the parcel is not more than 31 kg. duties are set at a rate of 30% of the established customs value of goods (single rate), however, the size of the Russian customs duty is set at least 4 euros per 1 kg of parcel weight.
Read more about Russian customs duties in the section -
Declaration of the Customs Union
Declaration of the Customs Union this is a legislative customs document that is used when importing and exporting goods from Russia, importing products to the countries of the Customs Union (Russia, Belarus, Kazakhstan).
The declaration of the customs union is drawn up by the manufacturer or supplier of products and registered at the certification center.
Lists of goods that require the mandatory execution of a Customs Union (CU) declaration are contained in the Unified List of Products established by the Decision of the Customs Union Commission dated April 7, 2011 No. 620.
In order to know the full list of required documents for carrying out foreign economic activity within the framework of the Customs Union, you need to find your niche (group of goods) in the list below.
Popular
- Determining the amount of accumulated wear Accumulated wear determined by the multiplicative method
- Responsibilities of the financial director
- International Financial Reporting Standards year
- Job description of financial director
- Legal aspects and issues of demand for project financing Features of project financing of commercial banks
- Organization of budgeting at the enterprise
- Well drilling rates
- Variable frequency asynchronous electric drive - a course of lectures Automated electric drive a course of lectures
- Variable frequency asynchronous electric drive - course of lectures
- Operating instructions for the stand for